CCNA2 Chap 5 Study Q..
advertisement

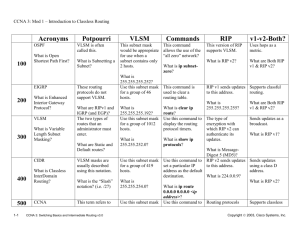
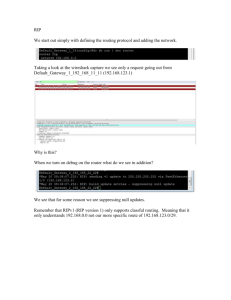
CCNA Exploration Chapter 5 RIP Routing. Study questions. 5.1 What type of routing protocol is RIP? Interior, distance vector. What routing metric(s) does RIP use, and what is the largest value allowed for this metric? Hop count. 15 hops is the maximum. 16 hops is regarded as infinity, unreachable. How are RIP updates encapsulated? In UDP segments. How often are RIP updates sent by default? Every 30 seconds What are the two RIP message types as specified in the Command field? Request message and Response message What is a triggered update? An update sent in response to some change in the network. E.g. new link comes up, router updates its table, sends out triggered update. These are in addition to regular timed updates. In a class A network how many bits are used for network addressing and how many for host addressing? 8 for network, 24 for hosts. In a class B network how many bits are used for network addressing and how many for host addressing? 16 for network, 16 for hosts. In a class C network how many bits are used for network addressing and how many for host addressing? 24 for network, 8 for hosts. SW 2/17/2016 106743234 1 In a classful system, which class of network are the following addresses in? A A A C B B C A B 192.168.1.1 10.10.10.6 100.0.0.1 223.224.0.1 172.16.0.1 191.14.2.3 200.1.1.7 126.8.255.1 129.5.5.5 What are the default subnet masks for class A, class B and class C? Class A 255.0.0.0 Class B 255.255.0.0 Class C 255.255.255.0 A router running RIP v1 has two directly connected networks. These are 192.168.2.0/24 and 172.16.4.0/24. What subnet masks will it use for the following networks if it learns paths to them and puts them in its routing table? 255.255.255.0 (/24) 255.255.0.0 (/16) 255.255.255.0 (/24) 255.0.0.0 (/8) 255.255.255.0 (/24) 192.168.3.0 172.17.0.0 200.15.0.0 15.0.0.0 172.16.15.0 Why does RIP v1 not support VLSM? It does not send subnet mask information in its routing updates. It uses default subnet masks, or assumes that the mask applied to directly connected subnets is to be applied to all subnets of the same major network. It cannot route correctly to subnets that use different masks. VLSM involves giving different masks to subnets of the same major network, so VLSM is not supported. RIP v1 networks cannot be discontiguous. What does this mean? Two subnets of the same major network must not be connected via a different major network or one of its subnets. In other words, all subnets of the same major network must be grouped together (contiguous). What is the default administrative distance for RIP, and how does this affect the choice of RIP routes as opposed to IS-IS, OSPF, IGRP, and EIGRP routes? RIP has default administrative distance 120. IS-IS, OSPF, IGRP, and EIGRP all have lower administrative distances, so routes found by any of these protocols would be preferred to RIP routes. SW 2/17/2016 106743234 2 5.2 A router has interfaces configured with IP addresses as shown. What commands would you use to configure RIP v1 routing and save the configuration? Start and finish at the privileged exec prompt. Router# Router#configure terminal Router(config)#router rip Router(config-router)#network 192.168.4.0 Router(config-router)# network 192.168.6.0 Router(config-router)#end Router#copy running-config startup-config What command would you give to stop all RIP routing? Router(config)#no router rip What would happen if you used a host address or a subnet address in a network command when configuring RIP v1? The address would be corrected to the classful main network address and put into the configuration. (But you would probably lose marks in an exam.) 5.3 What would the following commands show you, and in which order are you recommended to use them for troubleshooting? Show ip protocols, show ip route, debug ip rip, show ip interfaces brief. Show ip interfaces brief should be used even before routing is configured. It shows whether interfaces and protocols are up or down. It also shows the IP addresses configured on the interfaces. Show ip route shows the routing table so you can see which networks are known and how they are known: directly connected, static or learned using a routing protocol. Show ip protocols shows if RIP is configured. It shows which interfaces are sending and receiving updates, and which RIP version they use. It shows the values of timers. It shows which networks are being advertised and which routers are sending updates. Debug ip rip displays RIP updates as they are sent and received. You can see which networks are included in the updates. SW 2/17/2016 106743234 3 A router has learned a route using RIP v1. What information about this route is shown in the routing table? R (RIP route) Address and mask of destination network using prefix notation e.g. 192.168.5.0/24 Administrative distance and metric (number of hops) e.g. [120/2] Next hop router’s interface address, e.g. via 192.168.2.2, Time in seconds since last update, e.g. 00:00:23, Exit port, e.g. Serial0/0 How can you stop RIP debugging? no debug ip rip will stop RIP debugging. undebug all or no debug all will stop all debugging so one of these is often used instead. Why should you stop RIP debugging as soon as you have the information you need? Debugging takes up router resources, particularly processor time, so it can slow down network traffic. It should not be left running. You do not want to send routing updates out of port 192.168.4.1 as this port does not lead to another router, but only to workstations. Should you give the following commands? Router(config)#router rip Router(config-router)#no network 192.168.4.0 No. This will stop updates through the interface, but it will also stop updates about network 192.168.4.0 from being sent through any interface. How should you prevent routing updates from being sent out of port 192.168.4.1? Router(config)#router rip Router(config-router)#passive-interface 192.168.4.1 Why is it a good idea to prevent RIP v1 routing updates from being sent out through ports that do not lead to other routers? RIP v1 updates are sent broadcast every 30 seconds, so this takes up bandwidth. Hosts have to process all broadcast messages, so workstations are using processing power on messages that are no use to them. It is more efficient to stop sending routing updates if they are not needed. SW 2/17/2016 106743234 4 5.4 What is a boundary router in terms of a group of networks running RIP v1? A router that has interfaces on more than one major network. Network 192.168.1.0 has been subnetted. Culham router has an interface on 192.168.1.64/26. It has learned routes to 192.168.1.0/26 and 192.168.1.128/26 through this interface. Culham is configured for RIP v1, and sends updates to Didcot router via its other interface which is on network 192.168.2.0. Which networks will Didcot learn from Culham and include in its routing table? It will include a route to 192.168.1.0/24. It will not recognise the subnets of 192.168.1.0. This is because the updates arrived over a link that belongs to a different major classful network. Network 192.168.1.0 has been subnetted. Culham router has an interface on 192.168.1.64/26. It has learned routes to 192.168.1.0/26 and 192.168.1.128/26 through this interface. Culham is configured for RIP v1, and sends updates to Didcot router via its other interface which is on network 192.168.1.192/26. Which networks will Didcot learn from Culham and include in its routing table? It will include routes to 192.168.1.0/26, 192.168.1.64/26 and 192.168.1.128/26. It will use the /26 subnet mask since this is configured on its own interface through which it received the updates. If a router running RIP v1 receives a summary route to 192.168.1.0, but 192.168.1.0 is subnetted, does this mean that the router will not be able to send packets to the subnets? No. Providing that the subnets are contiguous and all using the same subnet mask, there should be no problem. The router will send all packets for the subnets on the summary route to 192.168.1.0. The packets should reach the router that originally made the summary, and this router should have paths to the different subnets. What is an advantage of summarising routes? It leads to smaller routing tables and therefore faster look-up. What is the major disadvantage of using RIP v1? It does not support VLSM (which is very widely used) and it cannot route correctly to discontiguous subnets. SW 2/17/2016 106743234 5 How is routing between ISPs and their customers normally carried out? The customer’s gateway router has a default route to the ISP, and this default route is propagated to the other customer routers. This takes care of outward traffic. The ISP has a static route that summarises the customer’s networks and this takes care of inward traffic. (NAT may be used, but the principle of default and static routes is the same.) What command can be used to propagate a default route to other routers running RIP? default-information originate SW 2/17/2016 106743234 6