Lecture 12: Refraction
advertisement

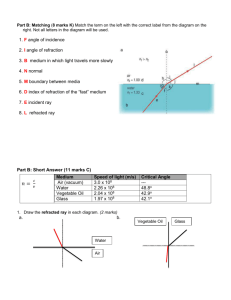
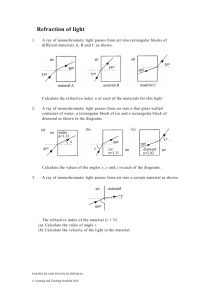
REFRACTION OF LIGHT. Refraction of light refers to the change in direction of light when it passes from one medium to another. When a ray of light AO passes from air into a rectangular block of glass , the light travels in a new direction OI in the glass and emerges along a direction IB parallel to AO. We say that the light is bent or refracted The direction AO is the direction of the incident ray and the angel between the incident ray and the normal is called the angle of incidence i The direction OI is the refracted ray and the angle between the refracted ray and the normal is called the angle of refraction r The glass is said to be optically denser than the air and r i 1. When a ray passes from one medium to a more optically dense medium the ray of light bends or is refracted towards the normal 2. Conversely when a ray passes from a medium to a less optically dense medium the ray bends away from the normal LAWS OF REFRACTION. 1. The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal all lie in the same plane. 2. For a given boundary between two media the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant sin i constant 1 n 2 sin r Snells Law Where 1n 2 is known as the refractive index when the light travels from medium 1 to medium 2. It can also be shown that velocity of light in medium 1 n 1 2 velocity of light in medium 2 If we take medium 1 as air and we know that the velocity of light in air is 3 x 108 m.s-1 given a special symbol c where c = 3 x 108 m.s-1 1. It should be noted that the light is refracted because light has different velocities in different media. 2. Usually medium 1 is taken to be air so that if only one medium is given the equation reads air nglass velocity of light in air velocity of light in glass 3x10 8 air nglass velocity of light in glass 3x10 8 velocity of light in glass air nglass The refractive index is usually written as nglass which always implies that the first medium is air. The equations can be used for all mediums air nwater air nwater velocity of light in air velocity of light in water 3x10 8 nwater velocity of light in water 3x10 8 velocity of light in water nwater The reversibility of light states that paths of light are reversible. Consider a ray of light travelling though air and then water. We use the angle formed between the light in air and the normal, which they would call the incident angle. They also use the angle between the light in water and the normal, which is called the refracted angle. What happens if light goes from water into the air? We imagine a mirror placed on the bottom of the aquarium, reflecting the laser light back upwards towards the surface. As we check things out, the pattern followed resembles the one below: It looks like the pattern upon entering water is just reversed when light leaves water. Indeed! If light bends closer to the normal upon entering water, it bends further from the normal upon leaving it. This is a nice example of the "reversibility" air n water n water sin i 1 sin r sin r sin i 1 water n air If the direction in which the ray is travelling is not mentioned it is assumed that the first medium is AIR. Some typical values for the index of refraction are given here: Substance n Air 1.00 Water 1.33 Glass 1.50± Plastic 1.40± Diamond 2.42 It is known that a pool of water appears more shallow than it actually is and this is due to the refraction of light, at the water air boundary. Consider an object O at an actual depth below the surface of water with refractive index n. Recall n is the refractive index from air to water. A ray travelling through the water makes an angle i with the normal at the water air boundary. The ray is refracted at this point along a direction at an angle r to the normal. An observer at C viewing the object sees it in the image position at an apparent depth below the surface of the water By reversibility of light air n water sin r sin i Which can be shown to be air nwater real depth apparent depth PROBLEM SHEET Take c = 3 x 108 m.s-1 Question 1. A glass plate is 0.6 cm thick and has a refractive index of 1.55. How long does it take light to pass through the plate. Question 2. The speed of light in a certain glass is 1.91 x 108m.s-1. Calculate the refractive index of the glass Question 3. A ray of light strikes the surface of water at an angle of incidence of 60o. Calculate the angle of refraction given n= 1.33 Question 4. A pool of water is 1 m deep. Calculate its apparent depth when viewed vertically. Question 5. A person looking down vertically into a pond sees a fish apparently 18 cm below the surface. Calculate the actual depth of the fish in the pond.