Classification
advertisement

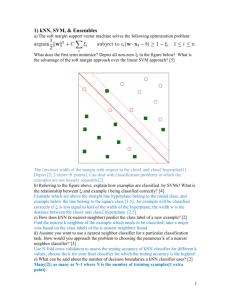
(don't forget to insert it into the 'table of contents') Classification Classification is an attempt to label a set of unlabeled conditions (assign them to classes) according to a set of conditions with known labels. Thus, the classification process consists of two stages: 1) Training the classifier using the pre-labeled set of conditions, and a selected subset of probes (regarded as the selected features). 2) Using the trained classifier to label other conditions. Currently, Expander only supports two class labels for each classification analysis. Expander utilizes the following algorithms to generate and train classifiers and to classify conditions accordingly: KNN (K-Nearest Neighbors) To train a classifier using this method, select Classification >> Train Classifier >> KNN. The KNN parameter (number of nearest neighbors used) can be set as input, or estimated by cross-validation (depending on the selection in the input dialog). For more information regarding the algorithm, refer to the References section. SVM (Support Vector Machine) Select Classification >> Train Classifier >> SVM to train a classifier using this method. For more details regarding the SVM algorithm and the implementation utilized by Expander see the References section. The train set of conditions can be imported from an external file (see the Files Format section for details) or defined manually, depending on the selection in the ‘Training Set’ section of the classifier train dialog box. The selected features (probes subset) can be defined in one of the following manners depending on the selection in the ‘Feature Set’ section of the classifier train dialog box: a) Imported from a file (see the Files Format section for details). b) Estimated using t-test, i.e. selecting the features which best separate the two classes according to the train set. c) Estimated using a correlation filter, i.e. searching for n probes which demonstrate the best correlation to an artificial vector, representing the train set classification. d) All features After training a classifier a classifier view is displayed. It contains, on its left pane, information regarding the used classification method and parameters, as well as a specification of the train set of conditions and their labels. In order to classify a set of conditions using one of the pre-trained classifiers, select Classification >> Classify. A dialog box will appear, allowing selection of one of the open classifiers from a combo-box. The set of conditions to be classified can be selected from a list containing all conditions in the data. After pressing ‘OK’ in the dialog box, classification is performed and the results appear as a table in the right pane of the relevant classifier view. The table contains, for each classified condition, the assigned label, and a level of confidence. References KNN Classification algorithm: D. Aha, D. Kibler. Instance-based learning algorithms. Machine Learning. 6:37-66, 1991. SVM Classification algorithm: S.S. Keerthi, S.K. Shevade, C. Bhattacharyya, K.R.K. Murthy. Improvements to Platt's SMO Algorithm for SVM Classifier Design. Neural Computation. 13(3):637649, 2001. J. Platt: Machines using Sequential Minimal Optimization. In B. Schoelkopf and C. Burges and A. Smola, editors, Advances in Kernel Methods - Support Vector Learning, 1998.