DME Based on Coastal Management
advertisement

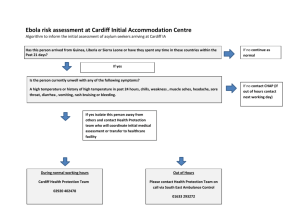
Developing a decision making task based on coastal management. Generic title: How can the problems of coastal flooding be controlled effectively? Key questions of specification: 2.1 What are the advantages and disadvantages of hard and soft engineering strategies used to manage our coasts? 3.2 What is the most sustainable way to manage our coastline in the face of rising sea levels? Contextual information for teachers: Decision making exercise based on a Shoreline Management Plan – a summary for Cardiff to Newport (Wentlooge or Wentloog) is available. A summary has been included below The land around the Severn Estuary is low lying. Sea level rise or an increase in the amount of coastal flooding could affect a large geographic area. Sea level rise is thought to pose the greatest real risk and be the most important consideration in deciding on the right policy option to manage coastal flooding and climate change. To work out which areas of the estuary would be affected by sea level rise, the change in Mean High Water Springs (MHWS) is seen as the most appropriate and has therefore been calculated to assist in policy making. Mean High Water Springs (MHWS) is the average height that the tide reaches on a Spring Tide. Spring Tides basically occur when there is a new moon or a full moon. Spring tides rise furthest up the shore at high tide and go out furthest at low tide (i.e. maximum tidal range occurs). MHWS gives the average highest level that the tides reach at high tide. As sea level rises, MHWS will rise as well, meaning that the tide will reach further and further up the shore profile and further and further in land, particularly where the land is low lying (as is found within this SMP2 area). Land which, over time, is affected by MHWS moving landwards becomes unusable without intervention for many purposes – it cannot be used for housing, commercial development, farming, etc. because it is regularly covered by the tide (approx. twice per month). Showing how MHWS changes over time in the SMP2 area is, therefore, very useful for people that make decisions about planning and land use because it will highlight areas that will become unusable. It is for this reason that this SMP2 has introduced a valid variance to the Defra Procedural Guidance. The UK Climate Impacts Programme scenarios (UKCIP02) suggest that by 2080 the sea level will rise by between 20cm and 80cm in the South West and by about 40cm around Wales. These predictions have recently been updated. The UK Climate Projections 2009 (UKCP09) estimate sea level rises between 37cm and 53cm in England and Wales. Possible titles: Are the Newport Levels worth saving from sea level rise? If so, what is the most sustainable way to do this? How and why should the shoreline at Wentlooge be managed in the future? How can the problems of coastal flooding be controlled in the future on the Newport levels? Teaching prior to the Research phase Teach about the management of the coastline in England and/or Wales. Consider the benefits and limitations of both hard and soft engineering techniques. Give students the opportunity to consider the economic, social and environmental impacts (good and bad) of each of the following options: Do nothing Retreat the line Hold the line Advance the line Use Hodder’s Option Topics book to practice a decision making exercise based on the Shoreline Management Plan for Borth on the Ceredigion Coast (pages 6 – 10) Student sheets for the research folder The decision making task < Put your chosen title here > Your task: You have been asked to write a report for the local council. In it you should recommend a future Shoreline Management Plan for the Wentloog Levels. Which of the following options will you recommend? Do nothing Retreat the line Hold the line Advance the line In your report you should: Describe the issue that faces people in this area; Consider various options that could be used to manage the coastline; Decide which option (or combination of options) you think should be used; Explain why you think your choice is best. Remember, you report will be marked using a mark scheme which will give good marks if you: Show that you understand why coasts are protected; Explain the limitations and benefits of various strategies for coastal defence; Consider why people have different views on this issue and recognise bias; Analyse evidence (eg from maps, photos, tables of data); Use a range of skills; Use evidence to support your conclusions. Student instructions There are two phases to your task: Phase 1 The Research phase You have 5 hours (this is a maximum – you can have less) You should spend about half of this time doing some basic processing of the data in your file. You are allowed to: Make notes Draw graphs Draw sketch maps and other types of map Label photos Plan the structure of your report Ask your teacher questions You could spend the other half of your time doing some research into: Land uses at Wentlloog Strategies for coastal defence – the benefits and limitations of each type Opinions about whether coastal defences are needed You will be able to collaborate with each other. You must not take any work home. Keep all your work in a folder. Phase 2 The Writing phase You have 8 hours (this is a maximum – you can have less) You must work independently. You must hand in your work to the teacher at the end of each session. Plan your time carefully when you are in this phase. You will not be allowed to add anything to your folder or use the internet in this phase. Evidence that you may find useful Figure 1 The value of agricultural land Agricultural land classification grade Value (£ per hectare) 1 6,290 2 6,290 3 5,050 4 4,500 5 4,500 Source: Middlesex University, Flood Hazard Research Centre Figure 2 The cost of coastal defences Defence type Cost to maintain (£ per km per year) Hard defences eg seawalls, rock 10,000 revetments Earth embankments, groynes etc 10,000 Beach management, 20,000 replacement of sand, shingle etc Source: Shoreline Management Plan Guidance Volume 2 Cost to build (£ millions per km) Replacement period (years) 2.7 100 0.6 50 5.1 30 Figure 3 How rising sea levels affect flat coastlines with and without a seawall Useful websites http://www.geograph.org.uk/ This site has lots of photos of landscapes in England and Wales, including many of the area between Newport and Cardiff. Each photo has a reference so you can locate it on an Ordnance Survey map. You can search the site using place names – try Wentloog or Wentlooge. Alternatively, use OS grid references. For example ST3083 is a grid square which has a reen (or drainage ditch) running through it. Another interesting square is ST2981 which shows sea defences. Start from one of these squares and use the pan buttons to explore the landscape. You could: Match photos to an OS map so that you can describe the landscape of the area Annotate the features of selected photos Use the photos to describe land use and estimate agricultural land values (using figure 1) http://www.environment-agency.gov.uk/homeandleisure/floods/default.aspx Follow the link to <flood map>. Use the search engine on this page to find maps of the coastline between Cardiff and Newport and discover whether or not they are at risk of floods. The post code CF10 2TN will get you to one interesting area. From here you can use the pan buttons to explore the rest of the coast. http://www.severnestuary.net/secg/docs/Issues%20and%20Objectives%20leaflet_Wentlooge.pdf This website summarises the Shoreline Management Plan for the area. http://www.caldandwentidb.gov.uk/ This is the website of the Caldicot and Wentlooge Internal Drainage Board. The Board is responsible for the Water Level Management of the Gwent Levels, an area of land between Chepstow and Cardiff. http://www.cardiff.gov.uk/objview.asp?object_id=3599 A fact sheet published by Cardiff Council http://www.wwf.org.uk/filelibrary/pdf/mu52.pdf A fact sheet published by WWF. Abbots Hall Farm, Essex, has experienced managed retreat. A hole was made in a coastal embankment and some parts of the farm are now flooded at high tide. This will eventually recreate a salt marsh which will be a natural defence against rising sea levels. Some opinions to consider Caldicot and Wentlooge Internal Drainage Board Extensive areas, including major centres of population and industry, are at risk of being flooded from the sea, rivers and smaller watercourses. Major flood events have been recorded through history and it is an exceptional year when no significant property flooding takes place. The land use of those areas within the Drainage Board Districts is totally dependent upon complex systems for Flood Defence and Land Drainage. Without such systems the development of homes and factories, the provision of public services and productive use of farmland, would not be possible. RSPB spokesperson The Gwent and Wenloog levels are areas of reclaimed land taken from the sea many centuries ago. It is drained by a network of reens (ditches and drains) that are now valuable for wildlife. Because of this, the whole area is a massive Site of Special Scientific Interest and an excellent place for bird watching. Spokesperson for Cardiff Council The Wentloog levels may not seem to be very valuable or important to some people. However, the levels are a beautiful area of countryside that are right on the doorstep of Cardiff. They provide a wonderful wild and peaceful place for people to walk or cycle. Local resident My family has farmed here for generations. I love this area and its wildlife. This is where I want my children and grandchildren to grow up. Resident in Newport I don’t see the point of spending money protecting this land. Hundreds of years ago it was salt marsh – it might as well go back to being salt marsh again. They would be better off spending the money they save on local schools or hospitals!