Reading - K - Oregon Department of Education
advertisement

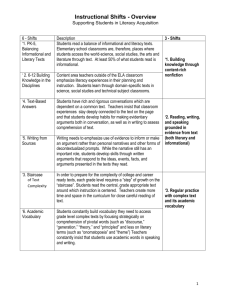
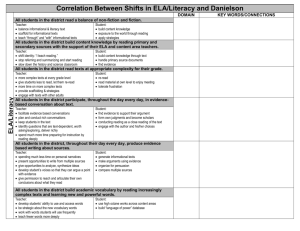
HOW TO READ A…Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer The ELA Literacy Concept Organizers* were created to assist teachers in aligning their instruction to the Common Core State Standards in ELA. These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. Knowledge: Refers to information such as vocabulary terms, definitions, and facts that may or may not need explicit instruction, however, are the foundation on which the lesson will be built. Understandings: Refers to the important ideas, principles, and generalizations that allow students to make connections and see patterns and relationships among content. These are the goals of the instruction, outcomes you expect to achieve. Dos: Refers to demonstration of skills. These are the skills that require explicit instruction. By the completion of a lesson/unit, students should have mastered the selected skill(s). GRADE 1-Key Ideas and Details Informational Reading Standard 1 College and Career Readiness (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard Key Ideas and Details (1): Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. This arrow indicates the CCSS of grade level prior to the grade level you are working. This allows you to see the progression of from grade to grade. These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Some of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. CCSS – Grade Specific Reading Standard 1 (Informational) Grade K: With prompting and Grade 1: Ask and answer Grade 2: Ask and answer such questions about key details in a support, ask and answer questions questions as who, what, where, text. about key details in a text. when, why and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in the text. KNOW (Factual) UNDERSTAND (Conceptual) DO (Procedural, Application and Extended Thinking) Make reasonable predictions as they read Use information from the text and background knowledge to make inferences Ask and answer questions which begin with who, what, where, when why, and how Ask and answer questions about key details in a text Texts Authors include key details in informational texts which can Questions help a reader ask and answer Answers questions. Key details Predictions Good readers know a question Inferences is different from a statement Background knowledge and requires an answer. 5 W’s + H questions (who, what, where, when, why and how) CCSS – Grade Specific Reading Informational Standard 10 (Grade 1) With prompting and support, read informational texts appropriately complex for grade 1. The shaded areas highlight both the College and Career Readiness Anchor Reading Standard Key Ideas and Details and the CCSS for the grade level indicated. This arrow indicates the CCSS of grade level above the grade level you are working. This allows you to see the progression of from grade to grade. The Know, Understand and Do columns align to the shaded grade level. Informational Text-Literary Nonfiction and Historical, Scientific, and Technical Texts Includes biographies and autobiographies; books about history, social studies, science, and the arts; technical texts, including directions, forms and information displayed in graphs, charts or maps; and digital sources on a range of topics Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Some of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Key Ideas and Details Literary Reading Standard 1 College and Career Readiness (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard Key Ideas and Details (1): Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. CCSS – Grade Specific Reading Standard 1 (Literary) Grade K: With prompting and support, Grade 1: Ask and answer questions about ask and answer questions about key key details in a text. details in a text. DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application (Factual) (Conceptual) and Extended Thinking) With prompting and Texts Authors include key support… details in literary texts Questions which can help a reader Make reasonable Answers ask and answer predictions about text Key details questions. Use information from Predictions the text and Inferences Good readers know a background knowledge Background knowledge question is different from to make inferences 5 W’s + H questions a statement and requires Ask and answer (who, what, where, an answer. questions which begin when, why and how) with who, what, where, when why, and how. Ask and answer questions about key details in a text CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 2 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Key Ideas and Details Informational Reading Standard 1 College and Career Readiness (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard Key Ideas and Details (1): Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. CCSS – Grade Specific Reading Standard 1 (Informational) Grade K: With prompting and support, Grade 1: Ask and answer questions about ask and answer questions about key key details in a text. details in a text. DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application (Factual) (Conceptual) and Extended Thinking) With prompting and Texts Authors include key support… details in informational Questions texts which can help a Make reasonable Answers reader ask and answer predictions about text Key details questions. Use information from the Predictions background knowledge Inferences Good readers know a and information from the Background knowledge question is different from text to make inferences 5 W’s + H questions a statement and requires Ask and answer (who, what, where, an answer. questions which begin when, why and how) with who, what, where, when why, and how Ask and answer questions about key details in a text CCSS-Grade Specific Reading Informational Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Informational Text-Literary Nonfiction and Historical, Scientific, and Technical Texts Includes biographies and autobiographies; books about history, social studies, science, and the arts; technical texts, including directions, forms and information displayed in graphs, charts or maps; and digital sources on a range of topics Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 3 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Key Ideas and Details Literary Reading Standard 2 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (2): Determine central ideas or themes of a text and analyze their development; summarize the key supporting details and ideas. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 2 (Literary) Grade K: With prompting and support, Grade 1: Retell stories, including key retell familiar stories, including key details, and demonstrate understanding of details. their central message or lesson. DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application (Factual) (Conceptual) and Extended Thinking) Literary texts Characteristics of familiar stories (e.g., beginning, middle, end) Difference between important (key) and unimportant details in a story Characteristics of an effective retelling/ recounting. Methods for demonstrating understanding of story • Authors of literary texts include details that help readers make sense of stories. • Good readers create an effective recounting or retelling of literary text(s) that includes key ideas and details. With prompting and support: Recognize key details in a story Recount/retell (or graphically represent) key details from literary texts Retell familiar stories, including key details Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 4 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Key Ideas and Details Informational Reading Standard 2 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (2): Determine central ideas or themes of a text and analyze their development; summarize the key supporting details and ideas. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 2 (Informational) Grade K: With prompting and Grade 1: Identify the main topic and retell key support, identify the main topic and details of a text. retell key details of a text. DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application and (Factual) (Conceptual) Extended Thinking) Authors of informational With prompting and support: Informational text text(s) include key Identify and retell key details (both literary details in order to help in an informational text nonfiction and readers make meaning Identify the main topic of an expository/technical of the text. informational text texts) Describe or graphically Main topic Good readers use key represent the relationship Difference between details in an between main topic and key the main topic and informational text to details key details identify the main topic. Identify the main topic and How to retell/restate retell key details of a text details Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Informational Text-Literary Nonfiction and Historical, Scientific, and Technical Texts Includes biographies and autobiographies; books about history, social studies, science, and the arts; technical texts, including directions, forms and information displayed in graphs, charts or maps; and digital sources on a range of topics Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 5 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Key Ideas and Details Literary Reading Standard 3 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (3): Analyze how and why individuals, events, and ideas develop and interact over the course of a text. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 3 (Literary) Grade K: With prompting and support, Grade 1: Describe characters, settings, and identify characters, settings, and major major events in a story, using key details. events in a story. KNOW UNDERSTAND DO (Factual) (Conceptual) (Procedural, Application and Extended Thinking) Authors write stories With prompting and support: Literary texts that have characters, Identify the major events in Major events in a story settings and major a story or play or play events. Identify the beginning, Beginning, middle, end middle and end of a story or Story & play elements Good readers write play o Problem/Solution stories that have Identify the characters in a o Character characters, settings and story or play o Setting (e.g., time, major events. Identify the setting of a story place) or play Identify characters, settings, and major events in a story Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 6 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Key Ideas and Details Informational Reading Standard 3 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (3): Analyze how and why individuals, events, and ideas develop and interact over the course of a text. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 3 (Informational) Grade K: Begin to identify essential Grade 1: Describe the connection between two information from text features (e.g., individuals, events, ideas, or pieces of information author and title) in a text. DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application and (Factual) (Conceptual) Extended Thinking) With prompting and support: Informational text (both Authors of literary nonfiction and informational texts use Identify text features such as expository/technical text features that help texts) readers identify the author and title in informational purpose of the text. texts How to identify Recognize that informational Text features Good readers begin to texts have a structure Informational texts have identify text features in key features such as order to make meaning of author and title informational texts. Informational texts have a structure Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Informational Text-Literary Nonfiction and Historical, Scientific, and Technical Texts Includes biographies and autobiographies; books about history, social studies, science, and the arts; technical texts, including directions, forms and information displayed in graphs, charts or maps; and digital sources on a range of topics Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 7 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Craft and Structure Literary Reading Standard 4 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (4): Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical, connotative, and figurative meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 4 (Literary) Grade K: Ask and answer questions Grade 1: Identify words and phrases in stories or about unknown words in a text. poems that suggest feelings or appeal to the senses. DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application and (Factual) (Conceptual) Extended Thinking) Literary Text Authors make Read and reread other words, purposeful language sentences, and non-linguistic Questions choices to create images (e.g., illustrations) in Answers meaning in stories, the text to identify context Picture clues poems, and songs. clues Words Use context clues to help Context clues unlock the meaning of Simple literary devices Good readers actively seek the meaning of unknown words/phrases (e.g., alliteration, unknown words/phrases Identify simple literary devices repetition, rhythm, by asking and Ask and answer questions rhyme) answering questions to about unknown words clarify meaning. Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 8 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Craft and Structure Informational Reading Standard 4 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (4): Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical, connotative, and figurative meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 4 (Informational) Grade K: With prompting and support, Grade 1: Ask and answer questions to help ask and answer questions about determine or clarify the meaning of words and unknown words in a text. phrases in a text. DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application and (Factual) (Conceptual) Extended Thinking) Informational text Authors make Read and reread other words, purposeful language sentences, and non-linguistic Questions choices to create images in the text to identify Answers meaning in context clues Picture/graphic clues informational text(s). Use context clues to help Words unlock the meaning of Context clues Good readers actively unknown words/phrases seek the meaning of Ask and answer questions unknown words/phrases about unknown words in a text by asking and answering questions to clarify meaning. Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Informational Text-Literary Nonfiction and Historical, Scientific, and Technical Texts Includes biographies and autobiographies; books about history, social studies, science, and the arts; technical texts, including directions, forms and information displayed in graphs, charts or maps; and digital sources on a range of topics Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 9 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Craft and Structure Literary Reading Standard 5 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Literary Reading Standard (5): Analyze the structure of text, including how specific sentences, paragraphs, and larger portions of the text (e.g., a section, chapter, scene, or stanza) relate to each other and the whole. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 5 (Literary) Grade K: Recognize common types of Grade 1: Explain major differences between texts (e.g. storybooks, poems). books that tell stories and books that give information, drawing on a wide reading of a range of text types. DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application (Factual) (Conceptual) and Extended Thinking) Literary text Authors write different Recognize a storybook types of texts. Types of text (e.g., Recognize a poem storybooks, poems) Good readers General features of a understand that storybook (e.g., storybooks and poems characters, setting, have different features. events) General features of a poem (e.g., rhyme, shorter text) CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 10 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Craft and Structure Informational Reading Standard 5 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Literary Reading Standard (5): Analyze the structure of text, including how specific sentences, paragraphs, and larger portions of the text (e.g., a section, chapter, scene, or stanza) relate to each other and the whole. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 5 (Informational) Kindergarten: Identify the front cover, Grade 1: Know and use various text features (e.g. back cover, and title page of a book. headings, tables of contents, glossaries, electronic menus, icons) to locate key facts or information in a text. DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application (Factual) (Conceptual) and Extended Thinking) Informational text Authors create books Identify the front cover of a book (both literary that have front covers, Identify the back cover of a nonfiction and back covers and title book expository/technical pages. Identify the title page of a book texts) Identify the front cover, back How to identify Good readers can cover, and title page of a book identify the front cover, Text features (e.g., back cover and title page front cover, back of a book. cover, title page) Books are read from front to back CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Informational Text-Literary Nonfiction and Historical, Scientific, and Technical Texts Includes biographies and autobiographies; books about history, social studies, science, and the arts; technical texts, including directions, forms and information displayed in graphs, charts or maps; and digital sources on a range of topics Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 11 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Craft and Structure Literary Reading Standard 6 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (6): Assess how point of view or purpose shapes the content and style of a text. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 6 (Literary) Grade K: With prompting and support, Grade 1: Identify who is telling the story at name the author and illustrator of a various points in a text. story and define the role of each in telling the story. DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application (Factual) (Conceptual) and Extended Thinking) Literary text(s) Authors of stories With prompting and support... How to define decide how the story is Identify the author of a story Author told to the reader. Identify the illustrator of a Illustrator story Roles of authors and Illustrators of stories Explain how the author tells a illustrators help the reader “see” story the story. Explain how the illustrator helps the reader see a story Good readers know that Name the author and authors and illustrators illustrator of a story and define have different roles in the role of each in telling the creating a story. story CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 12 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Craft and Structure Informational Reading Standard 6 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (6): Assess how point of view or purpose shapes the content and style of a text. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 6 (Informational) Grade K: Name the author and Grade 1: Distinguish between information illustrator of a text and define the role provided by pictures or other illustrations and of each in presenting the ideas or information provided by the words in a text. information in a text. CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application, and (Factual) (Conceptual) Extended thinking) Authors and illustrators Identify the author of an Informational text (both have different roles in informational text literary nonfiction and creating a text. Identify the illustrator of an expository/technical The author of an informational text texts) informational text Identify the ideas and How to define decides what ideas or information learned from the Author information is presented author Illustrator to the reader. Identify the ideas and Role of an author The illustrator of an information learned from the Role of an illustrator informational text helps illustrator the reader “see” the text. Good readers recognize that authors and illustrators have different roles. Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Informational Text-Literary Nonfiction and Historical, Scientific, and Technical Texts Includes biographies and autobiographies; books about history, social studies, science, and the arts; technical texts, including directions, forms and information displayed in graphs, charts or maps; and digital sources on a range of topics Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 13 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Integration of Knowledge and Ideas Literary Reading Standard 7 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (7): Integrate and evaluate content presented in diverse media and formats, including visually and quantitatively, as well as in words. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 7 (Literary) Grade K: With prompting and support, Grade 1: Use illustrations and details in a story to describe the relationship between describe its characters, setting, or events. illustrations and the story in which they appear (e.g., what moment in a story an illustration depicts). DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application, and (Factual) (Conceptual) Extended thinking) Authors • use With prompting and support : How to describe illustrations and details Identify story details Illustrations (e.g., in a text to tell a story. Describe information photos, pictures, obtained from illustrations drawings) Good readers use Describe the relationship Story details (e.g., illustrations/pictures to between illustrations and the character, setting, enhance their story in which they appear events) understanding of a story. Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 14 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K- Integration of Knowledge and Ideas Informational Reading Standard 7 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (7): Integrate and evaluate content presented in diverse media and formats, including visually and quantitatively, as well as in words. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 7 (Informational) Grade K: With prompting and support, Grade 1: Use the illustrations and details in describe the relationship between a text to describe its key ideas. illustrations and the text in which they appear (e.g., what person, place, thing, or idea in the text an illustration depicts). DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application and (Factual) (Conceptual) Extended Thinking) Topic With prompting and support Authors use Text details illustrations and details Identify the topic of a text Graphics/images/illustrations Identify details (e.g., in a text to present (e.g., photographs, person, place, thing, idea) information. diagrams, simple charts, in a text graphs, maps) Describe information Good readers use contained in illustrations illustrations to enhance contribute to the text their understanding of Describe the relationship text. between illustrations and the text in which they appear Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Informational Text-Literary Nonfiction and Historical, Scientific, and Technical Texts Includes biographies and autobiographies; books about history, social studies, science, and the arts; technical texts, including directions, forms and information displayed in graphs, charts or maps; and digital sources on a range of topics Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 15 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K- Integration of Knowledge and Ideas Literary Reading Standard 8 There is no Standard 8 for Literature. Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 16 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K- Integration of Knowledge and Ideas Informational Reading Standard 8 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (8): Delineate and evaluate the argument and specific claims in a text, including the validity of the reasoning as well as the relevance and sufficiency of the evidence. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard (Informational) Grade K: With prompting and support, Grade 1: Identify the reasons an author gives to identify the reasons an author gives to support points in a text. support points in a text. Do Know Understand (Procedural, Application and (Factual) (Conceptual) Extended Thinking) Informational text (both Authors provide With prompting and support literary nonfiction and Identify the author’s key reasons/examples in expository/technical ideas/points informational text to texts) Identify reasons/details that support their points and Author support the author’s key ideas. Main/key ideas/points ideas/points Supporting details Differentiate between Good readers identify Relevant/important vs. relevant and irrelevant the reasons/examples an irrelevant/unimportant reasons/details author uses to support details Identify the reasons an points and ideas to Reasons/examples author gives to support enhance their points in a text understanding of an informational text. Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Informational Text-Literary Nonfiction and Historical, Scientific, and Technical Texts Includes biographies and autobiographies; books about history, social studies, science, and the arts; technical texts, including directions, forms and information displayed in graphs, charts or maps; and digital sources on a range of topics Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 17 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K-Integration of Knowledge and Ideas Literary Reading Standard 9 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (9): Analyze how two or more texts address similar themes or topics in order to build knowledge or to compare the approaches the authors take. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard (9) (Literary) Grade K: With prompting and support, Grade 1: Compare and contrast the adventures compare and contrast the adventures and experiences of characters in stories. and experiences of characters in familiar stories. DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application and (Factual) (Conceptual) Extended Thinking) Compare With prompting and support Authors develop their Contrast Identify the characters within stories with the Characters and between texts adventures and Plot (e.g., main events, Identify the plots (including experiences of main problem/solution) adventures and experiences) characters. Adventures and within and between texts experiences Compare and contrast the Good readers Familiar stories adventures and experiences understand familiar of characters in familiar stories by learning about stories characters’ adventures and experiences. Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 18 Delaware English Language Arts Literacy Concept Organizer These ELA Literacy Concept Organizers are not replacements for teachers’ individual units. They are deconstructions of the Common Core State Standards. These Literacy Concept Organizers are a resource from which teachers can select appropriate Knowledge, Understandings, and Dos to develop their own unit(s) of instruction. GRADE K- Integration of Knowledge and Ideas Informational Reading Standard 9 College and Career Ready (CCR) Anchor Reading Standard (9): Analyze how two or more texts address similar themes or topics in order to build knowledge or to compare the approaches the authors take. CCSS – Grade Level Reading Standard 9 (Informational) Grade K: With prompting and Grade 1: Identify basic similarities in and support, identify basic similarities in differences between two texts on the same topic and differences between two texts on (e.g., in illustrations, descriptions, or procedures). the same topic (e.g., in illustrations, descriptions, or procedures). DO KNOW UNDERSTAND (Procedural, Application and (Factual) (Conceptual) Extended Thinking) Authors of informational With prompting and support… Informational text text provide information (both literary Identify basic similarities on topics using features nonfiction and between two texts on the such as illustrations, expository/technical same topic descriptions, and texts) Identify basic differences procedures. Similarities/compare between two texts on the same topic Differences/contrast Good readers make Illustrations/pictures Identify or graphically meaning of Descriptions/details represent basic similarities informational text by Procedures/steps in and differences identifying similarities (e.g., experiments, between two texts on the and differences directions, recipes) same topic between two texts. Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity CCSS-Grade Specific Standard 10 (Grade K/Kindergarten) Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. Informational Text-Literary Nonfiction and Historical, Scientific, and Technical Texts Includes biographies and autobiographies; books about history, social studies, science, and the arts; technical texts, including directions, forms and information displayed in graphs, charts or maps; and digital sources on a range of topics Reading Recursive Strategies: o Assimilating prior knowledge o Rereading to clarify information o Seeking meaning of unknown vocabulary o Making and revising predictions o Using critical and divergent thinking and assimilating prior knowledge to draw conclusions o Making connections and responding to text These recursive strategies are the basic reading strategies that students must know and use to become successful readers. Many of the strategies are not explicitly stated in the Common Core State Standards for ELA. Adapted from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2011). Reformatted by the Oregon Department of Education, January 2012. 19