Land & Ecosystem PPT Outline Notes
advertisement
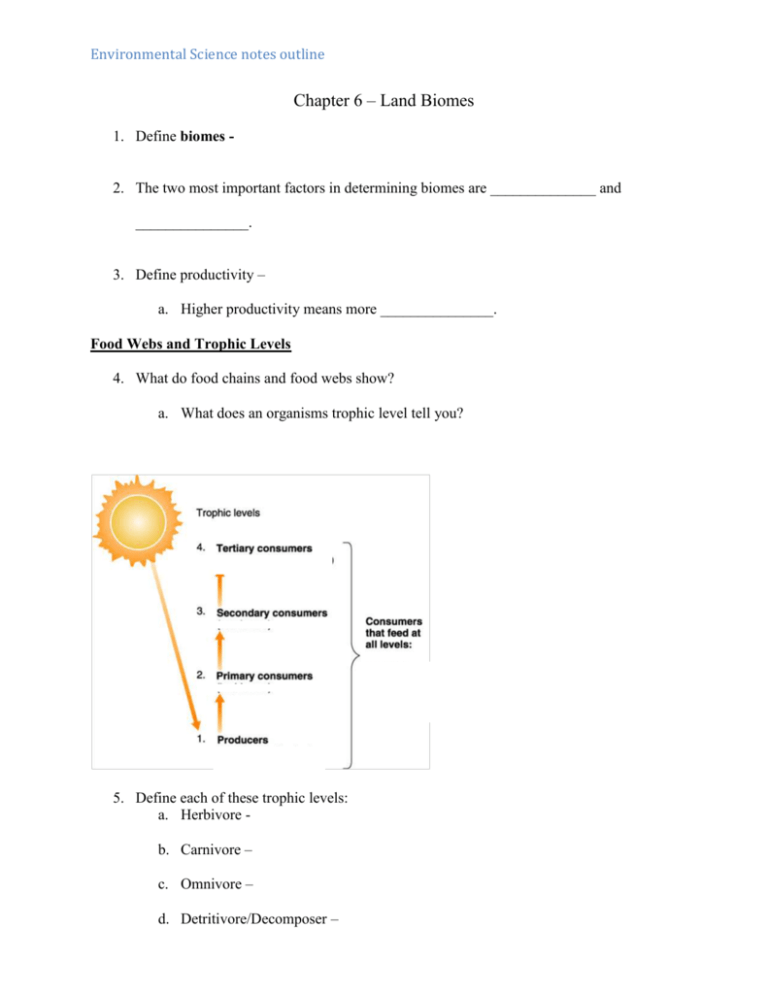
Environmental Science notes outline Chapter 6 – Land Biomes 1. Define biomes - 2. The two most important factors in determining biomes are ______________ and _______________. 3. Define productivity – a. Higher productivity means more _______________. Food Webs and Trophic Levels 4. What do food chains and food webs show? a. What does an organisms trophic level tell you? 5. Define each of these trophic levels: a. Herbivore b. Carnivore – c. Omnivore – d. Detritivore/Decomposer – Environmental Science notes outline 6. Give one example of each of these from the food web shown: a. Herbivore b. Carnivore – c. Omnivore – d. Detritivore/Decomposer – 7. In most ecosystems, which trophic level is there the most of? a. Which is there the least of? Energy in Ecosystems 8. The second law of thermodynamics states that __________________________________. a. Does this apply to ecosystems? b. How much energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next? c. How much energy is lost in this transformation? d. What happens to the lost energy? e. Example: If there are 1000 calories in the producer level, how many would make it to the tertiary consumer level? 9. Define climate a. How is climate different than weather? b. Which biome has the most heat and most precipitation? c. Which biome has the most heat and least precipitation? d. Which biome has the least heat and least amount of precipitation? 10. What does latitude measure? a. How does this relate to average temperature? 11. What does altitude measure? a. How does this relate to average temperature? Environmental Science notes outline Rain Shadow Effect 12. The windward side of the mountain is ____________________________. 13. The leeward side of the mountain is ______________________________. Ocean and Lake Effects 14. Why is the temperature more stable near oceans and lakes? a. How is precipitation affected? Types of Biomes 15. Fill out the climatograph. Celsius to Fahrenheit reference 30°C= 86°F 20°C= 68°F 10°C= 50°F 0°C= 32°F -10°C= 14°F 16. What city is this? 17. What is the latitude? 18. What is the elevation? 19. What type of ecosystem is this? Environmental Science notes outline Deserts 20. How much precipitation do deserts usually get? a. How is the rainfall unusual? 21. What side of mountains are deserts usually on? a. Why? 22. What is a common plant adaptation? 23. What is a common animal adaptation? 24. Compare the three types of deserts: Tropical Deserts Temperate Deserts Polar Deserts 25. Name three major human impacts on deserts: a. b. c. Grasslands 26. Grasslands have ____________ precipitation and _____________ temperatures than deserts. a. How do the temperatures fluctuate? 27. What kinds of plants do grasslands usually have? 28. Why are there so few trees in the grasslands? Environmental Science notes outline Tropical Grasslands 29. Where are they located? 30. How is the wet season and dry season different? 31. Sketch and label the climatograph to the right: Temperate Grasslands 32. Where are temperate grasslands usually found? 33. Describe the three types of grasslands: a. Shortgrass: b. Mixed: c. Tallgrass: 34. What does temperate mean? 35. How do they compare to tropical grasslands? 36. How is the wet season and dry season different? 37. Sketch the climatograph to the right. Environmental Science notes outline Polar Grasslands 38. Polar grasslands are also known as _________________. 39. What kinds of plants grow there? 40. Where are they located? 41. What is permafrost? 42. Sketch the climatograph to the right. Human Impacts on Grasslands 43. What is the single biggest human impact on grasslands? Chaparral 44. Where are chaparrals found? 45. What are the seasons like in a chaparral? 46. What kinds of plants are usually found there? 47. Sketch the climatograph to the right. Environmental Science notes outline Tropical Rainforests 48. How much rain falls in the rainforests? 49. Where are rainforests usually located? 50. Why is the soil so poor? a. Why is this poor soil a problem? 51. How much life is found in the rainforest? 52. Describe the three layers of the rainforest: a. Canopy: b. Understory: c. Forest Floor: 53. Sketch the climatograph to the right. Environmental Science notes outline Temperate Deciduous Forests 54. Where are they found? 55. What adaptations do the trees have for the frozen winters? 56. How much biodiversity is in the deciduous forests? 57. Describe the three layers of the forest: a. Canopy: b. Understory: c. Forest Floor: 58. Sketch the climatograph to the right: a. Where is this? b. What is the latitude? c. What is the elevation? Temperate Rain Forests 59. What kind of climate is found at a temperate rain forest? 60. Where are temperate rain forests usually found? 61. What two conditions have lead to the creation of the Pacific Northwest temperate rain forest in the United States? Environmental Science notes outline Coniferous Forests (Taiga) 62. Where are they located? 63. What is the climate like? 64. What are the two main adaptations of trees in this ecosystem? a. b. 65. What are the three advantages of having needles for leaves? a. b. 66. Sketch the climatograph to the right: a. Where is this? b. What is the latitude? c. What is the elevation? Forest Degradation 67. What is the single biggest reason for forests being degraded in the world? Environmental Science notes outline Mountain Biomes 68. Where are they located? 69. What is the climate like? 70. Describe the two main factors that effect climate: a. Elevation: b. Windward/Leeward Slopes: 71. What effect does the snow on the mountain tops have on the temperature? Mountain Degradation 72. Give three major examples of how mountain biomes are degraded by human activities: Boundary Areas 73. What is an ecotone?









