Tutorial (Atomic nature)
advertisement

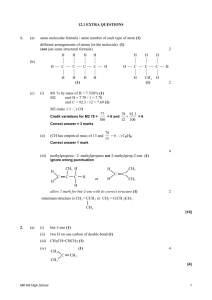
Tutorial (Structure and bonding) 1. Rank the following functional groups: hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, phenol and ether in the order of decreasing polarity. Give reasons. (10 marks) Two marks for correct arrangement Carboxyl: Two oxygen atom and one hydrogen atom available for hydrogen bonding. Electron delocalisation between the two oxygen atoms stabilises the carboxylate ion. (pKa 4.76) Phenol: One oxygen and one hydrogen atom available for hydrogen bonding Electron delocalisation confers stability to phenoxide ion (pKa 9.95) Hydroxyl: Oxygen available for hydrogen bonding (acceptor) Hydrogen bonded to oxygen available for hydrogen bonding (donor) Carbonyl: Only one oxygen atom for hydrogen bonding, no ions possible Ether: Steric factors inhibit hydrogen bonding 2. Calculate the ΔH°comb for 1 mol of methanol. Methanol burns in oxygen according to the equation below. (6 marks) 2 CH3OH + 3 O2 → 2 CO2 + 4 H2O Methanol The bond energy of the different bonds are as follows: C−O O=O C−H O−H C=O 358 kJ/mol 498 kJ/mol 413 kJ/mol 467 kJ/mol 799 kJ/mol CH3OH + 1.5 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O 3 C−H bonds: 3(413 kJ/mol) = 1239 kJ 1 C−O bonds: 1(358 kJ/mol) = 358 kJ 1 O−H bonds: 1(467 kJ/mol) = 467 kJ 1.5 O=O bonds: 1.5(498 kJ/mol) = 747 kJ ∑ ΔH°disassociation = 2811 kJ 2 C=O bonds: 2(−799 kJ/mol) = −1598 kJ 4 O−H bonds: 4(−467 kJ/mol) = −1868 kJ ∑ ΔH°formation = −3466 kJ ΔH°comb = ∑ ΔH°disassociation + ∑ ΔH°formation = 2811 + (−3466) = −655 kJ/mol 3. Ionic compounds tend to have a ∆EN >1.7. Based on their electronegativity, explain why Group 4 compounds (Carbon family) tend to be covalent rather than ionic. (3 marks) Group 4 elements have moderate EN ranging from 1.8 to 2.5. They are unable to form anions with most alkali metals that have low electronegativity (EN ~0.9) They are unable to form cations with most halogens except for fluorine (EN 4.0) 4. Arrange the following diatomic halogen molecules in terms of increasing bond length: F2, I2, Cl2 and Br2. Briefly explain the difference in bond length. (2 marks) Increasing bond length: F2 < Cl2 < Br2 < I2, Atomic size increases down a group 5. Do substances with stronger bonds or weaker bonds release more energy when burned? Briefly explain. (3 marks) Substances with weaker bonds release more energy Less energy would be required to break the molecular bonds This would result in a more exothermic enthalpy change when products are formed