Grade 4 comparison - Lawrence County Schools
advertisement

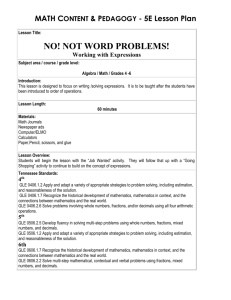
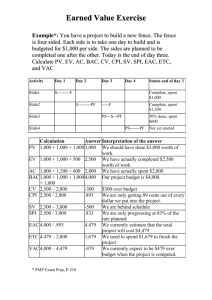
Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards page 1 of 18 Grade 4 Transition to New TN Mathematics Standards Grade 4 – Mathematical Processes New Grade Level Expectations GLE 0406.1.1 GLE 0406.1.2 GLE 0406.1.3 GLE 0406.1.4 GLE 0406.1.5 GLE 0406.1.6 GLE 0406.1.7 GLE 0406.1.8 Use mathematical language, symbols, and definitions while developing mathematical reasoning. Apply and adapt a variety of appropriate strategies to problem solving, including estimation, and reasonableness of the solution. Develop independent reasoning to communicate mathematical ideas and derive algorithms and/or formulas. Move flexibly between concrete and abstract representations of mathematical ideas in order to solve problems, model mathematical ideas, and communicate solution strategies. Use mathematical ideas and processes in different settings to formulate patterns, analyze graphs, set up and solve problems and interpret solutions. Read and interpret the language of mathematics and use written/oral communication to express mathematical ideas precisely. Recognize the historical development of mathematics, mathematics in context, and the connections between mathematics and the real world. Use technologies/manipulatives appropriately to develop understanding of mathematical algorithms, to facilitate problem solving, and to create accurate and reliable models of mathematical concepts. Checks for Understanding (Formative/Summative Assessment) 0406.1.1 0406.1.2 0406.1.3 0406.1.4 0406.1.5 0406.1.6 0406.1.7 0406.1.8 0406.1.9 0406.1.10 Understand the relationship between use of answers and the accuracy of the number. Identify the range of appropriate estimates, including over-estimate and under-estimate. Connect operations with decimals to money and make estimates. Use commutative, associative, and distributive properties of numbers including oral descriptions of mathematical reasoning. Measure using ruler, meter stick, clock, thermometer, or other scaled instruments. Identify geometric or physical attributes that are appropriate to measure in a given situation. Translate the details of a contextual problem into diagrams and/or numerical expressions, and express answers using appropriate units. Match the spoken, written, concrete (including base ten blocks), and pictorial representations of decimals. Develop a story problem that illustrates a given multiplication or division number sentence. Use age-appropriate books, stories, and videos to convey ideas of mathematics. State Performance Indicators SPI SPI SPI SPI 0406.1.1 0406.1.2 0406.1.3 0406.1.4 Verify a conclusion using the commutative, associative and distributive properties. Compare decimals using concrete and pictorial representations. Determine the correct change from a transaction. Compare objects with respect to a given geometric or physical attribute and select appropriate measurement instrument. Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards page 2 of 18 Grade 4 – Number and Operations Former Learning Expectations 1.1 Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number systems. 1.2 Understand meanings of operations and how they relate to one another. 1.3 Solve problems, compute fluently, and make reasonable estimates. New Grade Level Expectations GLE 0406.2.1 Understand place value of numbers from hundredths to the hundred-thousands place. GLE 0406.2.2 Develop fluency with multiplication and single-digit division. GLE 0406.2.3 Identify prime and composite numbers. GLE 0406.2.4 Understand and use the connections between fractions and decimals. GLE 0406.2.5 Add and subtract fractions with like and unlike denominators. GLE 0406.2.6 Solve problems involving whole numbers, fractions, and/or decimals using all four arithmetic operations. Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 Identify whole numbers as odd or even. A Count by 10’s, 100’s, or 1,000’s.A Represent whole numbers to 9,999 with models. A Skip count by 10’s from any whole number less than 1,000. D Read and write whole numbers to 9,999. D Identify the place value of a given digit up to thousands. A Represent whole numbers up to 10,000 in expanded form (e.g., 1,000’s + 100’s + 10’s + 1’s). A SPI 0306.2.1 Read and write numbers up to 10,000 in numerals and up to 1,000 in words. 0306.2.1 Represent whole numbers up to 10,000 using various models (such as baseten blocks, number lines, place-value charts) and in standard form, written form, and expanded form. Read and write numbers from hundred-thousands to hundredths. A Represent whole numbers to 9999. A SPI 0406.2.1 Read and write numbers from hundredths to hundred-thousands in numerals and in words. SPI 0306.2.2 Identify the place value of numbers in the ten-thousands, thousands, hundreds, tens, and ones positions. SPI 0306.2.3 Convert between expanded and standard form with whole numbers to 10,000. Identify the place value of a given digit from hundredthousands to hundredths. A Represent whole numbers up to 10,000 in expanded form (1,000’s + 100’s +10’s +1’s). A SPI 0406.2.3 Identify the place value of a specified digit in a number and the quantity it represents. 0406.2.1 Compose and decompose quantities according to place value. 0406.2.12 Understand and use decimal numbers up to hundredths and write them as fractions. SPI 0406.2.4 Find factors, common factors, multiples, and common multiples of two numbers. Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material Compare and order whole numbers up to 9999 using the appropriate symbol (i.e., <, >, and =). A Connect written and pictorial representations of fractions with denominators up to ten. A Compare fractions with numerators of 1 and denominators up to 10. A Order and sequence whole numbers up to 4 digits. D Connect the spoken or written word names and concrete or pictorial representations (regions or sets) of fractions with denominators up to ten. D Identify the position of 1/2, 1/3, or 1/4 on the number line. D Compare and order decimal amounts written as money. I New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards SPI 0306.2.4 Compare and order numbers up to 10,000 using the words less than, greater than, and equal to, and the symbols <, >, =. 0306.2.2Understand and use the symbols =, < and > to signify order and comparison. SPI 0306.2.10 Identify equivalent fractions given by various representations. SPI 0306.1.4 Match the spoken, written, concrete, and pictorial representations of fractions with denominators up to ten. SPI 0306.2.11 Recognize and use different interpretations of fractions. 0306.2.10 Understand that symbols such as ½, 1/3, and ¼ represent numbers called unit fractions. 0306.2.11 Identify fractions as parts of whole units, as parts of sets, as locations on number lines, and as division of two whole numbers. SPI 0306.2.12 Name fractions in various contexts that are less than, equal to, or greater page 3 of 18 Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 Compare and order whole numbers to 9999 using the appropriate symbols (>, <, and =). A Identify fractions as parts of whole units, as parts of sets, as locations on number lines, and as divisions of whole numbers A. Generate equivalent forms of whole numbers, commonly used fractions, and decimals. A Represent numbers as both improper fractions and mixed numbers. A Use concrete or pictorial representations to compare and order commonly used fractions. D Use concrete and pictorial representations to compare decimals. D Use various models and equivalent forms to represent, order, and compare whole numbers and commonly used fractions and mixed numbers (e.g., number lines, base ten blocks, expanded notation, Venn diagrams, and hundreds boards). D New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 0406.2.7 Identify factors of whole numbers and model factors and products beyond basic multiplication facts using arrays and area models. SPI 0406.2.2 Locate and place mixed numbers on the number line. SPI 0406.2.5 Generate equivalent forms of common fractions and decimals and use them to compare size. SPI 0406.2.6 Use the symbols < , > and = to compare common fractions and decimals in both increasing and decreasing order. SPI 0406.1.2 Compare decimals using concrete and pictorial representations. SPI 0406.2.7 Convert improper fractions into mixed numbers and/or decimals. 0406.1.8 Match the spoken, written, concrete (including base ten blocks), and pictorial representations of decimals. 0406.2.2 Understand decimal notation as an extension of the base-ten number system. 0406.2.8 Generate equivalent forms of whole numbers, decimals, and common fractions (e.g., 1/10, ¼, ½, ¾). 0406.2.9 Compare equivalent forms whole numbers, Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards than one. 0306.2.13 Understand that when a whole is divided into equal parts to create unit fractions, the sum of all the parts adds up to one. SPI 0306.2.13 Recognize, compare, and order fractions (benchmark fractions, common numerators, or common denominators). Compare fractions using drawings, concrete objects, and benchmark fractions. SPI 0306.2.14 Add and subtract fractions with like denominators. Solve real-world problems using addition or subtraction of whole numbers. A Add and subtract efficiently and accurately with singledigit whole numbers. A Add efficiently and accurately with two- and/or three-digit whole numbers. A Subtract efficiently and accurately with two- and/or three-digit whole numbers. A Recognize the value of combinations of coins and bills up to $5. A Determine the correct change from a transaction that is less than $1.00. A SPI 0306.2.9 Solve contextual problems involving the addition (with and without regrouping) and subtraction (with and without regrouping) of two- and three digit whole numbers. 0306.2.3 Use parentheses to indicate grouping. 0306.2.6 Solve a variety of addition and subtraction story problems including those with irrelevant information. SPI 0306.1.3 Determine the correct change from a transaction less than a dollar. 0306.1.2 Compare and order decimal amounts in the page 4 of 18 Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 fractions, and decimals to each other and to benchmark numbers. 0406.2.11 Use models, benchmarks, and equivalent forms to compare fractions/decimals and locate them on the number line. Add and subtract fractions with like denominators. A Add and subtract decimals (includes monetary units). A Explain the relationship between addition and subtraction. D SPI 0406.2.8 Add and subtract proper fractions with like and unlike denominators and simplify the answer. SPI 0406.2.9 Add and subtract decimals through hundredths. SPI 0406.1.3 Determine the correct change from a transaction. Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material Select and use an appropriate strategy to solve word problems (e.g., organized list, guess and check, diagram, and table). D Write and identify number sentences that describe situations involving addition, subtraction, and multiplication. D Write and explain related addition and subtraction sentences. Mentally calculate the sum or difference of any two numbers up to 100. I Use a variety of thinking strategies to add and subtract whole numbers (e.g., sums of ten, doubles plus one). D Explain and justify solution strategies used in problem solving. D Explain the reasonableness of a solution to a computation or to a word problem. D Use strategies, including rounding, to estimate in story problems. D Use estimation to select a reasonable solution in problem solving (addition and subtraction only). A New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards page 5 of 18 Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 context of money. 0306.1.3 Count the value of combinations of coins and bills up to five dollars. 0306.2.4 Use a variety of methods to perform mental computations and compare the efficiency of those methods. Select appropriate methods and tools for computing with whole numbers (e.g., mental computation, estimation, calculators, paper and pencil, guess and check). I SPI 0306.1.5 Represent problems mathematically using diagrams, numbers, and symbolic expressions. 0306.1.4 Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant from irrelevant information, and observing patterns. 0306.1.5 Determine when and how to break a problem into simpler parts. 0306.1.6 Use estimation to check answers for reasonableness, and calculators to check for accuracy. Solve one-step real-world problems involving addition or subtraction of whole numbers and/or decimals. A Solve one-step real-world problems involving multiplication of whole numbers and/or decimals. A Select the appropriate computational and operational method to solve word problems. D Solve story problems using whole numbers, fractions, and decimals (includes money). D Identify missing information SPI 0406.2.10 Solve contextual problems using whole numbers, fractions, and decimals including money. 0406.2.13 Solve multi-step problems of various types using whole numbers, fractions, and decimals. 0406.1.7 Translate the details of a contextual problem into diagrams and/or numerical expressions, and express answers using appropriate units. 0406.1.9 Develop a story Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material Relate skip counting to multiplication. I Connect division to sharing situations. I Demonstrate multiplication using repeated addition (e.g., arrays). I/D Relate adding doubles to multiplying by two. I Use the multiplication facts 0, 1, 2, 5, and 10 efficiently and accurately. A Use known multiplication facts to determine a related product (e.g., 9 x 7 is 7 less than 10 x 7). I page 6 of 18 New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 0306.1.7 Make and investigate mathematical conjectures. 0306.1.8 Explain and justify answers on the basis of mathematical properties, structures, and relationships. 0306.1.13 Create and use representations to organize, record, and communicate mathematical ideas. 0306.1.12 Analyze and evaluate the mathematical thinking and strategies of others 0306.2.5 Use highest order value (such as tens or hundreds digit) to make simple estimates. SPI 0306.2.5 Identify various representations of multiplication and division. 0306.2.7 Represent multiplication using various representations such as equalsize groups, arrays, area models, and equal jumps on number lines. 0306.2.8 Represent division using various representations such as successive subtraction, the number of equal jumps, partitioning, and sharing. 0306.2.9 Describe contexts for multiplication and division facts. SPI 0306.2.6 Recall basic and/or too much information in word problems I. Apply logical reasoning to solve real-world problems. I Estimate the results of wholenumber computations. D Use estimation to select a reasonable solution to a whole number computation involving addition, subtraction, or multiplication. A problem that illustrates a given multiplication or division number sentence. 0406.1.1 Understand the relationship between use of answers and the accuracy of the number. 0406.1.2 Identify the range of appropriate estimates, including over-estimate and under-estimate. 0406.1.3 Connect operations with decimals to money and make estimates. Multiply efficiently and accurately with single-digit whole numbers. A Multiply decimals (includes monetary units). I SPI 0406.2.11 Solve problems using whole number multidigit multiplication. 0406.2.3 Multiply two- and three-digit whole numbers. 0406.2.4 Understand and use a reliable algorithm for multiplying multi-digit numbers and dividing numbers by a single-digit divisor accurately and efficiently. SPI 0406.2.12 Solve problems using whole number division with one- or two-digit divisors. 0406.2.4 Understand and use a reliable algorithm for multiplying multi-digit numbers Divide efficiently and accurately with single-digit whole numbers. D Explain the relationship between multiplication and division. I Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards multiplication facts through 10 times10 and the related division facts. SPI 0306.2.7 Compute multiplication problems that involve multiples of ten using basic number facts. SPI 0306.2.8 Solve problems that involve the inverse relationship between multiplication and division. page 7 of 18 Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 Explain how addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division affect the size and order of numbers. I New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 and dividing numbers by a single-digit divisor accurately and efficiently. 0406.2.5 Understand that division by zero is undefined. 0406.2.6 Divide three-digit whole numbers by one-digit divisors fluently with pencil and paper. 0406.2.10 Use models to understand division as the inverse of multiplication, partitioning, and repeated subtraction 0406.2.14 Understand the role of the remainder in division. Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of grade level mathematical terms. D Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards page 8 of 18 Grade 4 – Algebra Former Learning Expectations 2.1 Understand patterns, relations, and functions. 2.2 Represent and analyze mathematical situations and structures using algebraic symbols. 2.3 Illustrate general properties of operations. 2.4 Analyze change in various contexts. New Grade Level Expectations GLE 0406.3.1 Extend understanding of a variable to equations involving whole numbers, fractions, decimals, and/or mixed numbers. GLE 0406.3.2 Use mathematical language and modeling to develop descriptions, rules and extensions of patterns. GLE 0406.3.3 Translate between different forms of representations of whole number relationships. Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 Show or represent and solve open sentences, involving addition, subtraction, and multiplication, with concrete objects or pictures. D Demonstrate understanding that an equation is a number sentence stating two quantities are equal. I Solve open sentences that involve addition and subtraction of whole numbers zero to twenty. A Connect open sentences to real-world situations. A Determine the output number for a particular input number given a one-operation function rule involving addition or subtraction. A SPI 0306.3.2 Express mathematical relationships using number sentences/equations. SPI 0306.3.3 Find the missing values in simple multiplication and division equations. 0306.3.5 Find unknowns in number sentences and problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division. Solve open sentences involving addition and subtraction A. Solve open sentences involving multiplication and division. A Connect open sentences to real-world situations. A Demonstrate understanding that an equation is a number sentence stating that two quantities are equal. D Represent the idea of a variable as an unknown quantity by using a letter or a symbol. I SPI 0406.3.1 Use letters and symbols to represent an unknown quantity and write a simple mathematical expression. 0406.3.1 Find an unknown quantity in simple equations using whole numbers, fractions, decimals, and mixed numbers. 0406.3.2 Translate between symbols and words to represent quantities in expressions or equations. 0406.1.7 Translate the details of a contextual problem into diagrams and/or numerical expressions, and express answers using appropriate units. Sort objects by two attributes. A Sort objects by two or more attributes. D Devise, carry out, and explain how a group of objects has been sorted. M SPI 0306.3.4 Describe or extend (including finding missing terms) geometric and numeric patterns. 0306.3.6 Analyze patterns in words, tables, and graphs to Generalize and extend or complete patterns involving geometric figures or numbers. D Extend numerical and geometric patterns. A SPI 0406.3.2 Make generalizations about geometric and numeric patterns. SPI 0406.3.3 Represent and analyze patterns using words, Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material Identify the rules by which objects or numbers have been sorted. A Recognize, describe, complete, translate, or create patterns of figures or numbers. D Extend repeating and growing numerical or geometric patterns. A Represent repeating geometric patterns as repeating numerical patterns. A Describe a growing pattern, involving objects, shapes, or numbers. D Describe qualitative change (e.g., a student growing taller). D Describe quantitative change (e.g., a student growing two inches in one year). D Demonstrate knowledge (with words or symbols) of the commutative properties of addition and multiplication. D Use the commutative property of addition and multiplication. D Show that subtraction is not commutative. D Apply the addition and subtraction properties of 0 (adding or subtracting 0 doesn’t change a number). M Apply the zero and identity properties of multiplication New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards page 9 of 18 Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 draw conclusions. 0306.3.7 Create different representations of a pattern given a verbal description. 0306.3.8 Analyze patterns in quantitative change resulting from computation. Represent and analyze patterns and relationships using words, tables, and graphs. D Determine the function rule for data in a function table. A Apply basic function rules. A function tables, and graphs. 0406.3.3 Create, explain and use a rule to generate terms of a pattern or sequence. 0406.3.4 Translate between symbolic, numerical, verbal, or pictorial representations of a whole number pattern or relationship. SPI 0306.3.1 Verify a conclusion using algebraic properties. 0306.3.1 Show that addition and multiplication are commutative operations. 0306.1.9 Use manipulatives to demonstrate that the commutative property holds for addition but not for subtraction. 0306.3.2 Show that subtraction and division are not commutative operations. 0306.3.3 Use commutative, associative, and distributive Use the commutative, associative, zero, and identity properties for addition and multiplication. D SPI 0406.1.1 Verify a conclusion using the commutative, associative and distributive properties. 0406.1.4 Use commutative, associative, and distributive properties of numbers including oral descriptions of mathematical reasoning. Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material (adding 0 or multiplying by 1 doesn’t change a number). I Use arrays to represent the commutative property of multiplication. I New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards page 10 of 18 Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 properties to multiply whole numbers. 0306.3.4 Solve problems using the commutative, associative, and distributive properties. Investigate how a change in one variable relates to a change in a second variable. I Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of grade level mathematical terms. D SPI 0306.1.8 Express answers clearly in verbal, numerical, or graphical (bar and picture) form, using units when appropriate. 0306.1.10 Use correct, clearly written and oral mathematical language to pose questions and communicate ideas. Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards page 11 of 18 Grade 4 – Geometry and Measurement Former Learning Expectations 3.1 Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and threedimensional shapes. 3.2 Specify locations and describe spatial relationships using coordinate geometry. 3.3 Apply transformations and use symmetry to analyze mathematical situations. 3.4 Use visualization, spatial reasoning, and geometric modeling to solve problems. 4.1 Understand measurable attributes of objects and the units, systems, and processes of measurement. 4.2 Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements. Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards New Grade Level Expectations GLE 0406.4.1 Understand and use the properties of lines, segments, angles, polygons, and circles. GLE 0406.4.2 Understand and use measures of length, area, capacity, and weight. GLE 0406.4.3 Solve problems that involve estimating and measuring length, area, capacity and weight. GLE 0406.4.4 Understand the representation of location and movement within the first quadrant of a coordinate system. Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 SPI 0406.4.1 Classify lines and line segments as parallel, perpendicular, or intersecting. 0406.4.15 Explore properties of paths between points. SPI 0406.4.4 Identify acute, obtuse, and right angles in 2dimensional shapes. 0406.4.3 Classify angles and triangles as obtuse, acute, or right. 0406.4.4 Measure and draw angles. 0406.4.2 Understand the definition of degree as it relates to the circle. Identify and draw horizontal and vertical lines. I 0306.4.3 Classify lines and segments as parallel, perpendicular, or intersecting. Identify points, lines, and rays. A Identify and draw points, lines, line segments, rays, and angles. D Create and describe mental images of objects, patterns, and paths. D Describe the relationships between lines and the characteristics of angles (e.g., parallel, perpendicular, intersecting, right, acute, and obtuse). I Recognize geometric figures that are the same size and shape. A Read thermometers with Fahrenheit and Celsius scales SPI 0306.4.2 Determine if two figures are congruent based on size and shape. SPI 0306.4.5 Choose reasonable units of measure, Recognize congruent geometric figures A. Select appropriate standard units to measure length, SPI 0406.1.4 Select appropriate measurement Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material (positive whole number temperatures). A Select and apply the most appropriate standard units of length, area, capacity, weight, time, and temperature. D Solve real-world problems involving measurement. D Determine when an estimate of a measurement is sufficient. D Demonstrate understanding of the concepts of perimeter, area, and capacity. D Use strategies to estimate or determine length, perimeter, area, capacity, weight, time, and temperature. D Measure to the nearest liter, cup, pint, quart, and gallon. D Measure to the nearest ounce, pound, kilogram, and gram. D page 12 of 18 New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards estimate common measurements using benchmarks, and use appropriate tools to make measurements. SPI 0306.1.7 Select appropriate units and tools to solve problems involving measures. SPI 0306.1.8 Express answers clearly in verbal, numerical, or graphical (bar and picture) form, using units when appropriate. 0306.4.5 Understand that all measurements require units. 0306.4.6 Recognize the use of fractions in liquid measures. 0306.4.7 Recognize the relationships among cups, pints, quarts, and gallons. 0306.4.8 Estimate and/or measure the capacity of a container. 0306.4.9 Measure weight to the nearest ounce or gram. 0306.4.10 Use reasonable units of length (i.e. kilometer, meter, centimeter. mile, yard, foot, inch) in estimates and measures. 0306.4.12 Make and record measurements that use mixed units within the same system of measurement (such as feet and inches, meters and Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 perimeter, area, capacity, volume, weight, time, temperature, and angles. A Read temperature using Fahrenheit and Celsius thermometers. A Identify, compare, and analyze attributes of two- and three-dimensional shapes. D Develop and use mathematical language to describe characteristics and properties of geometric figures. D Compare properties of twoand three-dimensional geometric figures. D Demonstrate understanding of the concepts of length, perimeter, area, weight, capacity, volume, time, and angle measure. D Select and use tools to measure weight and volume in customary or metric units. D New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 instrument and compare objects with respect to a given geometric or physical attribute. SPI 0406.4.7 Determine appropriate size of unit of measurement in problem situations involving length, capacity or weight. 0406.1.6 Identify geometric or physical attributes that are appropriate to measure in a given situation. 0406.1.5 Measure using ruler, meter stick, clock, thermometer, or other scaled instruments. 0406.4.13 Compare objects with respect to a given attribute such as length, area, and capacity. Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material Select an appropriate standard unit to measure length. A Use estimation to determine if a length measurement is reasonable. A Measure length to the nearest centimeter and inch. A Explain the relationships among inches, feet, and yards. D Measure to the nearest centimeter, foot, half-inch, and inch. D New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards centimeters). SPI 0306.4.6 Measure length to the nearest centimeter or half inch. 0306.4.11 Know common equivalences for length (1 meter = 100 centimeters, 1 yard = 3 feet, 1 foot = 12 inches). 0306.4.13 Use common abbreviations: km, m, cm, in, ft, yd, mi. page 13 of 18 Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 Demonstrate understanding of the relationships among units of length. D Measure length to the nearest 1/4 inch or nearest centimeter. A Use estimation to determine if a length or volume measurement is reasonable A. Estimate using standard units of measure. D Demonstrate understanding that measurements are approximations. I Identify a location on a grid using whole number coordinates. I Use appropriate mathematical language to find a point on a grid using whole number coordinates. A New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 Locate and specify points in Quadrant 1 of a coordinate system. A Construct and draw two- and three-dimensional geometric figures. D SPI 0406.4.6 Determine situations in which a highly accurate measurement is important. 0406.4.12 Estimate the size of an object with respect to a given measurement attribute (length, perimeter, area, or capacity). SPI 0406.4.2 Graph and interpret points with whole number or letter coordinates on grids or in the first quadrant of the coordinate plane. SPI 0406.4.3 Construct geometric figures with vertices at points on a coordinate grid. 0406.4.14 Explain how the components of a coordinate system are used to determine Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards Identify, build, draw, and compare two- and threedimensional geometric figures (e.g. rectangle, square, triangle, circle, cube, cylinder, sphere, and cone). D Name two-dimensional geometric figures (e.g., rectangle, square, triangle, circle, cube, cylinder, sphere, and cone). A Name three-dimensional geometric figures (e.g., rectangle, square, triangle, circle, cube, cylinder, sphere, and cone). A Identify and draw diagonals of polygons. I SPI 0306.4.1 Recognize polygons and be able to identify examples based on geometric definitions. SPI 0306.1.6 Identify and use vocabulary to describe attributes of two- and threedimensional shapes. 0306.4.1Describe properties of plane figures (such as circles, triangles, squares and rectangles) and solid shapes (such as spheres, cubes and cylinders). 0306.4.2 Classify polygons according to the number of their sides and angles. page 14 of 18 Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 Identify two- or threedimensional shapes given defining attributes. A Investigate and describe the results of subdividing and combining two-dimensional geometric figures. D Solve real-world problems involving addition and subtraction of one- or twodigit measurements. A SPI 0306.4.7 Solve problems requiring the addition and subtraction of lengths. 0306.1.11 Develop strategies Find the perimeter of rectangles. A Apply the formula for finding the area of a rectangle A New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 location. SPI 0406.4.5 Identify attributes of simple and compound figures composed of 2- and 3dimensional shapes. 0406.4.1 Identify the basic parts of circles. 0406.4.5 Determine if a figure is a polygon. 0406.4.21 Recognize twodimensional faces of threedimensional shapes. SPI 0406.4.8 Convert measurements within a single system that are common in daily life (e.g., hours and minutes, inches and feet, centimeters and meters, quarts and gallons, liters and milliliters). 0406.4.7 Measure liquids using both standard units and metric units. 0406.4.6 Recognize the use of decimals in metric measures. SPI 0406.4.9 Solve problems involving area and/or perimeter of rectangular figures. Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards page 15 of 18 Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 Find the perimeter of a rectangle on a grid. A Find the perimeter of polygons. D for solving problems involving addition and subtraction of measurements. SPI 0306.4.4 Calculate the perimeter of shapes made from polygons. Solve real-world problems involving addition and subtraction of measurements. A Explore perimeter and area using a variety of models (e.g., geoboards, graph paper). D Develop strategies for estimating the perimeters and areas (such as counting square units) of geometric figures. D Use geometric models to solve real-world problems. I 0406.4.8 Recognize that a measure of area represents the total number of same-sized units that cover the shape without gaps or overlaps. 0406.4.9 Recognize that area does not change when 2dimensional figures are cut apart and rearranged. 0406.4.10 Connect area measure to multiplication using a rectangular area model. 0406.4.10 Estimate areas of rectangles in square inches and square centimeters. Identify the result of a transformation that has been applied to a simple twodimensional geometric shape (i.e., flips or slides). A Identify the line of symmetry in a two-dimensional design or shape. A Draw lines of symmetry in two-dimensional designs and shape. D Predict and identify the results of sliding, flipping, or turning two-dimensional shapes. D SPI 0306.4.3 Identify the line of symmetry in a twodimensional design or shape. 0306.4.4 Identify, create, and describe figures with line symmetry. Identify lines of symmetry for two-dimensional geometric figures. A Identify the result of a transformation (flip or slide) that has been applied to a simple two-dimensional geometric shape. A Identify and draw lines of symmetry for two-dimensional geometric figures. D Identify, predict, and describe the results of transformations of two-dimensional geometric figures (i.e., slides, flips, and turns). D Describe a motion that will show that two shapes are congruent. I SPI 0406.4.10 Identify images resulting from reflections, translations, or rotations. 0406.4.16 Examine transformations in the coordinate plane. 0406.4.17 Predict the results of a transformation of a geometric shape. 0406.4.18 Determine whether a geometric shape has line and/or rotational symmetry. 0406.4.19 Design and analyze simple tilings and tessellations. 0406.4.20 Draw lines of symmetry in 2-dimensional figures. Solve real-world problems SPI 0306.1.1 Solve problems Tell time to the nearest Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material using a calendar. A Solve real-world problems involving elapsed time to the half-hour. A Read and write time at fiveminute intervals. A Read and write time to the nearest hour, half-hour, and quarter-hour. A New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards using a calendar. SPI 0306.1.2 Solve problems involving elapsed time 0306.1.1 Read and write time to the nearest minute. page 16 of 18 Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 minute. A Solve real-world problems involving elapsed time to the quarter-hour. A 0306.1.10 Use correct, clearly written and oral mathematical language to pose questions and communicate ideas. Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards page 17 of 18 Grade 4 – Data, Probability and Statistics Former Learning Expectations 5.1 Formulate questions that can be addressed with data and collect, organize, and display relevant data to answer questions. 5.2 Select and use appropriate statistical methods to analyze data. 5.3 Develop and evaluate inferences and predictions that are based on data. 5.4 Understand and apply basic concepts of probability. Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material New Grade Level Expectations GLE 0406.5.1 Collect, record, arrange, present, and interpret data using tables and various representations. GLE 0406.5.2 Use probability to describe chance events. New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 Write questions and gather data to answer questions. D 0306.5.1 Collect and organize data using observations, surveys, and experiments. Interpret and construct tables using tally marks. D Construct pictographs and bar graphs. D SPI 0306.5.1 Interpret a frequency table, bar graph, pictograph and line plot. SPI 0306.5.2 Solve problems in which data is represented in tables or graph. SPI 0306.1.8 Express answers clearly in verbal, numerical, or graphical (bar and picture) form, using units when appropriate. 0306.5.3 Compare and interpret different representations of the same data. 0306.5.2 Construct a frequency table, bar graph, pictograph, or line plot of collected data. Collect data using observations, surveys, and experiments. I Understand how datacollection methods could affect the results. I Design investigations to try to answer a question. I Construct tables, pictographs, line graphs, and bar graphs D. Interpret simple charts, tables, pictographs, line graphs, and bar graphs. D Interpret data displayed in bar graphs and pictographs. A Connect data in tables to pictographs, line graphs, or bar graphs. A Evaluate how well various representations show the collected data I. New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 SPI 0406.5.1 Depict data using various representations (e.g., tables, pictographs, line graphs, bar graphs). 0406.5.1 Create and label appropriate scales for graphs. 0406.5.2 Evaluate how well various representations show the collected data. 0406.5.3 Interpret and prepare pie charts using appropriate measurements of angles. 0406.5.4 Develop and use stem-and-leaf plots. Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008 Grade 4 Alignment between former TN DOE Mathematics Standards and new TN DOE Mathematics Standards Former Blueprint Standards 3rd Grade Review material page 18 of 18 New Standards 3rd Grade Building blocks for new standards Former Blueprint Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2008-2009 SPI 0306.5.3 Make predictions based on various representations of data. 0306.5.4 Solve problems using data from frequency tables, bar graphs, pictographs, or line plots. Make predictions from data. D SPI 0406.5.2 Solve problems using estimation and comparison within a single set of data. Explore and determine measures of central tendency (i.e., mean, median, and mode). D Determine the median of a data set. A SPI 0406.5.3 Given a set of data or a graph, describe the distribution of the data using median, range, or mode. 0406.5.5 Use measures of central tendency to compare two sets of related data. SPI 0406.5.4 List all possible outcomes of a given situation or event. Select all possible outcomes of a simple experiment (i.e., spinner, coin toss, number or color cube). A Describe the likelihood or chance of events as certain, possible, or impossible. M Explain whether an event is likely or unlikely. M Determine the most likely, least likely, or equally likely outcomes in simple experiments. A New Standards 4th Grade TCAP 2009-2010 0406.5.6 Determine a simple probability. 0406.5.7 Express a probability pictorially. Prepared through collaboration of Williamson County Mathematics Curriculum Specialists: Jackie Arthur (K-5) and Pat Tyree (6-12) and Franklin Special School District Curriculum Director Sharon Cooksey Spring 2008