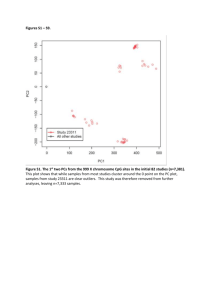
Methyl CpG binding protein 2 binding sites on chromosome 22 in
advertisement

Methyl CpG binding protein 2 binding sites on chromosome 22 in hepatocellular carcinoma B cells Cancer cells often have wide spread methylation across their genes. This methylation, especially on gene promoters, can result in gene repression. When tumor suppressor genes are methylated, they may be turned off resulting in a cancer phenotype. The methylation recruits methyl CpG binding proteins (MBDs) to bind to the nucleotides and recruit other proteins to deactivate the gene. By identifying the location of bound MBDs we can hypothesize which genes have been repressed. The purpose of this lab is to determine the binding sites of MBD2 on chromosome 22 in hepatocellular carcinoma B cells. To accomplish this, cells are cultured and harvested in Eagle’s medium and trypsinized. The nuclei are extracted, sonicated, and MBD2 antibody is introduced. The bound fragments are precipitated, purified and amplified with PCR. Finally, the amplified DNA is fluorescently labeled with Cy3 and hybridized to a microarray of chromosome 22. Unfortunately during the purification step during labeling the hybridization buffer was not given adequate time to dissolve the DNA. This prevented successful completion of the entire protocol, including the hybridization. The experiment should be repeated with the aforementioned warning, and possibly with others methyl CpG binding proteins. Degree project in Biology. Spring 10 p Anish Chari