ijca-march
advertisement
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Sect. A: Inorganic, Bio-inorganic, Physical, Theoretical & Analytical
VOLUME 41A
NUMBER 3
MARCH 2002
CONTENTS
Papers
457
Exponent-dependent properties of the
connectivity index
Ivan Gutman*, Mirko Lepović ,
Dušica Vidović & Lane H Clark
462
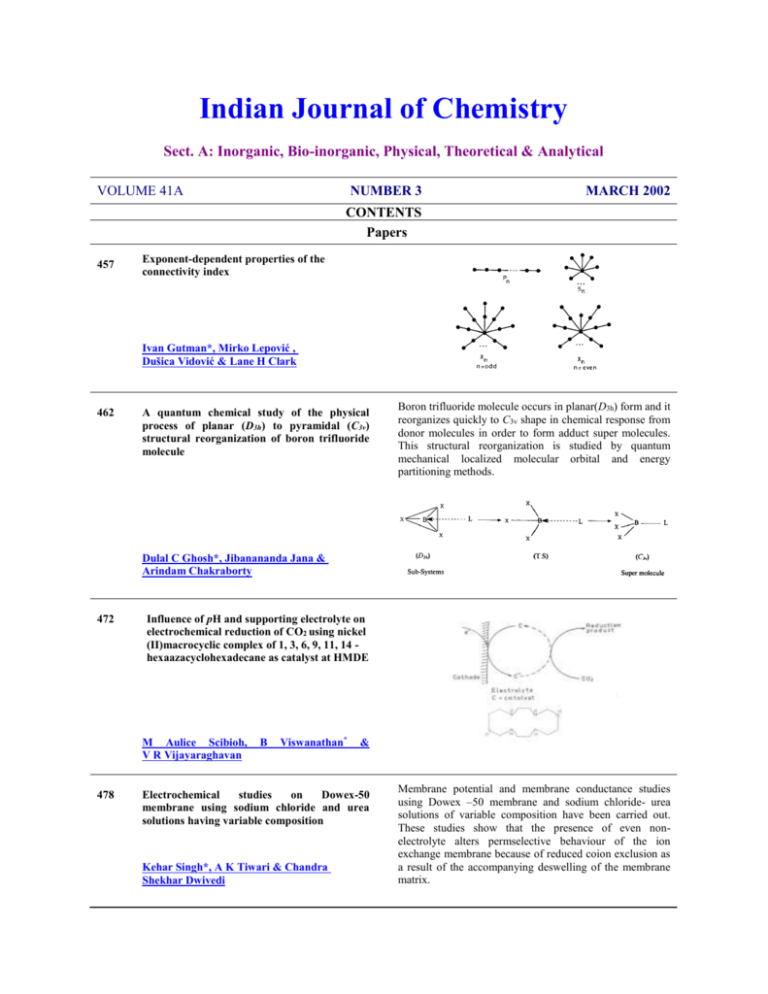
A quantum chemical study of the physical
process of planar (D3h) to pyramidal (C3v)
structural reorganization of boron trifluoride
molecule
Boron trifluoride molecule occurs in planar(D3h) form and it
reorganizes quickly to C3v shape in chemical response from
donor molecules in order to form adduct super molecules.
This structural reorganization is studied by quantum
mechanical localized molecular orbital and energy
partitioning methods.
Dulal C Ghosh*, Jibanananda Jana &
Arindam Chakraborty
472
Influence of pH and supporting electrolyte on
electrochemical reduction of CO2 using nickel
(II)macrocyclic complex of 1, 3, 6, 9, 11, 14 hexaazacyclohexadecane as catalyst at HMDE
M Aulice Scibioh,
V R Vijayaraghavan
478
B
Viswanathan*
&
Electrochemical
studies
on
Dowex-50
membrane using sodium chloride and urea
solutions having variable composition
Kehar Singh*, A K Tiwari & Chandra
Shekhar Dwivedi
Membrane potential and membrane conductance studies
using Dowex –50 membrane and sodium chloride- urea
solutions of variable composition have been carried out.
These studies show that the presence of even nonelectrolyte alters permselective behaviour of the ion
exchange membrane because of reduced coion exclusion as
a result of the accompanying deswelling of the membrane
matrix.
483
Transport studies of ion – solvent interactions
in acetonitrile – rich regions of benzene and
ethanol
M S Chauhan*, K Sharma & G Kumar
489
KE
[Rh(OH2)5(OH)]2+ + uridine Rh(OH2)5(OH)]2+.uridine
outersphere association
complex
ka
[Rh(OH2)5(OH)]2+. Uridine [Rh(OH2)4(OH)(uridine)]2+
+ H2O
Kinetic and mechanistic studies on the
interaction of uridine with
hydroxopentaaquarhodium (III) ion
S K Mukhopadhyay & A K Ghosh*
493
Oxidation of benzyl alcohol and some ortho-, meta- and
para-monosubstituted ones by quinolinium fluorochromate
in dimethyl sulphoxide leads to the formation of
corresponding banzaldehydes.
The oxidation of parasubstituted benzyl alcohols is more susceptible to the
delocalization effect than that of ortho- and metasubstituted compounds, which display a greater dependence
on the field effect.
Correlation analysis of reactivity in the
oxidation of substituted benzyl alcohols
by quinolinium fluorochromate
Itishri Dave, Vinita Sharma &
Kalyan K Banerji*
500
Exchange kinetics of the alkaline earth metal ions with
labile protons of the synthetic ion exchanger zirconium
antimonophosphate has been studied, using the limited bath
technique. Effect of concentration, particle size and
temperature on the extent of exchange at the solution-solid
interface are reported. The studies indicate that the effective
diffusion coefficient consists of an initial fast exchange and
later a slow exchange, representing the inter-diffusion of
counter ions through the pores of the exchanger matrix.
Exchange kinetic studies on zirconium
antimonophosphate
S K Mittal* & Pritpal Singh
506
Synthesis
and
characterization
of
azaphosphole complexes of ruthenium and
rhodium
Vimal K Jaina,
Raj K Bansal
513
Leena
Hemrajani
Structural studies on some trifluoro-diketonates of tin(IV) and lead(II)
Sudha Singh Vishnu D Gupta*
Molar conductance and viscosity of Bu4NBPh4, NaBPh4,
Bu4NBr, Bu4NI, LiClO4 and NaClO4 have been reported
in acetonitrile (ACN)–rich regions of benzene and ethanol
(EtOH) at 25oC. The analysis of the data show that Bu4N+
and Ph4B- lose their spherical shape, while Li+, Na+, Br-, Iand ClO4- behave as spherical entities during viscous flow
process.
&
521
Studies on the determination of palladium(II)
by fluorescence quenching method with mesotetra[4-carboxymethylenoxy)phenyl]porphyrin
Yan-jun Fang, Hui Chen,* Zhi-xian Gao &
Xiao-yong Jin
Notes
525
Phenol–amide chelates of iron (III) as catalysts
for hydrolysis of active esters
The iron(III) chelate of 1,2-bis (2-hydroxybenzamido)
ethane catalyses the hydrolysis of p-nitrophenol
acetate
Harapriya Rath, Guru C Pradhan, Prakash
Mohanty & Anadi C Dash*
528
An enhancement in the thermal stability and
acidity of hydrous zirconia in presence of
12-tungstophosphoric acid
12-Tungstophosphoric acid supported on hydrous
zirconium oxide has been prepared and characterized.
Shirish Patel & Anjali Patel*
532
A kinetic study of the chemical oscillating
system comprising mannitol-acetone-bromateH2SO4
A new type of chemical oscillating system
comprising mannitol-acetone-bromate-H2SO4 has
been studied by the potential method.
Shi-Gang Shen*, Han-Wen Sun,
Jin-Huan Shan & Jun-li Liu
537
Kinetics of acid-promoted dissociation
reactions of Cu [Ph4(14) tetraene N4]
macrocyclic complex
A K Singh*, Rupam Singh & Seema Baniwal
541
Correlation analysis of reactivity in the
oxidation of substituted benzylamines by
benzyltrimethylammonium tribromide
Rekha Sankhla & Seema Kothari*
The oxidation of benzylamine and twenty-seven
ortho-, meta- and para-monosubstituted benzylamines by benzyltrimethylammonium tribromide, in
dimethylsulphoxide, leads to the formation of
corresponding aldimines. The oxidation of parasubstituted benzylamines is more susceptible to the
delocalization effect than is the oxidation of orthoand meta-substituted compounds.
547
kI
Kinetics and mechanism of the
ruthenium (III) - catalysed oxidation of
some glycols by cerium (IV) in sulphuric
acid medium
S+Ru(VIII)
Intermediate
kI
Intermediate F+2H++Ru(VI)
HOH
F`+Ce(IV)
Product+H++Ce(III)
fast
Ru(VI)+Ce(IV)
Ru(VII)+Ce(III)
Fast
Ru(VII)+Ce(IV)
Bharat Singh*, Meera Singh &
Deepmala Kesarwan
550
Ru(VIII)+Ce(III)
Fast
Synthesis and characterization of
palladium(II) complexes containing
N-pyridiniodithiophosphinates
Vimal K Jain*, Leena Hemrajani &
Raj K Bansal
554
Synthesis, magnetic and spectral studies of
some cis-dioxomolybdenum(VI) complexes
derived from N, O- and N2O2- type Schiff bases
R C Maurya*, B Shukla, & A Pandey
560
Synthesis and characterization of
ruthenium(II) complexes of different types
of potential unsymmetrical hemilabile P-O
and P-S donors ligands
Pankaj Das, Manab Sharma, Nandini Kumari,
Dilip Konwar & Dipak Kumar Dutta*
563
A spectrophotometric method for the trace
determination of vanadium as V(V)-5-chloro8-hydroxy-7-iodoquinoline in aqueous medium
Vanita Sharma, Monica Nijhawan &
A L J Rao*
A simple and rapid spectrophotometric method for the
determination of vanadium(V) is developed in the presence
of 5-choloro-8-hydroxy-7-iodoquinoline under acidic
conditions using Triton X-100 as surfactant. The
applicability of the method has been tested by analysis of a
large number of different synthetic and commercial
samples.
Book Review
565
Metal Ions in Biological Systems,
Vol. 38(Editors: A. Sigel and H. Sigel)
D Banerjea
Authors for correspondence are indicated by (*)
Papers
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 457-461
Exponent-dependent properties of the connectivity index
Ivan Gutman, Mirko Lepović , Dušica Vidović &Lane H Clark
The connectivity index is defined as C() =(uv), where v is the degree of the vertex v of the respective
molecular graph, and where the summation embraces all pairs of adjacent vertices. The exponent is usually chosen
to be equal to -0.5 but other options have been considered as well, especially C(-1). We show that whereas C(-0.5)
correctly reflects the extent of branching of the carbon-atom skeleton of organic molecules, and is thus a suitable
topological index for modelling physico-chemical properties of the respective compounds, this is not the case when
the exponent assumes larger negative values, in particular when =1. The value of is established beyond which
C() fails to be a measure of molecular branching.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 462-471
A quantum chemical study of the physical process of planar (D3h) to pyramidal
(C3v) structural reorganization of boron trifluoride molecule
Dulal C Ghosh, Jibanananda Jana & Arindam Chakraborty.
The dynamic process of planar (D3h) to pyramidal (C3v) reorganization prior to the event of chemical reaction of
boron trifluoride, BF3, molecule has been studied by localized molecular orbital and energy partitioning methods.
The energy of reorganization, the stretching of B—F bond and alteration of charge density distribution are
computed for a wide range of molecular conformations generated by deforming the equilibrium geometry of the
molecule. The large activation barrier of the molecule is correlated to its high energy of reorganization prior to the
event of chemical reaction due to the elimination of partial double bond character and the weakening of the B—F
bond on to stretching. The B—F bond stretches through 0.023Aºº. The bonding in the equilibrium geometry is
computed in terms of localized molecular orbitals, LMO's. The quantum mechanical hybridization of orbitals on B
and F atoms forming the -(B—F) bond is computed for all the conformations of the molecule through the
generated LMO's. The total energy of the molecule at all its conformations is decomposed into one- and two center
components. The weakening of the B—F bond and variation of the percentage of the s-characters of the hybrids on
B and F atoms forming the bond in a series of conformations are correlated and has been found to be in accordance
with Coulson’s observation in similar situation.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 472-477
Influence of pH and supporting electrolyte on electrochemical reduction of CO2
using nickel (II) macrocyclic complex of 1, 3, 6, 9, 11, 14 hexaazacyclohexadecane as catalyst at HMDE
M Aulice Scibioh, B Viswanathan & V R Vijayaraghavan
Electrochemical studies on the title compound using cyclic voltammogram (CV) and control potential
electrolysis (CPE) techniques reveal that it reduces CO2 electrocatalytically at -1.36V/SCE at hanging mercury drop
electrode (HMDE) in aqueous medium using LiClO4 as a supporting electrolyte. The products are found to be CO
and H2 in 3:2 mole ratio in the gaseous phase as detected using gas chromatography (GC) and trace amounts of
formic acid in solution phase as detected using colorimetric technique. The Ik/ Id values (where Ik is the kinetic
current measured in the presence of CO2 and Id is the diffusion current measured in N2 atmosphere) observed at
various pH values show that pH 5.0 is best suited for CO2 reduction. In addition, the hydrophobicity/ hydrophilicity
near the electrode surface provided by the cation of the supporting salt and its influence on CO 2 reduction is
discussed.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 478-482
Electrochemical studies on Dowex-50 membrane using sodium chloride and urea
solutions having variable composition
Kehar Singh, A K Tiwari & Chandra Shekhar Dwivedi
Membrane potential and membrane conductance measurements have been carried out using Dowex-50 - Kynar
membrane, sodium chloride and urea mixtures of variable compositions to examine the effect of non-electrolytic
constituent of the mixture on electrochemical character of the membrane. A significant change in membrane
permselectivity is observed in the presence of urea due to changed coion exclusion because of the accompanying
alteration in the swollen state of the membrane matrix.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 483-488
Transport studies of ion – solvent interactions in acetonitrile – rich regions of
benzene and ethanol
M S Chauhan, K Sharma & G Kumar
Molar conductance and viscosity of Bu4NBPh4, NaBPh4, Bu4NBr, Bu4NI, LiClO4 and NaClO4 have been
reported in acetonitrile (ACN)–rich regions of benzene and Ethanol (EtOH) at 25oC. The conductance data
have been analyzed in terms of limiting molar conductance ( o) and ion-association constant (KA) using
Shedlovsky conductance equation. The viscosity data have been analyzed in terms of viscosity A and Bcoefficients of the Jones- Dole viscosity equation. Both o and B-coefficients have been resolved into ionic
components i.e., limiting molar ionic conductance, (io) and (B±) values for various ions on the basis of
Bu4NBPh4 assumption. The effective ionic radii (ri) of Bu4N+, Ph4B-, Li+, Na+, Br-, I- and ClO4- have been
determined from io values using Gill’s modification of the Stokes’ law. The ionic B ± values for these ions have
also been discussed in terms of Einstein’s equation. The analysis of the data show that Bu 4N+ and Ph4B- lose
their spherical shape, while Li+, Na+, Br-, I- and ClO4- behave as spherical entities during viscous flow
process.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 489-492
Kinetic and mechanistic studies on the interaction of uridine with
hydroxopentaaquarhodium (III) ion
S K Mukhopadhyay & A K Ghosh
Kinetics of interaction between uridine and [Rh(H2O)5OH]2+ has been studied spectrophotometrically as a
function of [Rh(H2O)5OH2+], [uridine], pH and temperature. The reaction has been monitored at 290 nm, the max of
the substituted complex and where spectral difference between the reactant and product is maximum. The reaction
rate increases with [uridine] and reaches limiting value at higher ligand concentration. From the experimental
findings an associative interchange mechanism for the substitution process is suggested. The activation parameters
(H = 46.5 1.4 kJ mol-1, S =-181 4 J K-1mol-1) support the proposition. The negative Go (-15.1 kJ mol-1) for
the first equilibrium step also supports the spontaneous formation of an outersphere association complex.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 493-499
Correlation analysis of reactivity in the oxidation of substituted benzyl alcohols by
quinolinium fluorochromate
Itishri Dave, Vinita Sharma & Kalyan K Banerji
Oxidation of benzyl alcohol and some ortho-, meta- and para-monosubstituted ones by quinolinium
fluorochromate (QFC) in dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) leads to the formation of corresponding banzaldehydes.
The reaction is first order each in both QFC and the alcohol. The reaction is promoted by hydrogen ions; the
hydrogen-ion dependence has the form kobs= a + b [H+]. Oxidation of ,-dideuteriobenzyl alcohol (PhCD2OH)
has exhibited a substantial primary kinetic isotope effect. The reaction has been studied in nineteen organic
solvents and the effect of solvent analysed using Taft's and Swain's multi-parametric equations. The rates of
oxidation of para- and meta-substituted benzyl alcohols have been correlated in terms of Charton’s triparametric
LDR equation whereas the oxidation of ortho-substituted benzyl alcohols with tetraperametric LDRS equation. The
oxidation of para-substituted benzyl alcohols is more susceptible to the delocalization effect than that of ortho- and
meta- substituted compounds, which display a greater dependence on the field effect. The positive value of
suggests the presence of an electron-deficient reaction centre in the rate-determining step. The reaction is subjected
to steric acceleration by the ortho-substituents. A suitable mechanism has been proposed.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 500-505
Exchange kinetic studies on zirconium antimonophosphate
S K Mittal & Pritpal Singh
Exchange kinetics of the alkaline earth metal ions with labile protons of the synthetic ion exchanger zirconium antimonophosphate has
been studied, using the limited bath technique. Effect of concentration, particle size and temperature on the extent of exchange at the
solution-solid interface are reported. The Boyd method for studying the kinetics of spherical particles is used to explain the results.
Distinction between particle diffusion and film diffusion has been made by interruption test. The overall studies indicate that the
effective diffusion coefficient consists of two components, an initial fast exchange and later a slow exchange, representing the interdiffusion of counter ions through the pores of the exchanger matrix. With increase in temperature, the contribution of the faster
component decreases, probably because the metal ions diffuse as dehydrated ions and the dehydration of the metal ions is easy at lower
temperature. The effect of concentration and particle size on the exchange rate are also discussed.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 506-512
Synthesis and characterization of azaphosphole complexes of ruthenium and
rhodium :
Vimal K. Jain*, Leena Hemrajani & Raj K Bansal
Reaction of azaphospholes (L) [2-phosphaindolizines (1) and 1,3-azaphospholo[5,1-a]isoquinolines (2)] with
[5-Cp*RhCl2]2 (Cp* = pentamethylcyclopentadienyl) and [Ru(6-cymene)Cl2]2 in 2:1 molar ratio in
dichloromethane yields mononuclear complexes of the type [Cp*RhCl 2(L)].H2O and [Ru(cymene)Cl2(L)].H2O.
These complexes were characterized by elemental analysis, FAB mass, IR and NMR (1H and 31P) spectral data.
Stereochemistry of these complexes has been discussed based on NMR data. NMR studies revealed a dynamic
equilibrium between covalent and ionic forms of the complexes derived from 1 in solution.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 513-520
Structural studies on some trifluoro--diketonates of tin(IV) and lead(II)
Sudha Singh Vishnu D Gupta
Organotin(IV), tin(IV) and lead(II) trifluoro--diketonates have been prepared and characterized on the basis
of IR, 1H and 13C NMR data. All the organotin(IV) complexes are thermally stable liquids. SnCl2(CF3COCHCOPh)2
(7) is characterized by X-ray crystallography which reveals a distorted cis-octahedral structure. X- ray diffraction
analysis of Pb(CF3COCHCOC6H4-p-Cl)2 (8) shows a highly distorted trigonal bipyramidal structure.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 521-524
Studies on the determination of palladium(II) by flourescence quenching method
with meso-tetra[4-(carboxymethylenoxy)phenyl]porphyrin
Yan-jun Fang, Hui Chen, Zhi-xian Gao & Xiao-yong Jin
The spectrofluorimetric determination of Pd(II) using meso-tetra[4-(carboxymethylenoxy)phenyl]porphyrin
(TCMOPPH2) as an emission reagent has been investigated by measuring the decrease of its fluorescence intensity
of the complexation of Pd(II)-TCMOPP. An emission peak of TCMOPPH2, which is decreased linearly by adding
of Pd(II), occurs at 394nm in aqueous solution with excitation at 306nm.The fluorescence intensity vary linearly
with the concentration of palladium(II) in the range 3.754×10-3~0.3625g/mL (SD = 0.034 for 10 times
measurements) and the detection limit down to 2.715×10-4 g/mL. The interference of other noble metals and some
of inorganic ions have been described, and the quenching mechanism has also been investigated according to the
Stern-Volmer equation.
Notes
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 525-527
Phenol–amide chelates of iron (III) as catalysts for hydrolysis of active esters
Harapriya Rath, Guru C. Pradhan, Prakash Mohanty & Anadi C. Dash
The hydrolysis of p-nitrophenylacetate has been studied in the presence of mononuclear iron(III) chelates of 1,2bis(2-hydroxybenzamido)ethane(I), 1,3-bis(2-hydroxybenzamido)pro-pane(II), 1,5-bis(2-hydroxybenzamido)-3aza-pentane(III), and 1,8-bis(hydroxybenzamido)-3,6-diazaoctane(IV) in 10 % (v/v) MeOH +H2O medium at pH =
8.3 – 9.5 (borate buffer), 26.5 ± 0.2ºC, and I = 0.1 mol dm-3. The amide NH-deprotonated chelate of I has been
found to be the most effective catalyst. Catalysis is attributed to both Fe III-OH and FeIIIN(CO)R moieties of this
chelate. The catalytic efficiency decreases with chelate ring expansion and the steric effects of the multidenate
ligands. The results further indicate that the metal-bound amide function and its deprotonated form are of much
reduced activity as compared to metal-bound hydroxo group.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 528-531
An enhancement in the thermal stability and acidity of hydrous zirconia in
presence of 12-tungstophosphoric acid.
Shirish Patel & Anjali Patel
A new solid acid catalyst, 12- tungstophosphoric acid, has been prepared, supported on hydrous zirconium(IV)
oxide and designated as PW/Z. The solid catalyst as well as zirconium(IV) oxide have been characterized by
chemical analysis, chemical stability, ion exchange capacity, FTIR, TGA and surface area measurement(BET
method). The catalytic activity has been examined by carrying out esterification as a model reaction.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 532-536
A kinetic study of the chemical oscillating system comprising mannitol-acetonebromate-H2SO4
Shi-Gang Shen, Han-Wen Sun, Jin-Huan Shan & Jun-li Liu
A new type of chemical oscillating system comprising mannitol-acetone-bromate-H2SO4 has been studied by the
potential method. The initial concentration range of the reactants in the oscillating system and affecting factors have
been examined. The empirical equation of the induction period and oscillating cycle with the concentrations of the
reactants and temperature has been obtained. The apparent activation parameters corresponding to the induction
period, oscillating cycle and oscillating life, Ei, Ep, El are 45.14 kJ mol-1, 60.20 kJ mol-1 and 67.30 kJ mol-1,
respectively. The oscillating characteristic and possible oscillation mechanism have been analyzed.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 537-540
Kinetics of acid-promoted dissociation reactions of Cu [Ph4(14)
tetraene N4] macrocyclic complex
A.K. Singh, Rupam Singh & Seema Baniwal
The kinetics of acid-promoted dissociation reactions of copper complex of 2,4,9,11-tetraphenyl-1,5,8,12tetraazacyclotetradeca-1,4,8,11-tetraene abbreviated as Cu [Ph4(14) tetraene N4], has been studied
spectrophotometrically under pseudo-first order conditions with HCl, HNO3 and H3PO4 in methanol, acetonitrile
and dimethylformamide at temperatures 30-45 ± 0.1 oC. First order kinetics have been observed in all the cases. The
rate constant values of Cu [Ph4(14) tetraene N4] increase linearly with acid concentration and the reaction proceeds
faster in media of higher dielectric constants. The rate of reactions decreases with the decrease in the acid strength
(HCl > HNO3 > H3PO4). A mechanism with the acid dependent reaction of the activated species [M(L*)] 2+ has been
proposed. Product analysis shows that the product is the protonated ligand.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 541-546
Correlation analysis of reactivity in the oxidation of substituted benzylamines by
benzyltrimethylammonium tribromide
Rekha Sankhla & Seema Kothari
The oxidation of benzylamine and twenty-seven ortho-, meta- and para-monosubstituted benzylamines by
benzyltrimethylammonium tribromide (BTMAB), in dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO), leads to the formation of
corresponding aldimines. The reaction is first order with respect to both BTMAB and the amine. The oxidation of
deuterated benzylamine exhibited a substantial kinetic isotope effect. Addition of benzyltrimethylammonium
bromide does not affect the rate. Tribromide ion has been postulated as the reactive oxidizing species. The rates of
the oxidation of para- and meta-substituted benzylamines showed excellent correlation in terms of both Taft’s dual
substituent-parameter and Charton’s triparametric LDR equations, whereas the ortho-substituted compounds
exhibited the best correlation with the Charton’s tetraparametric LDRS equation. The oxidation of para-substituted
benzylamines is more susceptible to the delocalization effect than is the oxidation of ortho- and meta-substituted
compounds, which display a greater dependence on the field effect. The low positive value of the suggests the
presence of an electron-deficient centre in the rate-determining transition state with less charge separation. A
suitable mechanism has been proposed.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 547-549
Kinetics and mechanism of the ruthenium (III) - catalysed oxidation of some
glycols by cerium (IV) in sulphuric acid medium
Bharat Singh, Meera Singh & Deepmala Kesarwani
The ruthenium(III) catalysis in ceric sulphate oxidation of methyl glycol (MG), ethylene glycol (EG), propylene glycol (PG) and 1,3butylene glycol (BG) in sulphuric acid medium was investigated. The reactions were found to be zero order with respect to cerium(IV)
ion and hydrogen ion. Zero order dependence of [Ce (IV)] clearly suggests its involvement in the fast step. First order kinetics with
respect to each glycols and ruthenium (III) chloride was observed. Various actvation parameters have been calculated and recorded. On
the basis of the experimental findings a suitable mechanism has been proposed.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 550-553
Synthesis and characterization of palladium(II) complexes containing
N-pyridiniodithiophosphinates
Vimal K Jain, Leena Hemrajani & Raj K Bansal
Palladium complexes of the type [PdCl2(L)(dithio)] with zwitterionic dithio ligands have been synthesized from the reaction
of [Pd2Cl2(-Cl)2L2] with pyridiniodithiophosphinates in 1:2 molar ratio in dichloromethane at room temperature. These
complexes have been characterized by elemental analysis, IR and NMR ( 1H and 31P) spectral data.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 554-559
Synthesis, magnetic and spectral studies of some cis-dioxomolybdenum(vi)
complexes derived from N, O- and N2O2- type Schiff bases
R C Maurya, B Shukla, & A Pandey
The synthesis of six new mononuclear and binuclear dioxomolybdenum(VI) chelates of compositions,
[MoO2(OH)(L)]2, where L = N- (4'-butyrylidene-3'-methyl-1'-phenyl-2'-pyrazolin-5'-one)-p-anisidine (BUMPHPPAH, I), N- (4'-butyrylidene-3'-methyl-1'-phenyl-2'-pyrazolin-5'-one)-m-phenetidine (BUMPHP-MPH, II) or N- (4'-
butyrylidene-3'-methyl-1'-phenyl-2'-pyrazolin-5'-one)-p-toluidine (BUMPHP-PTH, III), [MoO2(L)], where L = N,
N'-bis-(4'-butyrylidene-3'-methyl-1'-phenyl-2'-pyrazolin-5'-one)-o-phenylenediamine (BUMPHP- OPHDH2 ,IV),
[MoO2(H2O)(L)],
where
L
=
N,
N'-bis(4'-butyrylidene-3'-methyl-1'-phenyl-2'-pyrazolin-5'-one)-mphenylenediamine (BUMPHP- MPHDH2,V) and [{MoO2(OH)}2(L)], where L = N, N'-bis(4'-butyrylidene-3'methyl-1'-phenyl-2'-pyrazolin-5'-one)-benzidine (BUMPHP-BZH2,VI) have been reported. These chelates have
been prepared by the interaction of [MoO2(acac)2] ( where acacH = acetylacetone) with the respective pyrazolone
based Schiff base ligand in ethanol medium. The resulting chelates have been characterized on the basis of
elemental analyses, molar conductance, decomposition temperature, magnetic measurement, thermogravimetric
analyses, 1H-NMR, IR and electronic spectral studies and have been found to contain cis-MO2 structure.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 560-562
Synthesis and characterization of ruthenium(II) complexes of different types of
potential unsymmetrical hemilabile P-O and P-S donors ligands
Pankaj Das, Manab Sharma, Nandini Kumari, Dilip Konwar & Dipak Kumar Dutta
Various potential bidentate hemilabile ligands with different aliphatic backbones, such as
Ph2PCH2CH2COOC2H5(a),
Ph2PCH(CH3)COOCH3(b),
Ph2PCH2OCH3(c),
Ph2PCH2CH2OC2H5(d),
Ph2PCH2CH2SC2H5(e) react with [RuCl2(PPh3)3] in 3:1 molar ratio to produce complexes of the type
[RuCl2(P~X)2(PX)] (1a-e) [where P~X = 1- (P) coordinated; PX = 2- (P,X) coordinated ligand; X = O, S]. On
the other hand, reaction of a ligand containing an aromatic backbone unit such as o-Ph2PC6H4COOC2H5 with
[RuCl2(PPh3)3] produces a bis-chelate complex [RuCl2(PO)2] (2). The complexes have been characterized by
elemental analysis, IR, 1H, and 31P{1H} NMR spectroscopy.
Indian Journal of Chemistry
Vol. 41A March 2002, pp. 563-564
A spectrophotometric method for the trace determination of vanadium as V (V )5-chloro-8-hydroxy-7-iodoquinoline in aqueous medium
Vanita Sharma, Monica Nijhawan & A L J Rao
A simple and rapid spectrophotometric method for the determination of vanadium (V) is developed in the
presence of 5-choloro-8-hydroxy-7-iodoquinoline under acidic conditions using Triton X-100 as surfactant. Pb (II),
Zn (II ),Mn (II ), Co (II), Cr (III), Hg (II), Bi (III) do not interfere when added in large amounts while Fe (III), Fe
(II), Ni (II), Pd (VI), Zr (IV), Cr (II), Cu (II), Mo (VI), are tolerated in smaller concentrations. The applicability of
the method has been tested by analysis of a large number of different synthetic and commercial samples. The
method is highly reproducible with standard deviation of ± 0.005 and Sandell’s sensitivity 2.85x10 -3 µg V cm-2. The
stoichiometry of the complex has also been studied.