quantitative coronary angiography (qca) of
advertisement

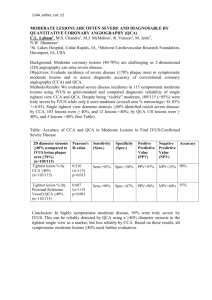
1146, either, cat: 12 QUANTITATIVE CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY (QCA) OF INDETERMINATE LEFT MAIN DISEASE CAN RELIABLY PREDICT SEVERITY C.L. Laham1, M.S. Chandra1, M.J. McMahon1, R. Venzon1, M. Jerin2, N.W. Shammas2 1 St. Luke’s Hospital, Cedar Rapids, IA, 2Midwest Cardiovascular Research Foundation, Davenport, IA, USA Background: Left main coronary lesions are considered severe if they have a minimum luminal area (MLA) of ≤5.9 mm2 by intracoronary ultrasound (IVUS). Based on Area stenosis= ∏ x (radius)2, MLA≤ 5.9 mm2 corresponds to a lesion minimum luminal diameter (MLD) of ≤2.74 mm. Given eccentricity of lesions, a single view angiographic assessment of disease severity is unreliable. Objective: We hypothesized, that applying 2-view QCA to symptomatic patients with indeterminate LM and large artery lesions using the conservative average of MLD ≤2.66 mm as cutoff marker, would predict MLA<5.9 mm2 by IVUS. Methods/Results: We evaluated 119 symptomatic indeterminate large artery lesions of which 47 were in LM’s (average vessel sizes and standard deviations 5.34 +/0.123mm and 6.22+/-0.965 respectively). There was a very strong correlation between mean angiographic 2-view lesion MLD and IVUS determined MLA using Pearson’s correlations, r = 0.822 (0.855 in true left mains, both p < 0.001). The positive predictive value of 2-view QCA overall (and in true left mains) was 98% (95%) with negative predictive value of 86% (85%). Figure. Lesion MLA (IVUS) vs MLD (QCA) 12 Lesion MLA (mm2) 10 8 6 4 2 0 0.0 .5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 Average MLD by QCA (mm) Conclusion: Average lesion MLD ≤2.66 mm by QCA in 2 orthogonal angiographic views is a strong predictor of MLA<5.9 mm2 by IVUS, suggesting that this method can reliably identify severe LM lesions in symptomatic patients with angiographically indeterminate LM disease.