tpj12167-sup-0007-MethodsS1
advertisement

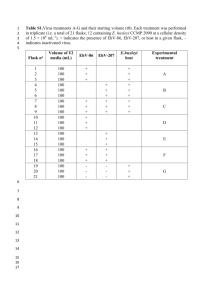
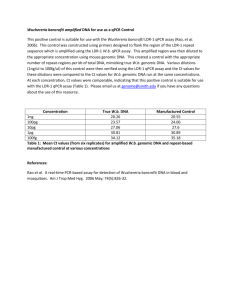
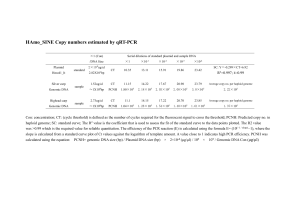
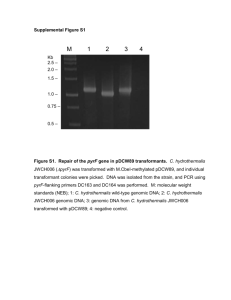
1 Supporting Information 2 Method S1 3 Isolation of total RNA and genomic DNA 4 Isolations of total RNA and genomic DNA were carried out by the phenol/chloroform 5 method. First, 10–20 mg of seeds were ground with a TissueLyser (Qiagen, Venlo, 6 Netherlands) pre-cooled with liquid nitrogen and immediately extracted with 900 l of 7 TLE buffer (0.18 M Tris-HCl pH 8.2, 90 mM LiCl, 4.5 mM EDTA, 1% SDS) and 1.1 8 ml of phenol/chloroform (5:1 = v/v). After vortexing at room temperature (RT) for 5 9 min and subsequent centrifugation at 19,000 × g for 2 min at RT, the aqueous phase was 10 mixed with an equal volume of phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1 = v/v/v), 11 and centrifuged at 19,000 × g for 2 min at RT. After extraction with 12 phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol twice more, the aqueous phase was further extracted 13 with an equal volume of chloroform. After centrifugation at 19,000 × g for 2 min at RT, 14 0.12 volume of 20% polyvinylpyrrolidone was added to the aqueous phase and the 15 mixture was centrifuged at 19,000 × g for 10 min at RT. The resultant supernatants were 16 mixed with 10 M LiCl to achieve a final concentration of 2 M and stored at –30°C 17 overnight. After thawing, mixing, and centrifugation at 25,000 × g for 30 min at 4°C, 18 the pellets containing total RNA were rinsed with 2 M LiCl and 70% (v/v) ethanol, then 19 dried and dissolved in TE buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 1 mM EDTA). Supernatants 20 containing genomic DNA were mixed with 0.6 volume of isopropanol, held at RT for 5 21 min, and centrifuged at 25,000 × g for 10 min at RT. After rinsing with 70% (v/v) 22 ethanol, the pellets were dried and dissolved in TE buffer. Isolated total RNA and 23 genomic DNA samples were stored at –80°C or –30°C, respectively, until use. 24 1 1 Quantitative reverse transcription PCR analysis 2 Quantitative reverse transcription PCR analysis was performed as described previously 3 (Yano et al., 2009) with minor modifications. Briefly, reverse transcription was 4 performed with the QuantiTect Reverse Transcription Kit (Qiagen) using 1 g of total 5 RNA, according to the manufacturer’s protocol, and qPCR assay was performed in an 6 Mx3000p QPCR System (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). For multiplex, singleplex, 7 and SYBR green qPCR, QuantiTect multiplex qPCR (Qiagen), Quantitect qPCR 8 (Qiagen), and Thunderbird qPCR kits (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan) were used, respectively. 9 The PCR primers and dual-labeled probes used for qRT-PCR analyses are listed in Data 10 S5. Welch’s t-test was carried out with the “t-test” function in R 2.13.0. 11 12 Dideoxy sequencing of the HD2B genomic DNA region 13 For dideoxy sequencing of the HD2B genomic DNA region, a 2.5-kb genomic DNA 14 fragment of HD2B was amplified by PCR in 83 accessions using the primers HD2B-F 15 (5’-CACCGCACTTCAAGGCTTCTTTTTTTGGTG-3’) 16 (5’-CTCAAAATAGCTCATCCGATAACAAG-3’). After eliminating the remaining 17 dNTPs and PCR primers with ExoSap-IT (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK), PCR 18 mixtures were directly sequenced with an ABI PRISM 3100 Genetic Analyzer (Applied 19 Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. DNA 20 primers used in sequencing were listed in Data S6. The resultant sequences were joined 21 with Perl scripts to obtain a 2.5-kb sequence of HD2B. Biallelic polymorphisms 22 including both SNPs and indels were identified with BioEdit software (Ibis Biosciences, 23 Carlsbad, CA, USA) and Microsoft Excel®. For GWA mapping, identified DNA 24 polymorphisms were joined with the AtSNPtile1 database to reconstruct a genotype 2 and HD2B-R 1 database, and computation of p-values was performed as described in the corresponding 2 section of EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES. 3 3