ALPHABET HUNT
advertisement

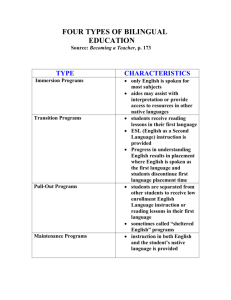
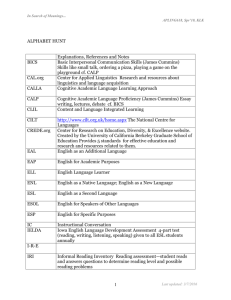
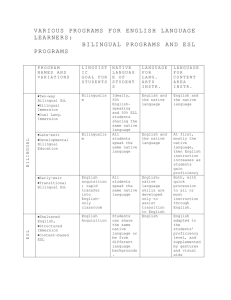
In Search of Meanings... DIXON - APLING618, Spr’12, LC ALPHABET HUNT BICS CAL.org CALLA CALP CLIL CILT CREDE.org EAL EAP ELL ENL ESL ESOL ESP I-R-E LEA Explanations, References and Notes Basic Interpersonal Communication Skills presented by Cummins in 1979. Refers to social or “playground” language that is easily acquired. Center for Applied Linguistics website with very valuable articles in reference to the teaching field as well. Cognitive Academic Language Learning Approach Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency presented by Cummins in 1979. Refers to academic language that encompasses abstract concepts that can take five to seven years to acquire. Content Language and Integrated Learning was coined by David Marsh and Anne Maljers in 1994 to refer to language immersion and content-based instruction. The National Centre for Languages which advocates for intercultural relationships and values all languages. More can be seen at http://www.cilt.org.uk/home.aspx. A resource for teachers that enhances and supports ESL, bilingual, and multicultural education. English as an additional language is very similar to ESL English for Academic Purposes is used largely in higher education settings with the purpose to prepare students for study. English Language Learner is a term usually used to describe a student learning English as a second language either in a bilingual or English only setting. English as a New Language is very similar to ESL English as a Second Language is a program that teaches English to students who have a native language other than English and have an LEP. English for Speakers of Other Languages English for Specific Purposes stems from EFL and is a term that has been used since the early 1960s. It's purpose is to meet the needs of specific learners. Initiate- Response- Evaluate is a model of traditional teaching style which gives all control of discourse to the teacher. Language-Experience Activity in which a teacher creates a natural opportunity to model, question, and instruct a group of students. For example, when a teacher leads a group in making peanut butter sandwiches. 1 Last updated: 2/17/2016 In Search of Meanings... DIXON - APLING618, Spr’12, LC LEP NNS Limited English Proficient is a classification of students who qualify for ESL or bilingual education depending on what the district provides. Massachusetts English Language Assessment- Oral assesses ELL students' in K-12 grades on listening and speaking proficiency. National Association for Bilingual Education. More can be found at http://www.nabe.org/ National Clearinghouse for English Language Acquisition supports high quality education for ELLs as well as their teachers. More can be found at http://www.ncela.gwu.edu/. Non-native speaker NS Native speaker SDAIE Specially Designed Academic Instruction in English is also called Sheltered Instruction. It is a curriculum that is formed to make material comprehensible for ELL students and aid them in being able to participate in all activities in the classroom. MELA-O NABE NCELA.org SILL SIOP TESOL. org TPR ZPD Sheltered Instruction Observation Protocol is a model of Sheltered Instruction is aimed to help teachers improve their instruction which is being used in all fifty states and several countries. Teachers of English to Speakers of Other Languages website Total Physical Response which was introduced by James Asher and became popular in the 1970s. It focuses on listening comprehension as the teacher uses commands as the primary way of instruction. Students are not forced to produce the language until they are ready. Zone of Proximate Development presented by Lev Zygotsky was presented in 1934. This hypothesis reflects the idea that what a child can do with help today is what they will be able to do alone tomorrow. Add your own..... 2 Last updated: 2/17/2016 In Search of Meanings... DIXON - APLING618, Spr’12, LC GLOSSARY HUNT TERM Acquisition Explanation, References, Notes, examples Refers to the learning of a language and usually elements that either enhance or impede the process. Affective filter Refers to the filter that is controlled by a human's emotional switches or needs. A strong affective filter can impede the acquisition process. Those that differ from traditional, such as checklists, portfolios, interviews, and performance-based tasks Alternative assessment Assessment Strategies Audiolingualism Authentic assessment Base word This was a very popular approach to teaching in the early 20th century that stemmed from the behaviorist theory and involved no explicit grammar but many oral drills to help students “practice” correct language. Term introduced by Ruddell and Ruddell in 1995 that encompasses assessments as ongoing and multidimensional but always reflects how students are engaged in everyday classroom learning tasks. It is a word that does not have either prefixes or suffixes. Benchmarks Standards set by the state or Federal government that students are expected to reach. Bottom-up processing Reading strategy that highly depends on the text and word for word reading of the text Care-giver Talk It is the language that is used while addressing young children. This differs from culture to culture. For example, in much of American culture “baby-talk” is often used, but not in African American culture. These include repetition, organising new language, summarising meaning, guessing meaning from context, using imagery for memorisation. All of these strategies involve deliberate manipulation of language to improve learning. Connected to CLT, it is the ability language in an effective and appropriate way. Cognitive Strategies Communicative competence 3 Last updated: 2/17/2016 In Search of Meanings... DIXON - APLING618, Spr’12, LC Communicative Language Teaching Comprehensible Input Also called CTL, it was developed first by British linguists along with the Council of Europe in the 1970s. It is now accepted both in Europe and by American linguists as an approach. Hymes has contributed much to CLT. Although there are several versions of it. Its strongest version puts much emphasis on the belief that language is acquired through communication. Introduced by Stephen Krashen in the 1980s. It is input that can be understood by the learner through visuals, gestures, or realia. Content area It is an area of instruction that focuses on a certain set of skills or area of knowledge such as science or math. Content Standards Content standard is a written description of what students should know and be able to do in a particular content or subject area. The expectations articulated in the content standard outline the knowledge, skills, and abilities for all students in the subject area. Integrates content instruction with language learning opportunities. Content-Based ESL Cognate Words in different languages that have common origins and are easily recognized. Cooperative assessment Declarative Knowledge It is the factual knowledge that one possesses. Decoding Refers to how a student processes print and gives them access to the words on the page. Developmental bilingual program These are also called late-exit bilingual programs that aim to produce bilingual and biliterate individuals. They give EL students sheltered instruction in English and instruction in their native language which value developing their native academic skills as well. Diagnostic assessment Direct Method It is a method of teaching was developed as a response to the Grammar-Translation method. It immerses the learner in the same way as when a first language is learned. All teaching is done in the target language, grammar is taught inductively, there is a focus on speaking and listening, and the teaching of everyday language. 4 Last updated: 2/17/2016 In Search of Meanings... DIXON - APLING618, Spr’12, LC Discourse It is either a spoken or written discussion of a subject. Extralinguistic Refers that which does not include or involve language, beyond its bounds. Formative assessment These are on-going observations or assessments in a classroom in order to improve instruction to aid students' learning process. Functionalism Looks at a school from the perspective that regards a school's feasibility to cope with society and all of the requirements society places upon the school to produce educated and capable adults. It wants to find out how a school correlates with other social institutions, has a desire to figure out how well the school can actually teach its students, and aims to determine how inclusive the school is in representing the local population in its student body and faculty. A term for a category or many different kinds of materials and works. Genre Grade level teacher Refers to a main classroom teacher who GrammarTranslation Approach Graphic Organizer It requires students to translate texts word-for-word and memorize grammar rules. This was largely used to teach classical languages in the 18th and 19th centuries. Visuals that organize information such as compare and contrast, mapping of definitions or concepts, or brainstorming bubbles. I+1 Krashen's theory that as students receive large amounts of comprehensible input, more complex forms are added to the learner's repertoire which gives them higher proficiency. It is when a word or phrase is used in a different way than its literal meaning and usually very colloquial in nature. Idiom Immersion Inflection Developed first in Canada, they are designed to teach language majority students a minority language. Students receive subject matter teaching through instruction in second language. These are bilingual programs with the ultimate goal of full bilingualism and biliteracy . It is the modification of a word in order to express a different grammatical category such as tense, mood, gender, or number. 5 Last updated: 2/17/2016 In Search of Meanings... DIXON - APLING618, Spr’12, LC Instructional Conversation Instrumental motivation Integrative motivation Jigsaw L1 L2 Lx Language Function Late-exit bilingual program Lau v. Nichols Learning Roots are founded by Vygotsky, IC is used to connect academic knowledge to students' personal knowledge of their families and communities through a dialogue in which the teacher listens carefully to the student and then responds in an encouraging and supportive way. It is intended for smaller groups of 5-7 students with the goal of providing meaningful language opportunities for the students. Classified by Garner and Lambert as the motivation to learn a language for practical reasons such as getting a job, getting into college, or getting a raise. Classified by Garner and Lambert as the motivation to learn a language in order to communicate and connect with a certain group of people. A group work technique in which a teacher assigns a member in each group with a specific learning task that they must become an “expert” in. The teacher meets with students to help them become experts and incorporates reading exercises. After students have become “experts”, they share what they have learned with the rest of the groups. First language, second language, and third, fourth ect. It is purpose of communication and can encompass persuasion; cause and effect; asking a question; compare and contrast; predicting; agreeing or disagreeing; and greeting. A transitional bilingual program that keeps students in native language classes for at least 40% of the time through elementary school, even after they have no longer been classified as an ELL. Supreme Court ruling in 1974 that ruled that equal education is the right of all students, therefore schools must provide some curriculum aid for EL students. It suggested bilingual education but allowed other forms of education. The process of acquiring new knowledge, experience, information or language. Learning Strategies Ways students aid their learning process. Literacy Cummin's Interdependence Hypothesis says that literacy as well as other academic skills transfer from L1 to L2. Metacognitive Strategies In reading it is the ability to monitor one's processing and help remedy the situation when one doesn't understand. 6 Last updated: 2/17/2016 In Search of Meanings... DIXON - APLING618, Spr’12, LC Metalinguistic The study of the interrelationship between language and other cultural behavior. Monitor model Morpheme Krashen's hypothesis explains the relationship between acquisition and learning. The learning system acting as a monitor and results in learned grammar. The usage of this monitor changes from learner to learner. The smallest meaningful unit of a language Mother Tongue Is one's native language. Negotiation of meaning It is a process that speakers go through in order to reach mutual understanding. Onset Monosyllabic words can be split into two parts - the onset and the (See also “rime”) rime - each of which are smaller than syllables, but may be larger than phonemes. The onset is the initial consonant sound (b- in bag, sw- in swim), and the rime is the vowel and the rest of the syllable that follows (-ag in bag, -im in swim). Paralinguistic The study of vocal (and sometimes non-vocal) signals beyond the basic verbal message or speech. Performance Standards The expected levels of student competency in a given assessment area, as defined by the content standards. Phoneme “...finite set of sounds that make a difference for meaning” (P&B, p. 36). Phonemic System The system of phonemes recognized in a language. Procedural Knowledge It is the knowledge that one possesses of how to do something. Proficiency level It is the ability or performance level one has in an acquired language. Realia Refer to any objects from real life that are used to aid instruction and enhance student comprehension as well as exchange cultural ideas. Refers to a variety of language that is used in a given context. Examples include formal, informal, or neutral. Register 7 Last updated: 2/17/2016 In Search of Meanings... DIXON - APLING618, Spr’12, LC Rime (See also “onset”) Rubric Scaffold Scanning Schema/ta Monosyllabic words can be split into two parts - the onset and the rime - each of which are smaller than syllables, but may be larger than phonemes. The onset is the initial consonant sound (b- in bag, sw- in swim), and the rime is the vowel and the rest of the syllable that follows (-ag in bag, -im in swim). Refers to a guideline that will rate a student's performance on an activity, task, writing, or project. Introduced by Lev Vygotsky which is associated with his ZPD theory. Scaffolding refers the help and assistance that helps students “do something today that they will be able to do alone tomorrow” (Peregoy & Boyle, 2005, p. 100). To look over a text in a quick but systematic way, while usually looking for specific information. It is a conceptual framework or outline that is based on previous experience and background knowledge. Semantic system Refers to the organization of words and their meanings. Sheltered Instruction Skimming Students are taught the subject matter only in English, but the lessons are written in order to enhance language acquisition while teaching age-appropriate material. To glance at a text quickly and superficially, usually to identify the main idea of a text. Social/Affective Strategies Learning strategies that involve interaction with others, such as asking for clarification or repetition. Submersion Refers to the sink or swim kind of language learning when a student is placed in a native speaker environment and expected to learn as much as possible. Refers to word order in a language. Syntax Summative assessment Task Teacher Talk It is usually used once a year (at the end of the year) to evaluate a program or school's effectiveness. It's goal is to find out a student's competence the school year is finished. It is a work assignment or activity a student is asked to complete which can add meaning to input. The language that is used by the teacher in the L2 which carefully planned and spoken clearly. This differs from what students will find while communicating with natives. 8 Last updated: 2/17/2016 In Search of Meanings... DIXON - APLING618, Spr’12, LC Teaching Strategies A wide variety of means that teachers use to improve student learning. Top-down processing Reading strategy that relies on on background knowledge and other aspects of the text such as chronology and type of text. Transitional Bilingual program Bilingual programs that are in place to serve LEP students. The purpose is to build students' literacy skills and comprehension of academic knowledge in their native language as they acquire the new language. Native instruction is provided for one to three years. Combine elements of Canadian immersion programs and maintenance bilingual programs. They serve both language minority and language majority students. The goal is full bilingualism and biliteracy for both groups of students. Refers to literacy philosophy which emphasizes that children should focus on meaning and strategy instruction. Language is treated as a complete meaning-making system, the parts of which function in relational ways. Two-way Bilingual program Whole language Add your own..... 9 Last updated: 2/17/2016