1835 Fundamentals of Graphic Communication Instruc Guide
advertisement
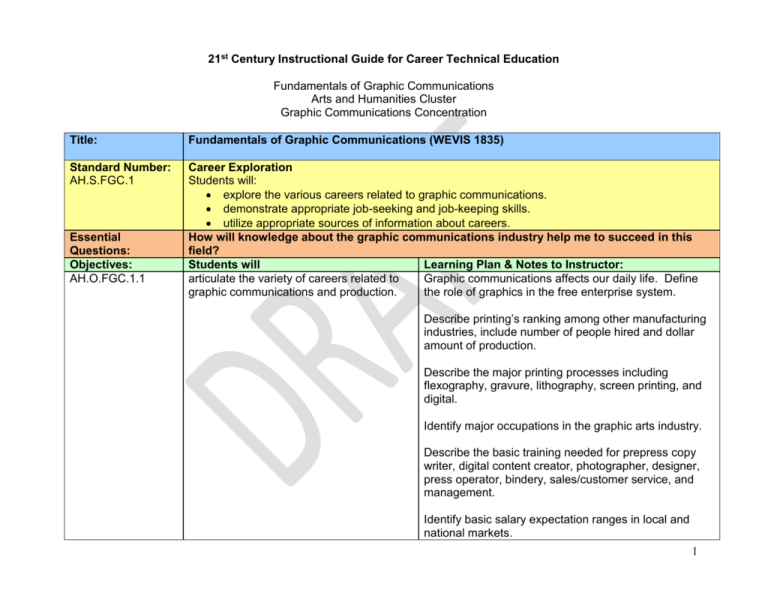
21st Century Instructional Guide for Career Technical Education Fundamentals of Graphic Communications Arts and Humanities Cluster Graphic Communications Concentration Title: Fundamentals of Graphic Communications (WEVIS 1835) Standard Number: AH.S.FGC.1 Career Exploration Students will: explore the various careers related to graphic communications. demonstrate appropriate job-seeking and job-keeping skills. utilize appropriate sources of information about careers. How will knowledge about the graphic communications industry help me to succeed in this field? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: articulate the variety of careers related to Graphic communications affects our daily life. Define graphic communications and production. the role of graphics in the free enterprise system. Essential Questions: Objectives: AH.O.FGC.1.1 Describe printing’s ranking among other manufacturing industries, include number of people hired and dollar amount of production. Describe the major printing processes including flexography, gravure, lithography, screen printing, and digital. Identify major occupations in the graphic arts industry. Describe the basic training needed for prepress copy writer, digital content creator, photographer, designer, press operator, bindery, sales/customer service, and management. Identify basic salary expectation ranges in local and national markets. 1 Use an online job search engine to explore jobs in graphic communications. Identify print markets and types of print businesses and major companies that employ people with graphic communications skills. Include commercial printers; inplant printers; book printers; packaging, label & wrapper printers; catalogs & directories printers; direct mail printers; business forms printers; financial & legal printers; inserts & coupon printers; magazine & periodical printers; trade binderies, and pre-press services. Observe a commercial printing operation and identify production departments. Sample assessment questions include: 1. Prepress activities include all of the following except: A. layout B. typesetting C. folding D. platemaking 2. Describe three major printing processes. Offset lithography, gravure, flexography, screen printing, and digital. AH.O.FGC.1.2 demonstrate appropriate job seeking and keeping skills. List desirable work ethics or required for industry employment. Examine want ads. Create a personal resume that includes three references. 2 Create a cover letter to obtain a job in the graphic communications industry. Examine and complete an employment application form. Practice job interview skills and the role of appearance in the job interview process. Complete a telephone interview for a printing job. Write a follow-up letter to telephone interview. Justify the reasons for making a follow-up call to a telephone interview. Evaluate an employment benefits package. Compare job opportunities in the graphic communication industry. Include wages, benefits, and job responsibilities. Sample assessment questions include: Which of the following would not be considered an employment benefit: A. health insurance B. paid vacation C. retirement plan D. withholding tax Identify three important items to remember when writing a resume. personal information Remember that an employer cannot ask age, gender, religious preference, race, or sexual 3 AH.O.FGC.1.3 locate sources of information about careers in graphic communications. preference. education, work experience cocurricular and extracurricular activities specialized training certifications Utilize a variety of sources to locate job listings in the field of graphic communications. Examples include the Internet, associations, trade magazines, newspapers, agencies, Sample assessment questions include: Which of the following is not a major source of information on the local job market: Newspaper Internet Trade magazine Word of mouth Standard Number AH.S.FGC.2 Essential Questions: Objectives: AH.O.FGC.2.1 Environmental Health and Safety Students will practice proper safe work habits in and around the lab. Who is responsible for safety in the workplace? Students will demonstrate job-related safety precautions and procedures regarding use of materials and equipment in the graphic communications lab. Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: Describe proper location and use of fire safety equipment in the facility. List the steps to be taken in case of injury in the lab. Identify location(s) of first aid kit(s), eye wash station(s), and panic button(s). Describe protective safety equipment and its use. Include gloves, goggles, and ear plugs. Describe appropriate safety procedures to follow when 4 operating equipment. Describe approved shop dress code for safe operation including necessary personal safety equipment. Pass a general lab safety test with a score of 100% or above. AH.O.FGC.2.2 assess proper precautions for handling toxic or flammable chemicals. Identify the safety color code. List safety rules involving toxic and/or flammable liquids. Read and interpret Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS). Identify and use OSHA approved methods to dispose of waste materials. Read, interpret and follow instructions on warning labels. Standard Number: AH.S.FGC.3 Essential Questions: Objectives: AH.O.FGC.3.1 AH.O.FGC.3.2 AH.O.FGC.3.3 AH.O.FGC.3.4 Equipment and Materials Students will: describe various pieces of graphic communications equipment, tools, and software. select the correct equipment, tool, or software application to complete a job. How will knowledge of equipment, tools, and software make me more proficient in the graphic communications industry? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: compare a variety of major graphic Include presses, bindery, scanners, cameras, communications equipment. computers, printers and imagesetters. utilize basic tools used in the graphic Include hand tools, pin register, line gauges, communications lab. proportional scales and densitometers. differentiate among types of graphic Include page layout software, graphic content creation communications software applications. software, photo manipulation, drawing and word processing. select the correct equipment, tool, or Provide a variety of activities for students to explore the software application to complete a job. selection of correct equipment, tools and software application. 5 Standard Number: AH.S.FGC.4 Essential Questions: Objectives: AH.O.FGC.4.1 Legal and Ethical Issues Students will: differentiate between copyright violations and fair use. differentiate between copyrights and trademarks. discuss the ethical considerations concerning plagiarism. How do copyrights protect the creators of original content? Students will differentiate among counterfeiting, copyright, and fair use laws. Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: Recall original author copyright lasts a lifetime plus 70 years. Examine the size, color, and number of side limits for currency reproduction. AH.O.FGC.4.2 correlate the elements of a copyright notice. AH.O.FGC.4.3 assess the purpose of registered trademarks. AH.O.FGC.4.4 AH.O.FGC.4.5 Explore limits on student use of materials. Include date, name of the copyright holder, copyright symbol (©), the word “copyright”, and the abbreviation of the word “copyright” which is “copr.” Trademarks are registered logos. distinguish between items that may and may not be copyrighted. Registered trademarks are good forever as long as the mark is continuously used. Items that can be copyrighted include original works or authorship fixed in any tangible medium such as books, literary works, musical compositions, artworks, choreographic works, photographs, films, and videos. research procedures for obtaining permission to reproduce copyrighted materials. Items that cannot be copyrighted include names, titles, tape measures, rulers, sports schedules, ingredients in a recipe, and slogans. Include identify the copyright owner(s). contact the copyright owner(s). secure permission. keep a detailed record of your quest for obtaining 6 AH.O.FGC.4.6 illustrate why plagiarism is illegal and/or unethical. permission. determine how to deal with “dead end” quests. visit http://www.copyright.iupui.edu/permsec.htm#three1 for more details. What constitutes intellectual/artistic property? The term "intellectual property" is an umbrella term, which encompasses the bundle of rights arising from intellectual creations such as creative and artistic works, inventions, marks, and proprietary information. As a general rule, intellectual property is considered to include four categories of intellectual creations: Copyrights Patents, Trademarks, and Trade secrets. Visit http://intellectual-property.lawyers.com/ask-alawyer/What-Constitutes-%22Intellectual-Property%226210.html for more details. According to Wikipedia, plagiarism is the unauthorized use or close imitation of the language and thoughts of another author and the representation of them as one's own original work Within academia, plagiarism by students, professors, or researchers is considered academic dishonesty or academic fraud and offenders are subject to academic censure. In journalism, plagiarism is considered a breach of journalistic ethics, and reporters caught plagiarizing typically face disciplinary measures ranging from suspension to termination. According to Wikipedia, plagiarism is different from copyright infringement. While both terms may apply to a particular act, they emphasize different aspects of the transgression. Copyright infringement is a violation of the rights of the copyright holder, when material is used 7 without the copyright holder's consent. On the other hand, plagiarism is concerned with the unearned increment to the plagiarizing author's reputation that is achieved through false claims of authorship. Standard Number AH.S.FGC.5 Essential Questions: Objectives: AH.O.FGC.5.1 AH.O.FGC.5.2 Standard Number AH.S.FGC.6 Essential Questions: Objectives: AH.O.FGC.6.1 Design Elements and Principles Students will describe appropriate design elements and principles. How does the proper use of design elements and principles affect my ability to communicate visually? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: incorporate basic design elements when Explore color, mass, line, shape, and texture. developing projects. incorporate basic design principles when Explore unity, contrast, balance, rhythm, and proportion. developing projects. Job Planning and Production Students will: determine the requirements for a specific project. develop and refine project concepts. complete a project to customer specifications. How does planning optimize work flow? Students will complete a job ticket. Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: A typical job ticket includes customer name project type due date size color quantity bindery information materials specifications shipping/delivery time limit (audio/video/multimedia) file format record keeping 8 AH.O.FGC.6.2 establish a timeline/work-flow for a project. AH.O.FGC.6.3 analyze the elements of page composition. AH.O.FGC.6.4 produce thumbnail sketches. AH.O.FGC.6.5 apply an appropriate scale during the design composition process. apply a variety of font styles and typefaces. AH.O.FGC.6.6 AH.O.FGC.6.7 incorporate artwork and screen tints. AH.O.FGC.6.8 use a variety of appropriate tools for composition. develop roughs. develop a project using appropriate layout, type, and artwork/digital content. AH.O.FGC.6.9 AH.O.FGC.6.10 Standard Number AH.S.FGC.7 Essential Questions: Objectives: AH.O.FGC.7.1 cost estimate Consider due date, complexity, assets, materials , ordering, outsourcing and “fudge” factor. Elements apply to both paper and digital composition headline subhead copy-block illustrations/photos white space (margins/gutters) A thumbnail is small drawing on paper used to explore multiple ideas quickly. Explore inch, point, pica, and pixel. Font styles include italic, bold, underline, etc. Typefaces refer to Roman, decorative, novelty, gothic, square serif, sans serif, cursive, script, etc. Artwork includes both hand and digitally created images. Software tools include the type tool, object editor, shape tools, etc. Full-size drawings of a project idea Sample projects include three-panel brochure CD cover retail package magazine covers advertising digital presentations Measurement and Math Students will solve math problems encountered in the graphic communications industry. Students will measure linear dimensions for printing Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: Provide opportunities for students to measure linear 9 materials in inches and fractions of inches. AH.O.FGC.7.2 AH.O.FGC.7.3 AH.O.FGC.7.4 AH.O.FGC.7.5 measure type in points and line length in picas. determine the resolution of a scanned or digital image. measure original images for reduction and enlargement using various methods to determine the percentage for final reproduction. calculate ratios for mixing chemicals. dimensions for printing materials in inches and fractions of inches. Provide opportunities for students to measure type in points and line length in picas. Discuss screen resolutions vs. output resolutions Provide opportunities for students to measure original images for reduction and enlargement using various methods to determine the percentage for final reproduction. Provide opportunities for students to calculate ratios for mixing chemicals. Provide activities to include converting inches to points, picas, and pixels reducing fractions paper cutting estimation AH.O.FGC.7.6 apply basic mathematical principles to solve common problems encountered in graphic communications. Standard Number: AH.S.FGC.8 Essential Questions: Objectives: AH.O.FGC.8.1 Student Organization Participation Students will participate in a local student organization. How can a student organization make me better prepared to work in a global society? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: examine the purposes and goals of student Encourage formation of a school chapter in local student organizations. organization such as SkillsUSA and/or TSA. AH.O.FGC.8.2 demonstrate leadership skills through Encourage membership in local student organization participation in student organization such as SkillsUSA and/or TSA. activities such as meetings, programs, projects, and competitions. AH.O.FGC.8.3 discover the benefits and responsibilities of Encourage attendance and competition at local, state, participation in student, professional, and and national SkillsUSA and/or TSA conferences. civic organizations as an adult. You may add your comments for 21st Century Skills at Google.docs. Invitation sent 8/24/08. 21st Century Skills Learning Skills & Technology Tools Teaching Strategies Evidence of Success Culminating Activity Information and 21C.O.9Student recognizes 10 Communication Skills: 12.1.LS1 21C.O.912.1.LS2 21C.O.912.1.LS3 21C.O.912.1.TT1 information needed for problem solving, can efficiently browse, search and navigate online to access relevant information, evaluates information based on credibility, social, economic, political and/or ethical issues, and presents findings clearly and persuasively using a range of technology tools and media. Student analyzes and interprets visuals and recognizes the impact digital media influences (e.g. design, technique, and rate of speed) have on audiences. The student’s visual products reflect a sophisticated understanding of subject, digital media and design techniques. Student creates information using advanced skills of analysis, synthesis and evaluation and shares this information through a variety of oral, written and multimedia communications that target academic, professional and technical audiences and purposes. Student makes informed choices among available advanced technology 11 21C.O.912.1.TT2 21C.O.912.1.TT3 21C.O.912.1.TT4 systems, resources and services (e.g., global positioning software, graphing calculators, personal digital assistants, web casting, online collaboration tools) for completing curriculum assignments and projects and for managing and communicating personal/professional information. Student routinely applies Students will utilize computer Completed assignments keyboarding skills, software on a routine basis keyboarding shortcut to complete assignments. techniques, and mouse skills with facility, speed and accuracy. Student uses advanced utilities (e.g., zipping or compressing files, file level anti-virus scans), converts files to different formats (e.g., .doc, .xls, .mdb, .htm, .pdf) and saves finished products to multiple media sources (e.g., CDRW, DVDR, USB drives, shared folders, webbased file storage). Student uses audio, video, pictures, clip art, moviemaker programs, webpage design software, electronic documents and other files to collaborate for the creation of electronic products that 12 21C.O.912.1.TT5 21C.O.912.1.TT6 21C.O.912.1.TT7 21C.O.912.1.TT8 inform multiple audiences both inside and outside the school environment. Student uses advanced features of word processing software (e.g., outline, table of contents, index feature, draw tool, headers and footers, track changes, macros, hyperlinks to other file formats, etc.). Student uses advanced features and utilities of spreadsheet software, (e.g., formulas, filters, pivot tables, pivot charts, macros, conditional formatting), to perform calculations and to organize, analyze and report data. Student uses advanced features and utilities of presentation software (e.g., slide transitions, master slides, narrations and timings, creating web-enabled presentations, creating a nonlinear presentation) to communicate ideas to multiple audiences. Student uses advanced features and utilities of database software (e.g., to create tables, forms, perform table relationships, advanced queries, and simple reports) 13 21C.O.912.1.TT9 21C.O.912.1.TT10 21C.O.912.1.TT10 21C.O.912.1.TT11 to test hypotheses or research questions and to report results. Student uses advanced telecommunication tools (e.g., email, video conferencing, interactive websites, newsgroups, video phones, chats) to create collaborative projects that are relevant to real world situations and contribute to the communication process among various groups. Student implements various Internet search techniques (e.g., Boolean searches, meta-searches, web bots) to gather information; student evaluates the information for validity, appropriateness, content, bias, currency, and usefulness. Student implements various Internet search techniques (e.g., Boolean searches, meta-searches, web bots) to gather information; student evaluates the information for validity, appropriateness, content, bias, currency, and usefulness. Student imports and exports multiple data formats and integrates to multiple productivity programs (e.g., 14 Thinking and Reasoning Skills: 21C.O.912.2.LS1 21C.O.912.2.LS2 21C.O.912.2.LS4 21C.O.912.2.TT1 exports comma delimited files, standard data formats) and understands transferability of data among different programs. Student engages in a critical thinking process that supports synthesis and conducts evaluation using complex criteria. Student draws conclusions from a variety of data sources to analyze and interpret systems. Student visualizes the connection between seemingly unrelated ideas and independently produces solutions that are fresh, unique, original and well developed. Student shows capacity for originality, concentration, commitment to completion, and persistence to develop unique and cogent products. Student knows how to find information necessary to solve advanced problems related to hardware, software, networks, and connections (e.g., by accessing online help, Internet searches, technical documentation, system utilities, and communication with technical 15 21C.O.912.2.TT2 21C.O.912.2.TT3 21C.O.912.2.TT4 experts). Student collaborates with peers, experts, and others to contribute to a content-related knowledge base by using technology to compile, synthesize, produce, and disseminate information, models, and other creative works. Student uses multiple electronic sources of information and multiple technology tools and resource tools (e.g., digital cameras, graphing calculators, probes, mp3 players, handheld devices, other emerging technologies, simulations, models, browsers, word processing, authoring tools, spreadsheets, databases) to collaborate with others, to formulate a hypothesis, to solve problems, make decisions, and present and justify the solutions. Student uses technology tools and multiple media sources to analyze a real-world problem, design and implement a process to assess the information, and chart and evaluate progress toward the solution. 16 Personal and Workplace Skills: 21C.O.912.3.LS1 21C.O.912.3.LS2 21C.O.912.3.LS3 21C.O.912.3.LS4 Student remains composed and focused, even under stress, willingly aligns his/her personal goals to the goals of others when appropriate, approaches conflict from winwin perspective, and derives personal satisfaction from achieving group goals. Student independently considers multiple perspectives and can represent a problem in more than one way, quickly and calmly changes focus and goals as the situation requires, and actively seeks innovations (e.g. technology) that will enhance his/her work. Student demonstrates ownership of his/her learning by setting goals, monitoring and adjusting performance, extending learning, using what he/she has learned to adapt to new situations, and displaying perseverance and commitment to continued learning. Student demonstrates ethical behavior and works responsibly and collaboratively with others in the context of the school and the larger community, and 17 21C.O.912.3.LS5 21C.O.912.3.LS6 21C.O.912.3.TT1 he/she demonstrates civic responsibility through engagement in public discourse and participation in service learning. Student exhibits positive leadership through interpersonal and problemsolving skills that contribute to achieving the goal. He/she helps others stay focused, distributes tasks and responsibilities effectively, and monitors group progress toward the goal without undermining the efforts of others. Student maintains a strong focus on the larger project goal and frames appropriate questions and planning processes around goal. Prior to beginning work, student reflects upon possible courses of action and their likely consequences; sets objectives related to the larger goal; and establishes benchmarks for monitoring progress. While working on the project, student adjusts time and resources to allow for completion of a quality product. Student protects software, hardware and network Students will participate in SkillsUSA or TSA and become a chapter or state officer or serve as chairpersons of committees. Students will work cooperatively in the classroom taking leadership roles. SkillsUSA or TSA meeting minutes Class work 18 21C.O.912.3.TT2 21C.O.912.3.TT3 21C.O.912.3.TT4 resources from viruses, vandalism, and unauthorized use and employs proper techniques to access, use and shut down technology equipment. Student works collaboratively to acquire information from electronic resources, conducts online research, and evaluates information as to validity, appropriateness, usefulness, comprehensiveness and bias. Student evaluates current trends in information technology, discusses the potential social, ethical, political, and economic impact of these technologies, and analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of widespread use and reliance on technology in the workplace and society. Student adheres to Students will sign and acceptable use policy and adhere to a school-wide displays ethical behaviors acceptable use policy. related to acceptable use of information and communication technology (e.g., privacy, security, copyright, file-sharing, plagiarism); student predicts the possible cost and effects of unethical use of technology Ethical use of technology 19 21C.O.912.3.TT5 21C.O.912.3.TT6 21C.O.912.3.TT7 (e.g., consumer fraud, intrusion, spamming, virus settling, hacking) on culture and society; student identifies the methodologies that individuals and businesses can employ to protect the integrity of technology systems. Student models ethical behavior relating to security, privacy, computer etiquette, passwords and personal information and demonstrates an understanding of copyright by citing sources of copyrighted materials in papers, projects and multimedia presentations. Student advocates for legal and ethical behaviors among peers, family, and community regarding the use of technology and information. Student evaluates and applies technology tools for research, information analysis, problem-solving, content learning, decision making, and lifelong learning. Student protects his/her identity online and in email and/or websites, limits the distribution of personal information/pictures, and evaluates the authenticity of Students will sign and adhere to a school-wide acceptable use policy. Ethical use of technology 20 emails that solicit personal information. Student identifies the methodologies that individuals and businesses can employ to protect the integrity of technology systems. 21C.O.9Student uses technology to 12.3.TT8 seek strategies and information to address limits in their own knowledge. Learning Skills & Technology Tools Entrepreneurial Skills: Culminating Assessment: Student understands the personal traits/behaviors associated with successful entrepreneurial performance. Teaching Strategies Culminating Activity Students take available online quizzes to learn their entrepreneurial aptitudes such as: http://www.bizmove.com/oth er/quiz.htm Evidence of Success Results from self-quizzes Student understands Students will utilize computer Completed assignments concepts and procedures software and hardware to needed for basic computer complete assignments. operations. Student understands Students will interview Interviews/reports concepts and strategies individuals in the graphics needed for career exploration, industry to learn how their development and growth. career paths developed. Culminating Assessment: End of Concentration Performance Evaluation Students will participate in TSA’s competitive events: Promotional Graphics, Desktop Design, Leadership Development Contests: Career Comparisons, Written and Oral Chapter Team, Extemporaneous Presentation, and Prepared Presentation 21 Links and Other Resources: Students will participate in SkillsUSA’s competitive events: Graphic Communications, Leadership Development Contests: Action Skills, American Spirit, Chapter Business Procedure, Chapter Display, Community Service, Extemporaneous Speaking, Job Interview, Job skill Demonstration A, Job Skill Demonstration B, Occupational Health and Safety, Opening and Closing Ceremonies, Outstanding Chapter, Prepared Speech, Promotional Bulletin Board, and Quiz Bowl Links and Other Resources Related Websites: Pathways to Success http://careertech.k12.wv.us/pathwaystosuccess/ U.S. Department of Labor in the 21st Century http://www.dol.gov/ Advanced Distributed Learning www.adlnet.org America's Career InfoNet www.acinet.org America's Job Bank www.ajb.org America's Service Locator www.servicelocator.org CareerOneStop www.careeronestop.org Employment & Training Administration www.doleta.gov The Job Accommodation Network (JAN) http://www.jan.wvu.edu Monthly Labor Review Online: Labor Force Archives 22 http://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/indexL.htm#Labor force Occupational Information Network www.doleta.gov/programs/onet Office of Disability Employment Policy www.dol.gov/odep Career Voyages http://www.careervoyages.gov/index.cfm Workforce West Virginia https://www.workforcewv.org/ West Virginia Earn A Degree Graduate Early (EDGE) http://www.wvtechprep.wvnet.edu/edge.htm West Virginia Career and Technical Education http://careertech.k12.wv.us/ Contacts: Contacts CTE Teachers: See CTE Directory Cluster Coordinator: Kathy Gillman, kgillman@access.k12.wv.us OCTI Assistant Executive Director and EOCTST Coordinator: Donna Burge-Tetrick OCTI Executive Director: Gene Coulson 23








