Algebraic Reasoning 1
advertisement

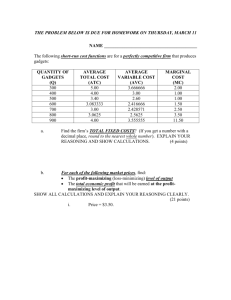
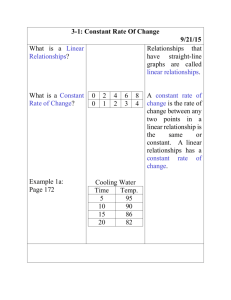
Draft Summer 2008 Examples for Student Performance Standards IAR Math Course: Math 8 Numerical and Proportional Reasoning 2.2a NOTES: During the spiral review of arithmetic skills & CMT Strands students review, learn, and develop calculation & estimation skills with positive numbers (whole numbers, decimals, and fractions). Students are assessed on these skills (without a calculator) on paper and pencil “calculation quizzes” and common quarterly calculation tests. During the unit “Working with Signed Numbers”, students learn and develop calculation strategies and skills for positive and negative numbers. These, too, are assessed without a calculator. These are included in the Math 8 curriculum because students have not mastered these expected performances from the grade 7 expected performances. Students also do additional work with writing and solving proportions in Math 8. (See example on next page.) Numerical and Proportional Reasoning 2.2a, page 1 Draft Summer 2008 Examples for Student Performance Standards IAR Math Course: Math 8 Example 2.2a Impact 2, Ch. 8.2 Using Proportions Inv.4 p.550 Numerical and Proportional Reasoning 2.2a, page 2 Draft Summer 2008 Examples for Student Performance Standards IAR Math Course: Math 8 (1) Estimate and solve problems involving percent of increase and decrease. Example 1: From test practice for “Percent” Test – (with calculator available) 1. A fruit drink that was sold in 16-ounce containers is now sold in 20-ounce containers. What is the percent of increase in the amount of fruit drink? 2. The price of a computer system at an electronics store is $1099. Determine the percent of decrease in price if the computer system sold for $1349 a month earlier. Example 2: From CMT practice bank – Strand 11 – (without calculator available) 1. Last year, Pat made $508 per week. This year, he received a raise of $24.50 per week. What is a good estimate of the percent of increase in Pat’s pay? SHOW and EXPLAIN how you made your estimate. 2. A bicycle regularly costs $814. If you receive a 26% discount, show and explain how you could estimate the discounted price of the bicycle. Numerical and Proportional Reasoning 2.2a, page 3 Draft Summer 2008 Examples for Student Performance Standards IAR Math Course: Math 8 Example 3: From Impact Mathematics, Course 2, p. 563 Problem Set A –This is not a percent of increase/decrease example but illustrates how percent diagrams are introduced. On the unit test, students need to label the intervals on a percent diagram and use it to make an estimate. – Part of “Percent” Unit Numerical and Proportional Reasoning 2.2a, page 4 Draft Summer 2008 Examples for Student Performance Standards IAR Math Course: Math 8 Example 4: From Impact Mathematics, Course 2, p. 576 (On Your Own Exercises) – Part of “Percent” Unit Numerical and Proportional Reasoning 2.2a, page 5