Master`s Degree Philosophy
advertisement
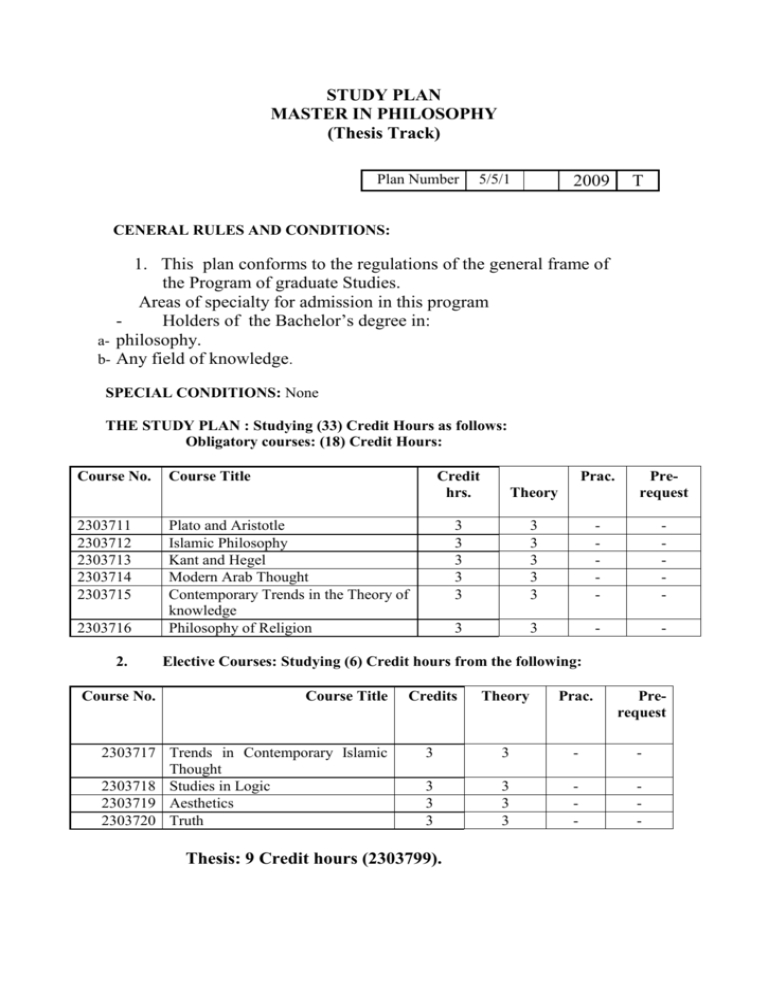
STUDY PLAN MASTER IN PHILOSOPHY )Thesis Track( Plan Number 9002 5/5/1 T CENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1. This plan conforms to the regulations of the general frame of the Program of graduate Studies. Areas of specialty for admission in this program Holders of the Bachelor’s degree in: a- philosophy. b- Any field of knowledge. SPECIAL CONDITIONS: None THE STUDY PLAN : Studying (33) Credit Hours as follows: Obligatory courses: (18) Credit Hours: Course No. 9303022 9303029 9303023 9303022 9303022 9303022 2. Course No. Course Title Credit hrs. Theory 3 3 3 3 3 3 Plato and Aristotle Islamic Philosophy Kant and Hegel Modern Arab Thought Contemporary Trends in the Theory of knowledge Philosophy of Religion Prac. Prerequest 3 3 3 3 3 - - 3 - - Elective Courses: Studying (6) Credit hours from the following: Course Title 9303020 Trends in Contemporary Islamic Thought 9303022 Studies in Logic 9303022 Aesthetics 9303090 Truth Credits Theory Prac. Prerequest 3 3 - - 3 3 3 3 3 3 - - Thesis: 9 Credit hours (2303799). Course Description PLATO AND ARISTOTLE (2303711 ) (3 Cr. hours) A comparative study of Plato’s and Aristotle’s theories of being and knowledge; an analysis of selected texts from Plato’s dialogues: Theatetus, Parmenides, Republic, Sophist…. . and from Aristotle’s Metaphysics. ISLAMIC PHILOSOPHY (2303712 ) (3 Cr. hours) Discussion of the theories of Islamic thinkers on specific topics of physics, such as : body and soul, movement and space and other topics in metaphysics such as creation, the necessary being and the contingent. KANT AND HEGEL (2303713 ) (3 Cr. hours) A comparative study of Kant’s and Hegel’s philosophies concerning knowledge and being; Hegel’s science of logic and his attempt to surpass Kant’s “ Critique of Pure Reason”; selected texts from the “ Critique “ and the “ Phenomenology of Mind”. MODERN ARAB THOUGHT (2303714 ) (3 Cr. hours) A critical study tackling the trends of Arab thought in the 19th century Concerning the principle of reformation with respect to the social, political and religious realms; together with the texts representing these trends. CONTEMPORARY TRENDS IN THE THEORY OF KNOWLEDGE (2303715 ) (3 Cr. hours) A critical examination of the major trends in contemporary philosophy, focusing on the nature of knowledge, its limits, conditions and justification. Idealistic school, modern logical positivism, materialism, critical school, Phenomenological school, New-Kantianism, Analytic school. PHILOSOPHY OF RELIGION (2303716) (3 Cr. hours) Religion: its nature and significance; a critical analysis of the problem of divinity; theological and natural religion: critical analysis of the relationship between religion and morality; the problem of evil; sources of religions knowledge; the philosophical evaluation of the revelation’s words : nature of belief and faith; the meaning of human existence : human soul and its fate ; the Divine-human relation : man’s freedom and the human’s hope for eternity. TRENDS IN CONTEMPORARY ISLAMIC THOUGHT (2303717 ) (3 Cr. hours) A study of the main trends in Islamic thought: Salafism-movement, AlGehadi trend, the enlightenment reform trend, a study in the sources and beliefs of these systems and their impacts on the contemporary Islamic societies. STUDIES IN LOGIC (2303718 ) (3 Cr. hours) Logic and language ; arguments and fallacies; categorical logic; symbolic logic: arguments; replacement and proofs; inductive reasoning: analogy , causation; the development of philosophical logic; logical analysis of concepts and arguments central to philosophy inquiry: necessity, knowledge, reasoning ; epistemic logic ; applied logic; logic of relations . AESTHETICS (2303719) (3 Cr. hours) Theories on the nature of art; the theory of imitation; emotionalism; formalism; problems in the philosophy of art; the paradox of tragedy; truth in art; aesthetic value, artistic creation; metaphors and interpretation. TRUTH (2303720 ) (3 Cr. hours) what is truth ? what sorts of things can be true. Is truth a property of sentences or a property of propositions ? ; Theories of truth : Correspondence theory, the semantic theory, the deflationary theory, the coherence theory, the pragmatic theory. Can claims about the future be true now ? Can the predicate “is true” be completely defined in other terms or it can be eliminated without loss of meaning, from any context in which it occurs ? to what extent do theories of truth avoid paradox ? is the goal of scientific research to achieve truth ? .