Collaborative Teaching - Team Reflection Rubric
advertisement

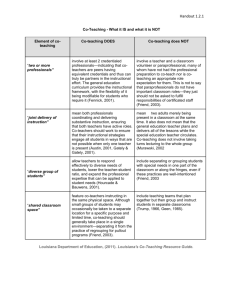
Collaborative Teaching: Team Reflection Rubric Component Planning prior to implementation Curriculum planning On-going planning Knowledge of content for planning Beginning Planning and Preparation Emerging Compromising Team has not discussed or agreed upon any issues before beginning; team was scheduled to begin before discussions could occur Team has not met to plan curriculum (units, lessons, scope/sequence, frameworks); no/little evidence of long-range planning Team does not meet for on-going planning; no evidence of on-going planning One partner exhibits knowledge about the curriculum (standards, frameworks, objectives, sequence) but the other partner is not familiar with the curriculum Team has discussed a few of the issues but has reached agreement on few items Team has discussed and agreed on the majority of issues, including: philosophy, procedures, methods, curriculum, roles/responsibilities, etc Team has met to discuss Team has met to discuss Team has met to outline curriculum but has long-range planning for long-range plan, has minimal long-range curriculum and has negotiated content and plans; has not negotiated negotiated content, but scope and sequence, and content or planned units has not planned units or has planned units and or lessons lessons in advance lessons in advance Team meets sporadically Team meets consistently Team meets weekly to for on-going planning face-to-face to plan and plan, co-creates lesson (and sometimes plans by plans consistently by plans, and discusses phone, email, etc); little phone, email, etc.; some adjustments to plans; evidence of on-going evidence of on-going clear evidence of onplanning planning going planning One partner is more One partner is more Both partners possess a knowledgeable about the knowledgeable about the general knowledge of entire curriculum but the entire curriculum but the the curriculum and one other partner displays other partner displays partner exhibits more insome knowledge of the sufficient knowledge of depth knowledge content the content Draft: Created by: Bev Colombo, February, 2003; revised March, 2004 Adapted by River Region Cooperative, Oct. 2007 Team has discussed all of the considerations and has reached agreement on most issues; team is still negotiating some Collaborating Collaborative Teaching: Team Reflection Rubric Component Willingness to collaborate Parity Communication Shared expertise and definition of roles Characteristics of Collaboration/Collaborators Beginning Emerging Compromising One or both do not exhibit desire to work together (team members were assigned to work together) Team members do not have equal role/status in classroom; one person is functioning as assistant or responsibilities are not shared Willingness to co-teach is minimal or emerging Team members exhibit enthusiasm for coteaching Partners volunteered to work together Team members are Team members have Team members have working to establish equal status and roles are equal, active roles in equal role/status but one nearly equal; team is still classroom, display equal person is more dominant working to establish status, evenly divide or exhibits higher status equal responsibilities responsibilities, and value the contribution of each member Team engages in Team sometimes Team consistently Team members openly, minimal communication communicates outside of communicates outside of honestly communicate; outside of class; does not class; communication class, uses effective use active listening discuss (or rarely often deals with surface communication skills skills; and manage discusses) concerns, issues; conflicts are not generally; some issues conflict with effective issues or feelings discussed or resolved are difficult to discuss negotiation skills Expected roles are not Expected roles have Expected roles are Expected roles have defined and team has not been defined but one or defined and both been defined and both determined how to use both partners are not partners are generally partners are clear; their individual expertise clear or disagree; one satisfied; team is still partners are flexible partner is dissatisfied working to determine about changing roles; with role or opportunity how to use the expertise both partners contribute to share expertise of both partners their expertise Draft: Created by: Bev Colombo, February, 2003; revised March, 2004 Adapted by River Region Cooperative, Oct, 2007 Team members exhibit some willingness to work together Collaborating Collaborative Teaching: Team Reflection Rubric Component Co-teaching arrangements Differentiation Teaching methods Learning strategies Components and Instructional Strategies Beginning Emerging Compromising Team has not discussed various co-teaching arrangements; one person usually takes the lead and the other shadows (monitors, helps students, etc) Team is not applying differentiation process or strategies; generally all students are involved in whole group instruction with little differentiation Team primarily uses one teaching method (e.g. lecture and discussion); team has not discussed a variety of methods to meet students’ needs Learning strategies are not taught and students are not cued to use strategies to learn or perform Team knows about various co-teaching arrangements but one person is still mostly responsible for teaching; other arrangements are not in evidence One partner is aware of process and strategies for differentiation; but use of differentiation is limited to adaptations for individual students Team is aware of many teaching methods but primarily uses only a few methods; few/some students are actively engaged A few learning strategies have been taught but students do not use strategies; strategies are not research-based Draft: Created by: Bev Colombo, February, 2003; revised March, 2004 Adapted by River Region Cooperative, Oct, 2007 Collaborating Team members mainly use one co-teaching arrangement and share roles; team is discussing how to use other arrangements Team members flexibly use a variety of coteaching arrangements: team teaching, complementary and supplemental Team knows process and strategies for differentiation; uses some strategies Team has implemented plan for differentiation; demonstrates use of differentiation in units and lessons consistently Team is experimenting with a variety of teaching methods but still searching for ways to engage students and increase achievement Some research-based learning strategies have been taught and students are beginning to use and apply strategies; use is cued by both partners Team is comfortable using a variety of teaching methods for active engagement, and increasing achievement A variety of researchbased learning strategies have been taught and students demonstrate knowledge/application of strategies Collaborative Teaching: Team Reflection Rubric Component Classroom management Classroom Organization and Integration Beginning Emerging Compromising Team has not discussed or agreed on rules and routines before beginning; team was scheduled to begin before discussions could occur Tasks have not been divided; one partner does all of the routine tasks Team has discussed rules and routines and has reached agreement on some; but one person enforces rules or defers to the other for final authority Team has discussed tasks; one partner does most of the routine tasks Student perception of collaboration Students perceive one teacher as “the teacher” and the other teacher as “the assistant” or the “other teacher” Integration of students in the classroom Little to no planning for integration; students are minimally integrated; team views students as “mine” and “yours” Students perceive that one teacher has more authority or status most of the time while the other teacher has a limited role or status Some initial planning the placement of students; students are becoming integrated; teachers sometimes work with all students Routine classroom tasks Draft: Created by: Bev Colombo, February, 2003; revised March, 2004 Adapted by River Region Cooperative, Oct, 2007 Collaborating Team has reached agreement on rules and routines; team is beginning to share responsibility for monitoring and intervening Team has divided tasks equally; partners are beginning to feel comfortable with different tasks Students perceive each teacher as having more authority or status at designated times Team has reached agreement on rules and routines and both partners share the responsibility for monitoring and intervening Team has divided tasks and is flexible about trading tasks Placement of students was well-planned but scheduling problems interfered; students are more integrated; teachers work with all Placement of students was carefully planned; students and teachers are fully integrated as a learning community Heterogeneous mix Student perceive both teachers as having equal authority and status Collaborative Teaching: Team Reflection Rubric Component Evaluation of student outcomes Evaluation of Program and Outcomes Beginning Emerging Compromising Collaborating Student achievement data are not used to make decisions; data are not reviewed Student achievement data are reviewed by one or both partners but are not used to evaluate or change instruction Student achievement data are reviewed at intervals (e.g. quarterly) to make decisions about instruction; a few sources of data are used Evaluation of coteaching program Team does not evaluate the program and there no other evaluation of the success of their efforts Team self-evaluates using more data sources and is becoming more objective in evaluation Evaluation of individual students Special educator is solely responsible for monitoring progress of students with disabilities Each teacher evaluates program individually; evaluation is based solely on subjective data, e.g. their feelings about their success Special educator is sharing information about progress of students with disabilities but mostly responsible Student achievement data are used to make decisions about instruction on an ongoing basis; a variety of data are used (test scores, products, curriculum-based assessment, etc) Team self-evaluates using a variety of data and is willing to reflect and make changes Team is beginning to monitor progress of all students together and sharing responsibility for students with special needs Partners share equal responsibility for monitoring each student and tracking group progress toward curriculum benchmarks Draft: Created by: Bev Colombo, February, 2003; revised March, 2004 Adapted by River Region Cooperative, Oct., 2007 Collaborative Teaching: Team Reflection Rubric Component Administrative support Administrative and Contextual Supports Beginning Emerging Compromising Administrators are aware that staff members are co-teaching, but have not participated in any staff development and are not supportive Administrators have some basic knowledge about co-teaching but do not fully understand what is necessary to support the model Administrators have participated in staff development and verbally support the coteaching model Staff development Neither partner has Only one partner has participated in any staff participated in staff development activities to development learn about how to teach in a cooperative class Team has attended an overview of co-teaching but has not participated in any other staff development activities Classroom composition Placement of students in the class was haphazard; class is not balanced; has too many students with different types of special needs for success Classroom composition was planned; the mix of students is close to a heterogeneous mix Classroom composition was considered; some attempt to limit the number of students with special needs but the mix of students creates some difficulties in the classroom Draft: Created by: Bev Colombo, February, 2003; revised March, 2004 Adapted by River Region Cooperative, Oct., 2007 Collaborating Administrators have participated in staff development and provide verbal support as well as hands-on support with scheduling and other issues Team has attended staff development sessions (or participated in other staff development activities, e.g. study group) to learn about coteaching, instructional strategies, etc. Classroom composition was planned and is a heterogeneous mix of students with a natural proportion of students with special needs (or alternative credit course designed for at-risk students)