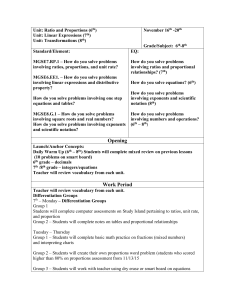
3rd grade - Gull Lake Community Schools
advertisement
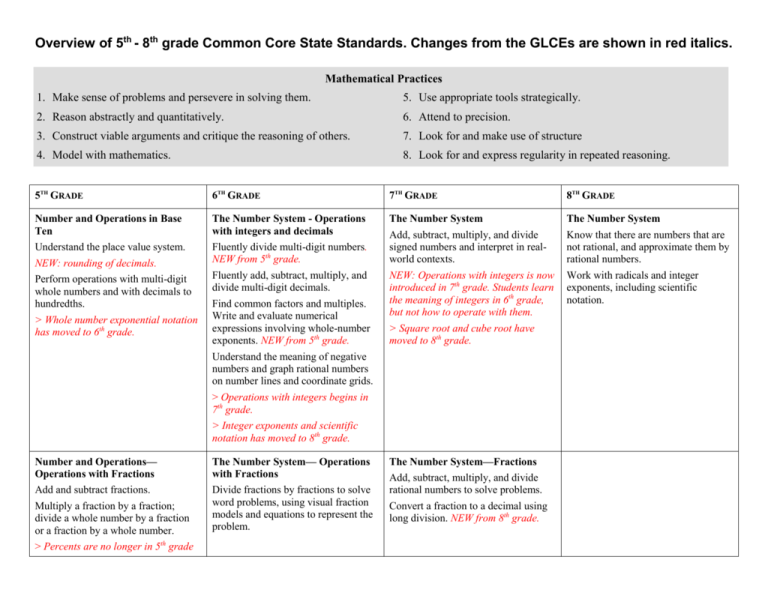
Overview of 5th - 8th grade Common Core State Standards. Changes from the GLCEs are shown in red italics. Mathematical Practices 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 6. Attend to precision. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 7. Look for and make use of structure 4. Model with mathematics. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. 5TH GRADE 6TH GRADE 7TH GRADE 8TH GRADE Number and Operations in Base Ten Understand the place value system. The Number System - Operations with integers and decimals Fluently divide multi-digit numbers. NEW from 5th grade. Fluently add, subtract, multiply, and divide multi-digit decimals. The Number System Add, subtract, multiply, and divide signed numbers and interpret in realworld contexts. NEW: Operations with integers is now introduced in 7th grade. Students learn the meaning of integers in 6th grade, but not how to operate with them. > Square root and cube root have moved to 8th grade. The Number System Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. Work with radicals and integer exponents, including scientific notation. NEW: rounding of decimals. Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers and with decimals to hundredths. > Whole number exponential notation has moved to 6th grade. Find common factors and multiples. Write and evaluate numerical expressions involving whole-number exponents. NEW from 5th grade. Understand the meaning of negative numbers and graph rational numbers on number lines and coordinate grids. > Operations with integers begins in 7th grade. > Integer exponents and scientific notation has moved to 8th grade. Number and Operations— Operations with Fractions Add and subtract fractions. Multiply a fraction by a fraction; divide a whole number by a fraction or a fraction by a whole number. > Percents are no longer in 5th grade The Number System— Operations with Fractions Divide fractions by fractions to solve word problems, using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. The Number System—Fractions Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers to solve problems. Convert a fraction to a decimal using long division. NEW from 8th grade. (see 6.RP.3c) > Prime factorization is no longer in 5th grade. > Ratios are no longer in 5th grade. Ratios and Proportional Relationships Understand and solve problems with ratios and rates. Ratios and Proportional Relationships Compute unit rates. Use proportional relationships to solve real-world and mathematical problems including multistep ratio and percent problems such as simple interest, tax, markups and markdowns, gratuities and commissions, fees, percent increase and decrease, percent error. (see Functions below) > Working with derived quantities (e.g. density) has moved to high school geometry. Operations and Algebraic Thinking Write and interpret numerical expressions. NEW from 6th grade Expressions and Equations Write, read, and evaluate expressions with whole number exponents. Write, read, and evaluate expressions with variables; identify and generate equivalent expressions. Solve one-variable single-step equations with positive coefficients. Represent solutions of inequalities of the form x > c or x < c on number lines and relate to real-world problems. NEW: previously inequalities started in 8th grade. Analyze patterns and relationships. NEW, including graphing ordered pairs, from 6th grade Expressions and Equations Use properties of operations to add, subtract, factor and expand expressions. Expressions and Equations Analyze and solve linear equations involving rational number coefficients. Solve multi-step real-life and mathematical problems using numerical and algebraic expressions, equations and inequalities with positive and negative rational numbers. NEW: Inequalities, moved from 8th grade. Analyze and solve pairs of simultaneous linear equations. > Factoring quadratic expressions and solving quadratic equations is moved to Algebra I. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies. Express relationships between dependent and independent variables in tables, graphs and equations. Represent proportional relationships with equations and graphs. Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, 2 Functions Understand the connections between proportional relationships, lines, and linear equations; understand slope and diagrams, and verbal descriptions of proportional relationships. use the equations y = mx and y = mx + b. > The term “slope” is not introduced until 8th grade, although the concept is presented here. Interpreting the intercepts of graphs of linear functions has also moved out of 7th grade. Use linear functions to model relationships between quantities. Compare properties of linear functions represented algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions > Inversely proportional relationships are not explicitly contained in the CCSS. Define, evaluate, and compare functions. (Function notation is not required in 8th grade.) > Quadratic expressions, equations and functions are not addressed until high school. Exponential functions are not addressed formally until high school. Measurement … Convert like measurement units within a given measurement system. Geometric measurement: understand concepts of volume and relate volume to multiplication and to addition. … and Data Represent and interpret data using line plots. Statistics and Probability Develop understanding of statistical variability. Statistics and Probability Use random sampling to draw inferences about a population. > Mean/mode are no longer in 5th grade (see 6.SP.5c) Display, summarize and describe data sets. Draw informal comparative inferences about two populations. th th NEW from 4 grade: median; from 5 grade: mean; from 7th grade: interquartile range. > Probability has moved to 7th grade. Investigate chance processes and develop, use, and evaluate probability models. NEW from 6th and 8th grades. > Represent and interpret data using graphs has moved to 6th grade. > Scatter plots and line of best fit has moved to 8th grade. 3 Statistics and Probability Investigate patterns of association in bivariate data. NEW from 7th grade and Algebra I > Probability is no longer addressed in 8th grade – see 7.SP.6-8 > Measures of central tendency is now in 6th grade; bias in presentation of data is in high school. Geometry Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems. NEW from 6th grade Classify two-dimensional figures into categories based on their properties. > Area of rectangles, triangles and parallelograms is no longer in 5th grade (see 6.G.1) Geometry Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area of triangles, special quadrilaterals and other polygons (NEW from 5th grade), surface area, and volume. > Transformations and congruence has moved to 8th grade. > Problems involving angle measure has moved to 7th grade. > Informal paper-folding constructions has moved to high school geometry. Geometry Solve real-life and mathematical problems involving angle measure, area, surface area (not cones or spheres), and volume. (Problems involving angle measure is new from 6th grade.) Geometry Understand and solve problems involving congruence and similarity using physical models, transparencies, or geometry software. This is the first time that transformations are addressed. Know the formulas for the area and circumference of a circle and use them to solve problems. NEW from 8th gr. Draw, construct and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. Understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem. > Formal compass and straight-edge constructions has moved to high school geometry. 4 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving volume of cylinders, cones, pyramids and spheres. Not surface areas of cones or spheres. Circles moved to 7th grade. > Sketching 2-D views of solids is no longer in 8th grade.