ST_GUIDE EARTH_CBA`13 / Microsoft Word 97
advertisement

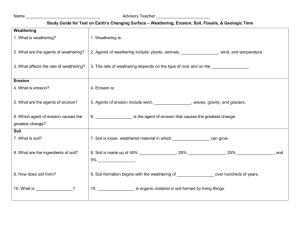
STUDY GUIDE FOR EARTH COMMON ASSESSMENT ALL QUESTIONS/STATEMENTS IN BOLD SHOULD BE ANSWERED (in complete sentences) ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER Earth’s Surface: Key ideas *Topography is the shape of the land and is determined by elevation, relief, and landforms. (Pgs. 14-18) *Topographic maps: What type of information does a topographic map provide about landforms? How would you recognize a river? A depression? A hilltop? (Pgs. 29-33) VOCABULARY TO KNOW: topographic map - contour line - contour interval - index contour – elevation - relief Weathering: Key Ideas *What causes mechanical weathering? Freezing and thawing, heating and cooling/release of pressure, growth of plants, actions of animals, and abrasion - Provide examples of these. (Pgs. 41-42) *What causes chemical weathering? Water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, living organisms, acid rain - Provide examples of these. (Pgs. 43-44) *What two factors determine the rate of weathering? Type of rock and climate – Explain why these are factors. (Pg. 45) VOCABULARY TO KNOW: Weathering –Erosion – Mechanical weathering - Chemical weathering – Permeable Soil Formation and Composition: Key Ideas (Pgs. 49-55) *Soil is loose weathered rock and other materials on Earth’s surface. What is the composition of the other materials? *What determines the rate of soil formation? *What are the soil horizons? What do we find in each horizon? *How do living organisms help the soil? VOCABULARY TO KNOW: soil – bedrock – humus – loam - soil horizon – litterdecomposers Rock Cycle *What is the rock cycle? *What are the three types of rock? How do each form? Use the worksheet “The Rock Cycle” in your binder to help with these questions. Erosion and Deposition: Key Ideas *What are the four types of mass movement? Can you explain each? (use chart in notes) *How does erosion and deposition work to constantly wear down and build up the earth’s surface? Read pages 66 – 69 in you book. *What is the major agent of erosion? What is the result of deposition along the course of a stream? Review exploring the course of a river (pages 72-81 in book) VOCABULARY TO KNOW: Erosion - Deposition – Sediment - Meander Fossils: Key ideas (Pgs. 106-112) *How do most fossils form? *What does the fossil record show us? VOCABULARY TO KNOW: Fossil – Paleontologist – Mold – Cast Trace fossil – Scientific Theory - Evolution – Extinct – Preserved remains – Petrified fossil Ages of Rocks: Key Ideas (Pgs. 113-117) *What is the Law of Superposition? *What are index fossils and why are they useful? VOCABULARY TO KNOW: Relative and absolute age – Index fossil - Intrusion Extrusion – Fault – Unconformity Geologic Time: Key Ideas & Earth’s History (Pgs. 123-140) *Geologic time scale – record of life forms and geologic events on Earth *What are the three ERAS of geologic time? VOCABULARY TO KNOW: Era – invertebrate – period – epoch – mass extinction