Ch 18 Classification
advertisement

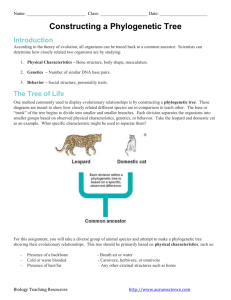
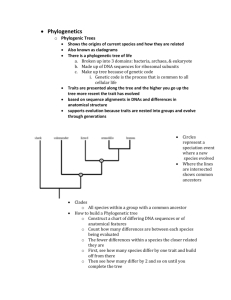
Biology I (H) Study Guide: CH 18 CLASSIFICATION E. S. Gustafson NAME:_____________________________ _______ PERIOD: ____ SECTION 18-1: HISTORY OF CLASSIFICATION EARLY SYSTEMS OF CLASSIFICATION Define taxonomy. Explain the classification system used by the Greek philosopher Aristotle more than 2000 years ago. Discuss the problem with using common names to identify organisms. Provide some examples. LINNAEUS’S SYSTEM What criteria did Linnaeus use to categorize organisms? List the seven levels or organization in Linnaeus’s hierarchy from the most inclusive to the most exclusive. (1) (5) (2) (6) (3) (7) (4) Write a mnemonic aid to help remember the categories above in descending order of hierarchy. Distinguish between phylum & division. Is “division” still commonly used in taxonomy? Explain the aspects of binomial nomenclature. Provide an example. 1 What is a variety? Provide examples of two varieties. What is a subspecies? Provide examples of two subspecies. What do modern taxonomists consider when classifying organisms? Define phylogeny. SECTION 18-2: MODERN PHYLOGENETIC TAXONOMY SYSTEMATICS What is systematics? List 5 lines of evidence used by modern systematic taxonomists to construct a phylogenetic tree. (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) What is a phylogenetic tree? Examine the phylogenetic tree at right. Numbers represent modern species; letters represent points of divergence from a common ancestor. What position indicates the common ancestor of species 1 through 4? Which species are most closely related? Which species are most distantly related? Which position marks the most remote ancestor of all the species? Which position marks the most recent common ancestor of all the species? 2 Provide an example of how the fossil record might be used to establish a phylogenetic relationship between different organisms. Provide an example of how morphology might be used to establish a phylogenetic relationship between different organisms. Provide an example of how embryological patterns of development might be used to establish a phylogenetic relationship between different organisms. Provide an example of how chromosomal karyotypes might be used to establish a phylogenetic relationship between different organisms. Provide an example of how macromolecular homologies might be used to establish a phylogenetic relationship between different organisms. CLADISTICS How is cladistics used to establish evolutionary relationships? What is a derived character? 3 Use your text to write in the derived characters in the cladogram of terrestrial vertebrates below (see Figure 18-6) . According to the cladogram, what two groups are most closely related? ____________________________ SECTION 18-3: TWO MODERN SYSTEMS OF CLASSIFICATION SIX-KINGDON SYSTEM The original modern classification system consisted of _______ kingdoms. Use your text to fill in the missing information in the table below. (See Table 18-2.) 4 Provide 3 examples of where archaebacteria might live. Provide 3 examples of eubacteria. Note that most eubacteria are beneficial. Provide 2 examples of common protistan groups. One unicellular & one multicellular Provide 6 examples of fungal groups. How many species of fungi are currently identified? ____________ Provide 4 examples of plant groups. How many species of plants are currently identified? ____________ Provide 11 examples of animal groups. How many species of animals are currently identified? ________ THREE-DOMAIN SYSTEM Use the illustration below to list the 3 domains & associate them with the members of the 6-kingdom system. 5