QBasic Lesson 3: REMark and Additonal PRINT Options (6)
advertisement

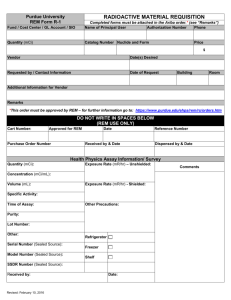
106742927 Zones, TAB, LPRINT
QBasic Lesson 3: REMark and Additonal PRINT Options (6)
OBJECTIVES:
Using the REM command
Printing string constants
Printing more than one value in a line
Printing with tabs
Printing to the printer
The REM (short for remark) command is used to make the code more understandable to humans.
The computer ignores the command and everything that follow.
The format of the REM command
REM any message you choose to explain to fellow programmers what the
REM program is doing
You can insert as many remarks in your program as you want anywhere you want.
You will use the REM command at the beginning of each program to record you name, the file
name and the purpose of the program. You will use the REM command through out the program to
explain what your code is trying to accomplish.
Since the REM command appears so often in programs there is an abbreviation for the statement.
Instead of typing REM, you can type and apostrophe.
REM Programmers name: John Doe
REM Filename: Les2_1.bas
‘ Blank REMarks like the following one help separate
‘ the remark’s comments from surrounding code.
REM
REM This program puts a few values in variables
REM and then prints them to the screen
REM
CLS
LET age = 32
‘stores the age
LET salary = 25000
‘Yearly salary
LET dependents = 2
‘Number of dependents
‘Print the results
PRINT age
PRINT salary
PRINT dependents
END
106742927 Zones, TAB, LPRINT
PRINTing String Constants
A string constant is one or more groups of characters inside quotation marks (“ “).
You can use string constants (sometimes called string literals) with a PRINT statement to label your
output by printing names, titles, addresses, and other messages on the screen and printer.
String Constant Examples:
“This is a string constant.”
“ABC 123 $#@ - - - +={] x”
“X”
“123.45”
When you print string constants, everything inside quotation marks, including typed spaces, prints
exactly as it appears in the string constant.
What would be the output of the following program?
REM Programmers name: John Doe
REM Filename: Les3_3.bas
‘ Prints the company’s name and address on-screen
REM
CLS
PRINT “Widgets, Inc.”
PRINT “307 E. Midway”
PRINT “Jackson, MI 03882”
END
106742927 Zones, TAB, LPRINT
What would be the output of the following program?
REM Programmers name: John Doe
REM Filename: Les2_1.bas
‘ Blank REMarks like the following one help separate
‘ the remark’s comments from surrounding code.
REM
REM This program puts a few values in variables
REM and then prints them to the screen
REM
CLS
LET age = 32
‘stores the age
LET salary = 25000
‘Yearly salary
LET dependents = 2
‘Number of dependents
‘Print the results
PRINT “age”
PRINT age
PRINT “salary”
PRINT salary
PRINT “dependents”
PRINT dependents
END
Formatting Results (pg 96)
To print more than one value on a line, you must separate each value with a semicolon or a comma.
You choose either a semicolon or a comma based on how closely you want the values to print.
To print two or more values next to each other, separate the values by using a semicolon in the
PRINT statement.
PRINT value1;value2;value3; . . .
If you put more than one value (the values can be variables, constants, or a combination of both)
after PRINT and separate them with semicolons, QBasic prints those values next to each other on
one line, instead of on two separate lines.
106742927 Zones, TAB, LPRINT
Print Zones
To print multiple values separated by several spaces, you use commas between the values. You can
use the commas in a PRINT statement to print columns of output.
PRINT value1,value2,value3,
The number of spaces separating the values varies. QBasic uses print zones to determine the
spacing between two printed values separated by commas. To QBasic you screen has five print
zones, and each print zone occupies 14 columns. Each comma represents the next print zone.
Print Zone 1
Print Zone 2
Print Zone 3
Print Zone 4
Print Zone 5
1,2,3,4,5,6,7, . . . . 14
Screen
Column 1
Screen
Column 15
Screen
Column 29
Screen
Column 43
Screen
Column 57
If your data is longer than a print zone, the data extends into the next print zone and the next value
prints one print zone over.
If there are more items listed in a PRINT statement than there are print zones in a line, the print
zones of the next line are also used, starting with the first zone
Example:
PRINT , , , “QBasic”
PRINT “Male”, “19”, “Junior”, “CS”, 18, 2.5
OutPut:
Print Zone 1
Male
2.5
Print Zone 2
Print Zone 3
19
Junior
Print Zone 4
QBasic
CS
Screen
Screen
Screen
Print Zone 5
18
Screen
1,2,3,4,5,6,7, . . . . . 14
Screen
106742927 Zones, TAB, LPRINT
Column 1
Column 15
Column 29
Column 43
Column 57
Printing Numbers
What is the output of the following program?
REM Programmers name: John Doe
REM Filename: Les3_3.bas
‘ Blank REMarks like the following one help separate
‘ the remark’s comments from surrounding code.
REM
REM This program puts a few values in variables
REM and then prints them to the screen using semicolons for better
REM looking output.
CLS
LET age = 32
‘stores the age
LET salary = 25000
‘Yearly salary
LET dependents = 2
‘Number of dependents
‘Print the results
PRINT “The age is”; age
PRINT
PRINT “The salary is”; salary
PRINT
PRINT “The number of dependents is”; dependents
END
Output:
The age is 32
The salary is 25000
The number of dependents is 2
Press any key to continue
Note that in the printed output, a blank space occurs before each variable, although you did not type
a space in the program.
106742927 Zones, TAB, LPRINT
QBasic inserts a space after every number.
For positive numbers QBasic also prints spaces preceding the number. Think of this space as an
imaginary plus sign. You can not override this imaginary plus sign, so you can expect every
positive number to have an extra blank space in front of it.
For negative numbers, QBasic prints the negative sign (-) in front of the number.
QBasic does not insert a blank space before string constants or negative numbers.
Example:
REM Programmers name: John Doe
REM Filename: Ex3_1.bas
REM
REM This program prints three sets of values showing
REM how QBasic handles the spacing between them.
REM
CLS
‘Three string constants
PRINT “Books”; “Movies”; “Theatre”
‘Three positive numbers
PRINT 123; 456; 789
‘Three negative numbers
PRINT -123; -456; -789
END
Output:
B o o k s M o v i
1 2 3
-
1 2 3
-
e s T h e a t r e
4 5 6
7
8 9
4 5 6
- 7
8 9
Press any key to continue
106742927 Zones, TAB, LPRINT
How could I change the code to place spaces between the works in the first line?
Place semicolon between the strings
You can suppress the carriage return-line feed sequence by putting a semicolon at the end of a
PRINT statement.
REM Programmers name: John Doe
REM Filename: Ex3_1.bas
REM
REM This program suppresses the automatic carriage return-line feed
REM by leaving a trailing semicolon at the end of the PRINT statement
REM
CLS
PRINT “Books ”;
‘semicolon keeps the cursor on the same line
PRINT “Movies ”;
PRINT “Theatre”
END
Output:
B o o k s
M o v i
Press any key to continue
e s
T h e a t r e
106742927 Zones, TAB, LPRINT
Example of Comma usage:
REM Programmers name: John Doe
REM Filename: Ex3_3.bas
‘
REM Use the comma between printed values. Each comma
REM forces the next animal name into a new print zone.
‘
CLS
PRINT “Lion ”, “Whale ”, “Monkey ”, “Fish ”
PRINT “Alligator ”, “Bat ”, “Seal ”, “Tiger ”
PRINT “Dog ”, “Lizard ”, “Cat ”, “Bear ”
END
Output:
Lion
Alligator
Dog
Whale
Bat
Lizard
Monkey
Seal
Cat
Fish
Tiger
Bear
Press any key to continue
Printing with TAB
Printing with commas is similar to using tabs; a comma acts like a tab by moving the next value to
the next print zone.
A print zone occurs every 14 spaces.
The format of the TAB command:
TAB (tab value)
The tab value is the number of characters that you want QBasic to tab over from the beginning of
the screen before printing the next value.
106742927 Zones, TAB, LPRINT
Never use TAB by itself; always combine it with a PRINT statement.
This format is:
PRINT TAB
(tab value1); data1; (tab value2); data2
The semicolons before and after TAB are not required but considered good programming. The
semicolons tell you that the tab occurs immediately after the last value is printed.
Example of TAB usage:
REM Programmers name: John Doe
REM Filename: Ex3_3.bas
‘
REM Use the TAB between printed values. Each TAB’s value
REM forces the next animal name over to that tab stop.
‘
CLS
PRINT “Lion ”; TAB(20); “Whale ” ; TAB(40); “Monkey ”;
PRINT TAB(60); “Fish ”
PRINT “Alligator ” ; TAB(20); “Bat ” ; TAB(40); “Seal ”;
PRINT TAB(60); “Tiger ”
PRINT “Dog ” ; TAB(20); “Lizard ” ; TAB(40); “Cat ”;
PRINT TAB(60); “Bear ”
END
Output:
Lion
Alligator
Dog
Whale
Bat
Lizard
Press any key to continue
Monkey
Seal
Cat
Fish
Tiger
Bear
106742927 Zones, TAB, LPRINT
The LPRINT Command
The LPRINT command is identical to PRINT except it sends output to the default printer rather
than to the screen.
If your printer is out of paper or turned off you will see the following error message:
Device fault
REVIEW QUESTIONS
1. What does REM stand for?
2. What does the computer do when it finds a REM statement?
3. True or False: The following section of a program puts a 4 in the variable called R, a 5 in
ME, and 6 in REM.
R=4
ME = 5
REM = 6
4. True or False: PRINT sends output to the screen.
5. What is the difference between using a semicolon and a comma in a PRINT statement?
6. How many characters wide is each print zone?
7. Why would you put a semicolon at the end of a PRINT statement?
8. In what column would the word Computer start, given the following LPRINT command?
LPRINT TAB(20), “Computer”
9. In what column would the number 765 start, given the following LPRINT command?
LPRINT -21; 21, 0; TAB(30); 765
10. List three ways to print Hello in column 28.
11. What is the output of the following program?
REM ----------------------------------------------------REM
SECRET AGENTS
REM ----------------------------------------------------PRINT 86;
PRINT “ and”;
PRINT 99;
106742927 Zones, TAB, LPRINT
PRINT “ are secret agents.”
Lesson 3 Exercises
Write the code for each of the following exercises and save them to your Hdrive. Name your
programs Exer3_1.bas, Exer3_2.bas, etc. You will be required to run these programs. I will be
around to check your results.
1. Write a program that stores your weight (you can fib), height in feet, and shoe size in three
different variables. Print the values with descriptions in three separate lines. Then print the
values next to each other in the same line. Use appropriate REM statements to document the
program.
2. Modify the preceding program to print your weight in column in 15, your height in column
25, and your shoe size in column 35.
3. Write a program that prints (on the printer) the names and phone numbers of your three best
friends. Add appropriate REM statements to document the program. Make sure that you
print nicely underlined titles over the names and phone numbers and that the report’s
columns line up. You can use print zones or TAB.
4. For the linear equation y = (2/3) x – 4 complete the following table of values.
(2/3)x - 4 y
(x, y)
Write a program that will print this completed table of values to the printer.
5. Find and correct the three errors in the following program:
REM This program prints payroll information
pay = 2,102.23
dependents = 3
taxRate = .35
REM This is the percentage tax rate
PRINT
PRINT “The pay is:”; pay
PRINT “The number of dependents is:”; dependents
CLS
PRINT “The tax rate percentage is:”; taxRate
106742927 Zones, TAB, LPRINT
6. You can use PRINT to print pictures on the screen. Use a series of PRINT statements,
commas, semicolons and TAB with different keyboard characters to print your “picture” to
the screen.