CanMEDS Roles - Pediatric Critical Care (PICU) at Stollery
advertisement

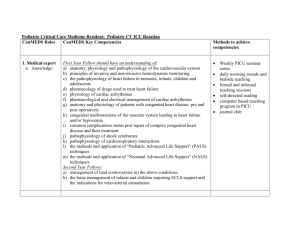
Pediatric Critical Care Fellowship: Pediatric Critical Care Rotation CanMEDS Roles CanMEDS Key Competencies Methods to achieve competencies 1. Medical expert a. knowledge: First Year Fellow should have an understanding of: a) anatomy, physiology and pathophysiology of the respiratory system b) the principles and theory of mechanical ventilation and other methods of respiratory support c) principles of invasive and non-invasive hemodynamic monitoring d) the pathophysiology of heart failure e) physiology of cardiac arrhythmias f) anatomy and physiology of patients with congenital heart disease; pre and post operatively g) pathophysiology, monitoring and investigation of raised intracranial pressure h) criteria required for the clinical diagnosis of brain death i) the major pathophysiologic entities associated with neuromuscular disease j) the indications and ethical implications of long term mechanical ventilation in neuromuscular disease k) the pathophysiology of renal failure and renal transplantation l) indications for peritoneal and/or continuous veno-venous hemofiltration m) the interaction between drugs and the kidney in normal and diseased states n) the differential diagnosis of an acute abdomen o) diagnosis of GI bleeds and the presentation of abdominal trauma p) the normal function of the liver and the pathophysiology of liver failure q) the physiology of a patient following liver transplantation r) the complications of pediatric oncologic diseases and their treatment s) the pathogenesis and management of thrombocytopenia, anemia, and neutropenia Updated April 2014 Weekly PICU seminar series daily morning rounds and bedside teaching formal and informal teaching sessions self-directed reading computer based teaching program in PICU journal club simulation sessions 1 t) u) v) w) differential diagnoses of thrombotic states and bleeding disorders fluid, electrolyte and nutritional requirements of critically ill patients transport physiology and problems associated with patient transport recognition of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome and implications for prognosis Second Year Fellows: a) management of (and controversies in) the above conditions. b) the basic management of infants and children requiring ECLS support and the indications for veno-veno or veno-arterial cannulation b) skills: First Year Fellows: a) recognition and management of basic life support measures in a critically ill child b) obtain and perform measurement of all vital signs including oxygen saturations and non-invasive blood pressures c) intravenous access in a critically ill child d) insertions of femoral, internal jugular and subclavian venous lines e) insertion of an intraosseous f) airway management including performance of oro and nasotracheal intubations, including use of the laryngeal mask g) insertion of oro and nasogastric tubes and foley catheters h) insertion of percutaneous hemodialysis catheters i) insertion of chest tubes and thoracentesis j) performance of lumbar punctures performance of procedures on patients in the PICU Anesthesia and Adult ICU rotations PALS, ATLS and NALS courses Simulation/Task trainer sessions Second Year Fellows: a) familiarity with insertion of a Swan-Ganz catheter b) pericardiocentesis with supervision Updated April 2014 2 c) proficiency in the skills listed under the requirements for first year fellows 2. Communicator First Year and Second Year Fellows: a) to understand the issues involved in communicating bad news to families b) to be able to explain complicated medical diagnoses and treatment in simple terms to families c) to explain life support measures clearly and concisely to patients and family members d) to develop the ability to communicate with families and the medical team in tense situations or crises e) to resolve conflict between families and members of the health care team during times of stress or crisis f) to effectively communicate appropriate positive and negative feedback on performance of junior trainees observation of family meetings held by attending staff daily communication with families to update them on the condition observation of nursing interaction and families participation in monthly rotating ICU resident evaluations simulation – breaking bad news run family meetings with staff present as appropriate Second Year Fellows: a) to perform the above skills more independently b) clearly explain the concept of brain death and the potential for organ donation if indicated to families 3. Collaborator Updated April 2014 First and Second Year Fellows: a) to communicate effectively and in a timely manner with consulting services b) to communicate care plans clearly and precisely to all members of the allied fill out consult forms specifically and speak to consultants directly about reasons for consults 3 health teams c) to manage differing opinions from all members of the health care team c) to work in a collaborative manner with fellow learners 4. Manager First and Second Year Fellows: a) effectively balance time between patient care, learning and stress management b) manage fatigue and recognize when they are unsafe c) effectively prioritize a heavy workload Second Year Fellows: d) learn the practical skills necessary to effectively run the Unit e) be the final person in the decision making ladder f) understand the basic principles and develop a proactive role in regard to risk management g) triage beds according to severity of illness and resource allocation h) organize and manage off-site transportation of critically ill infants and children Updated April 2014 summarize the care plan at the end of daily work rounds learn about all patients in the unit during rounds and regularly ask fellow learners about their need for help simulation discussing strategies with attending staff retreats, informal one on one sessions with staff use of organizational aids such as to do lists, etc run rounds independently several times per week function as the junior attending Bi-monthly Critical Care section meeting monthly PICU and pediatric morbidity and mortality reviews MD management workshops as they are available 4 5. Health Advocate First and Second Year Fellows: a) Be aware of the relative costs of different diagnostic and treatment modalities b) Be aware of the programs available for prevention of many PICU conditions such as motor vehicle collisions, bike safety, and near-drowning. c) Be familiar with post injury rehabilitation programs and how to access them d) Demonstrate proficiency with obtaining informed consent for medical and diagnostic procedures as well as for research studies e) counsel parents and families accordingly when patients face a terminal illness or very poor prognosis 6. Scholar First Year Fellows: a) learn the skills necessary to research and present critical care rounds and journal club b) facilitate education of other learners in the PICU c) demonstrate a basic understanding of biostatistics, study design, grant and manuscript preparation Second Year Fellows: a) organize and present critical care rounds b) lead informal teaching sessions on basic critical care topics to both fellow residents and other members of the health care team Updated April 2014 discuss cost issues on rounds with attending and pharmacists discussions on rounds and with families obtaining informed consent from families for blood transfusions and research studies ethics seminars and patient centred discussions present PICU noon rounds teach junior house staff and allied health professionals using both informal and formal teaching methods membership and participation in the PICU research committee participation in at least one research project fellow seminars 5 7. Professional First and Second Year Fellows: a) ensure detailed and complete follow-up and handover of all patients under the resident’s care b) develop the appropriate conflict resolution skills necessary in a high stress environment c) understand the responsibility, and the liability involved with the transfer of a patient from an institution to another Second Year Fellows: a) ensure that there is continuity of care and that all details of the patient’s care have been attended to prior to transfer to another attending Updated April 2014 morning sign in and sign out rounds family meetings, discussions with staff and ethicists organize transfers of patients to and from referring hospitals under the supervision of the attending physician function as a junior attending 6