What is co-teaching? - Taipei European School
advertisement

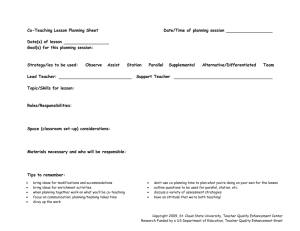
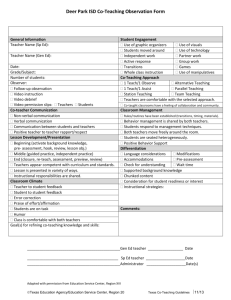
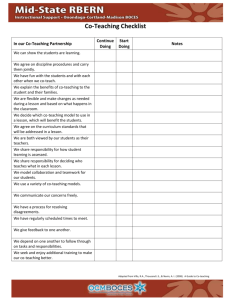
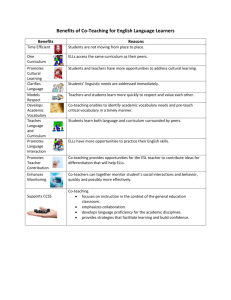
What is co-teaching? Co-teaching describes the collaboration of two teachers to meet the needs of the students in a single class using one, or a combination, of strategies from the 6 listed below. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Parallel teaching Alternative teaching Teaming Station teaching One teach - one assist One teach - one observe Originally developed in the field of Special Needs Education in the United States in recent years co-teaching techniques have been increasingly utilized in the field of teaching EAL/ESL. In co-teaching the skills of the general classroom practitioner and the language specialist complement each other maximizing the impact of having two professionals in the classroom. The most appropriate method of co-teaching will change according to the activities/lesson objectives, dynamics of the class and the confidence/experience of the teachers involved in relation to co-teaching. It is inevitable that teachers feel more comfortable with some methods than others and they need to experiment and evaluate each in terms of the impact it has on learning and language acquisition and consolidation in particular. 1)Parallel teaching – Two teachers teach the same material to two different groups using different strategies or methods of differentiation. Classroom teacher and support teacher collaboratively organise the content of the lesson. Classroom teacher and support teacher identify strategies and technology needed for group and individual students. Classroom teacher and support teacher divide the students into two equal groups. 1 Classroom teacher and support teacher independently deliver the lesson plan to one of the groups. The delivery can be in the same classroom or a different classroom. Classroom teacher and support teacher each monitor their own group of students and evaluate their learning. Classroom teacher and support teacher collaboratively discuss student learning and evaluate the teaching and learning. Strategies guided or choral reading think-pair-share learning style groups exploring content small group discussion scaffolding direct instruction - cycles of teaching and learning cycle sharing-reader’s theater, author’s chair, presentations assessment review 2) Alternative teaching The classroom teacher conducts formal teaching. The support teacher implements supplemental activities for small groups, or individuals before or after the formal lesson Classroom teacher and support teacher pre-assess the students to plan for alternative lessons. Classroom teacher and support teacher assess the students during formal lessons to identify students who would benefit from the alternative lessons. Classroom teacher and support teacher make decisions about the content and organisation of the alternative lessons. Classroom teacher and support teacher determine the appropriate structures for alternative lessons that would promote more student learning. 2 Using this model the support teacher can: 1. Activate background knowledge 2. Teach particular skills, knowledge or understanding in smaller steps. These will be related to your assessments. 3. Extend students 3) Teaming The class teacher and support teacher teach one class of children as a whole class. Both teachers implement the teaching. Both teachers share the instruction to students in a coordinated fashion. While one teacher is instructing, the other teacher may be assisting and then they swap. The class teacher and support teacher have: • Equal knowledge of the content • A shared philosophy • A commitment to all students in the class 3) Station Teaching Children in a class are grouped into three (or more) groups and rotate around fixed “stations” in the classroom giving the teachers at each station the opportunity to adapt the activity to the needs of the children in each group. The class teacher and support teacher can independently plan their station after deciding on the objective of their station. Example: Teacher directed task: Station 1: Objective - I will reinforce the structure of a biography. Teacher directed task: Station 2: Objective - I will reinforce the use of past tense. Independent task: Station 3: Objective - I will reinforce the use of subheadings in a biography. 5) One teach – one assist (teach and drift) Although there are times that this method is useful it should be used sparingly and judiciously. It should not be the default co-teaching strategy. 3 6) One Teach – One Observe This approach should be used minimally and only for the purpose of ascertaining the specifics of how a student learns or interacts in lessons. The observation should be: • Planned • On a timed-schedule • Recorded • Used in future planning and teaching 4