Stephen W - East Carolina University
advertisement
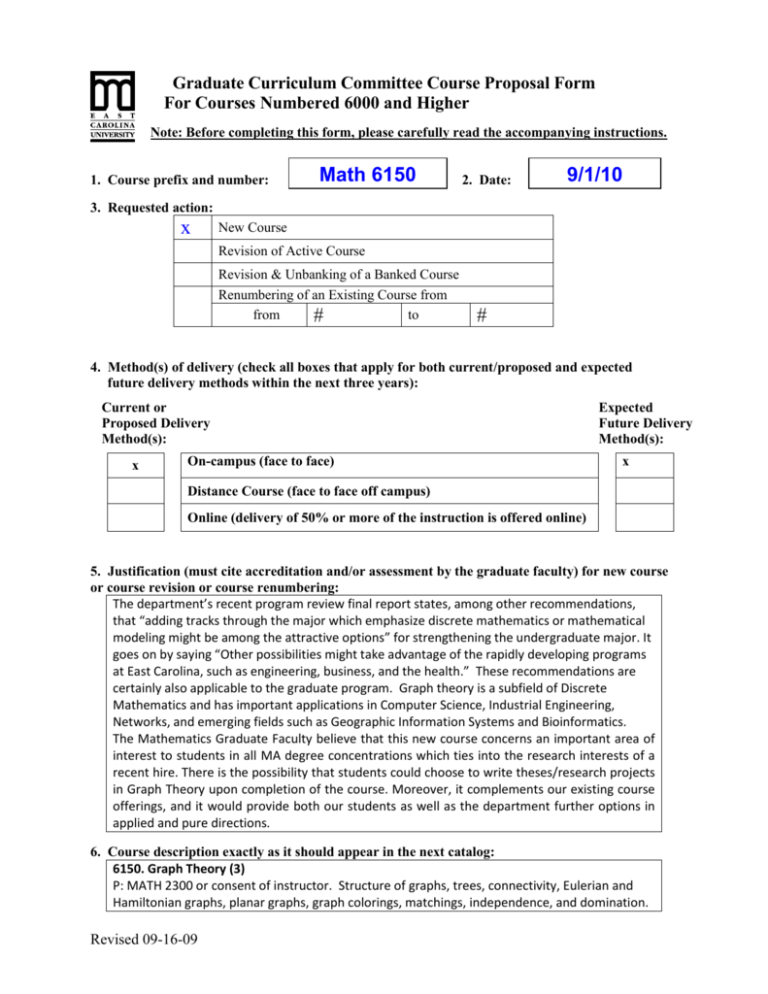
Graduate Curriculum Committee Course Proposal Form For Courses Numbered 6000 and Higher Note: Before completing this form, please carefully read the accompanying instructions. 1. Course prefix and number: Math 6150 2. Date: 9/1/10 3. Requested action: x New Course Revision of Active Course Revision & Unbanking of a Banked Course Renumbering of an Existing Course from from to # # 4. Method(s) of delivery (check all boxes that apply for both current/proposed and expected future delivery methods within the next three years): Current or Proposed Delivery Method(s): x On-campus (face to face) Expected Future Delivery Method(s): x Distance Course (face to face off campus) Online (delivery of 50% or more of the instruction is offered online) 5. Justification (must cite accreditation and/or assessment by the graduate faculty) for new course or course revision or course renumbering: The department’s recent program review final report states, among other recommendations, that “adding tracks through the major which emphasize discrete mathematics or mathematical modeling might be among the attractive options” for strengthening the undergraduate major. It goes on by saying “Other possibilities might take advantage of the rapidly developing programs at East Carolina, such as engineering, business, and the health.” These recommendations are certainly also applicable to the graduate program. Graph theory is a subfield of Discrete Mathematics and has important applications in Computer Science, Industrial Engineering, Networks, and emerging fields such as Geographic Information Systems and Bioinformatics. The Mathematics Graduate Faculty believe that this new course concerns an important area of interest to students in all MA degree concentrations which ties into the research interests of a recent hire. There is the possibility that students could choose to write theses/research projects in Graph Theory upon completion of the course. Moreover, it complements our existing course offerings, and it would provide both our students as well as the department further options in applied and pure directions. 6. Course description exactly as it should appear in the next catalog: 6150. Graph Theory (3) P: MATH 2300 or consent of instructor. Structure of graphs, trees, connectivity, Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs, planar graphs, graph colorings, matchings, independence, and domination. Revised 09-16-09 7. If this is a course revision, briefly describe the requested change: 8. Graduate catalog page number from current (.pdf) graduate catalog:Page Page114 114 9. Course credit: Lecture Hours 3 3 Weekly OR Per Term Credit Hours s.h. Lab Weekly OR Per Term Credit Hours s.h. Studio Weekly OR Per Term Credit Hours s.h. Practicum Weekly OR Per Term Credit Hours s.h. Internship Weekly OR Per Term Credit Hours s.h. Other (e.g., independent study) Please explain. 3 Total Credit Hours 10. Anticipated annual student enrollment: 10 11. Affected degrees or academic programs: Degree(s)/Program(s) Current Catalog Page M.A. Mathematics s.h. p. 111 (pdf) Changes in Degree Hours none 12. Overlapping or duplication with affected units or programs: Not applicable x Notification & response from affected units is attached 13. Council for Teacher Education (CTE) approval (for courses affecting teacher education): Not applicable x Applicable and CTE has given their approval. 14. Service-Learning Advisory Committee (SLAC) approval x Not applicable Applicable and SLAC has given their approval. 15. Statements of support: a. Staff x Current staff is adequate Additional staff is needed (describe needs in the box below): b. Facilities x Current facilities are adequate Additional facilities are needed (describe needs in the box below): Revised 09-16-09 c. Library x Initial library resources are adequate Initial resources are needed (in the box below, give a brief explanation and an estimate for the cost of acquisition of required initial resources): d. Unit computer resources x Unit computer resources are adequate Additional unit computer resources are needed (in the box below, give a brief explanation and an estimate for the cost of acquisition): e. ITCS resources x ITCS resources are not needed The following ITCS resources are needed (put a check beside each need): Mainframe computer system Statistical services Network connections Computer lab for students Software Approval from the Director of ITCS attached 16. Course information (see: Graduate Curriculum and Program Development Manual for instructions): a. Textbook(s) and/or readings: author(s), name, publication date, publisher, and city/state/country Chartrand, G. and Zhang, P., (2004) Introduction to Graph Theory, McGraw-Hill, New York, New York. b. Course objectives for the course (student – centered, behavioral focus) Upon successful completion of this course students will be able to Demonstrate knowledge of the syllabus material; Write precise and accurate mathematical definitions of objects in graph theory; Validate and critically assess a mathematical proof; Use a combination of theoretical knowledge and independent mathematical thinking in creative investigation of questions in graph theory; 5. Reason from definitions to construct mathematical proofs; 6. Write about graph theory in a coherent and technically accurate manner 1. 2. 3. 4. Revised 09-16-09 c. Course topic outline 1. Introduction: Graphs and Graph Models; Connected Graphs; Common Classes of Graphs; Multigraphs and Digraphs. 2. Degrees: The Degree of a Vertex, Regular Graphs, Degree Sequences. 3. Isomorphic Graphs: The Definition of Isomorphism, Isomorphism as a Relation, Graphs and Groups, Reconstruction and Solvability. 4. Trees: Bridges, The Minimum Spanning Tree Problem, The Number of Spanning Trees. 5 Connectivity: Cut-Vertices, Blocks, Connectivity, Menger's Theorem, Geodetic Sets. 6 Traversability: Eulerian Graphs, Hamiltonian Graphs, Hamiltonian Walks and Numbers. 7 Digraphs: Strong Digraphs, Tournaments, Decision-Making, Wine Bottle Problems. 8 Matchings and Factorization: Matchings, Factorization, Decompositions and Graceful Labelings, Excursion: Instant Insanity, The Petersen Graph, Labeling of Graphs. 9. Planarity: Planar Graphs, Embedding Graphs on Surfaces, Graph Minors, Embedding Graphs in Graphs. 10 Coloring: The Four Color Problem, Vertex Coloring, Edge Coloring, The Heawood Map Coloring Theorem, Local Coloring. 11 Ramsey Numbers: The Ramsey Number of Graphs, Turan's Theorem, Rainbow Ramsey Numbers, Erdös Numbers. 12 Distance: The Center of a Graph, Distant Vertices, Locating Numbers, Detour and Directed Distance, Channel Assignment, Distance Between Graphs. 13 Domination: The Domination Number of a Graph, Stratification. d. List of course assignments, weighting of each assignment, and grading/evaluation system for determining a grade Tests (2 tests) = 50% Final Exam = 50% Grade in course: 100% ≥ A ≥ 90% ; 89% ≥ B ≥ 80% ; 79% ≥ C ≥ 70%; 69% ≥ F Revised 09-16-09






