Normal Labor and Delivery
advertisement

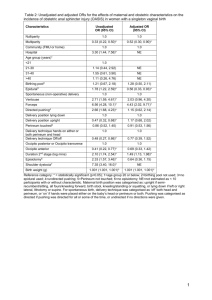
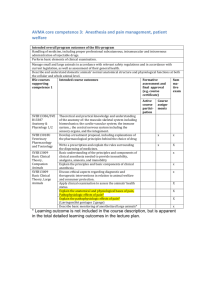
Normal Labor and Delivery Nursing Care STAGES Stage I: LATENT PHASE 0-3 cm SUPPORTIVE DATA MOTHER’S RESPONSE Contractions: mild. Duration: 30-45 sec. Frequency: 5-20 min. Scant discharge, pink show. Surge of energy and excitement. Talkative; outgoing. Anxiety low. Learning. NURSING INTERVENTIONS Orient to the hospital Monitor VS and FHT’s Assess goals Assess history and physical Labor Assessment (lie, presentation, position, station, condition of BOW) Admission Procedures – IV, NPO, Enema, EFM Assess support and if had childbirth classes Non-pharmacological measures Relaxation techniques Breathing techniques – shallow breathing Diversional techniques Assess voiding ACTIVE PHASE 4-7 cm Contractions: moderate. Duration: 45-60 sec. Frequency: 2-5 min. More serious. Dependent. Restless or edgy. Focuses on self. Anticipate needs: 1. sponge face 2. keep bed clean, dry 3. mouth care 4. assess voiding Use non-pharm. measures. Stay at bedside praise! Point out progress. Modified-paced breathing. Offer analgesia or anesthesia. TRANSITION PHASE 8-10 cm Contractions: strong. Irregular with multiple peaks. Duration: 60-90 secs. Frequency: 2 min. Desires companionship. Withdrawn. Drowsy. Amnesia between contractions. Nausea, Provide support- may need to breathe with the patient – get in her face, maintain eye contact. Back rub Assist with pant-blow breathing trembling. Irritable, aggressive. Urge to push. Leg shakes. Nausea and vomiting. Watch for hypervention – have breathe in mask and slow down the breathing Do NOT allow to push by having patient blow-blow-blow with urge. Do not be offended by irritability STAGE II Contractions: strong Duration: 50-90 sec. Frequency: 1-2 min. Sudden Appearance of sweat on upper lip. An episode of vomiting, Bulging, perineum. Increased bloody show. Pressure on rectum. Mechanisms of labor. Relief with pushing. Exhausted. Direct pushing efforts and teach how to push correctly, “Quality pushing”. Keep perineum clean and dry. Environment quiet. Help to delivery position. Repeat Doctor’s instructions. STAGE III Placenta delivers. S&S of placental separation: 1. Globular rise in abdomen. 2. Sudden gush of blood. 3. Lengthening of umbilical cord. Relief, euphoria. Cries with joy. Talkative. Focused on infant and husband. Congratulate. Coach in relaxation for delivery of placenta. Initiate contact with infant. Admission to the Hospital: 1. Initial Assessment a. Vital signs and FHT’s (make sure baby is doing O.K.) b. Is she in labor? c. How far progressed? d. Have membranes ruptured? e. Psychological response *verbal interaction-talkative, speaks freely, support person with her. *Body posture and set - relaxed or tense. *Cultural background influences the response. 2. History and Physical a. Data related to this pregnancy b. Labor examination (presentation, position, lie, station, etc.) 3. Procedures a. Vital signs and FHTs, history and physical b. Enema - Never give enema if: bleeding, premature labor, or too advanced in labor. Give an enema to: stimulate labor, remove material from bowel, impede descent, prevent contamination c. Perineal prep - “mini-prep” d. IV - provides Alifeline@ if complications occur e. NPO - ice chips, candy on a stick usually no food because gastric emptying slows during labor f. EFM - apply electronic fetal monitor and run a strip Stage Two of Labor Signs and Symptoms 1. 2. 3. Increase in body show Pressure on rectum B involuntary bearing down Bulging of perineum Stage two is the pushing stage and the key is Quality Pushing. Teach mom how to push! Optimum position for pushing is in a vertical position. Pelvic inlet points forward and outlet points downward. Stage 2 – Mechanisms of Labor The baby moves through the birth canal in the following manner: 1. Descent 2. Flexion 3. Internal Rotation 4. Extension 5. External Rotation 6. Expulsion Episiotomy vs. Laceration Episiotomy- Laceration- Stage 3 of Labor Signs and Symptoms of Placental Separation: 1. A globular rise in the abdomen the placenta changes from a discoid to a globular shape 2. Sudden gush of blood 3.Lengthening of the cord Stage 3 – Nursing Care Congratulate on delivery of baby Coach in relaxation for delivery of the placenta Initiate contact with the infant May allow to breast feed if desires __________________________________________________________ Test Yourself! The cardinal movement that facilitates the emergence of the fetal head ____________. a. Flexion b. Extention c. External rotation Cardinal movement that allows the smallest diameter of the head to pass through the pelvis is__________________. a. Flexion b. Internal rotation c. Extension Cardinal movement that occurs as the fetal shoulders engage and descend through the pelvis is termed ______. A. Internal rotation B. External rotation Pain Management During Labor I. Causes of Pain Stage One: Stretching of the cervix during dilatation and effacement Uterine anoxia due to compressed muscle cells during (decreased blood flow and therefore local oxygen deficit) Stretching of the uterine ligaments **This type of pain is visceral. Usually the woman feels contraction the pain only during a contraction. Stage Two: Uterine anoxia Distention of the vagina and perineum Compression of the nerve ganglia in the cervix and lower uterine segment Pressure on the urethra, bladder, rectum during fetal descent Traction on and stretching of the perineum **This pain is perceived as an intense burning sensation that is felt as the tissue stretches. Pain may also be referred, in which the discomfort is felt in the back, flanks, and thighs. Notes: II. Factors Affecting the Mothers Response to Pain Knowledge and confidence gained through childbirth classes Cultural influences on expression of pain Maternal fatigue and anxiety Previous experiences with pain III. Methods of Pain Relief A. Nonpharmacologic 1. Childbirth methods a. Breathing techniques b. Relaxation techniques; progressive relaxation c. Touch d. Focusing attention on one object 2. Effleurage B gentle, rhythmic stroking of abdomen or thigh during contraction 3. Sensory stimulation a. Listening to music; subdued lighting b. Applying heat and cold c. Warm showers: water hydrotherapy d. Lower back massage e. Counterpressure f. Position changes g. Imagery B. Pharmacologic Methods 1. Analgesia Demerol, Stadol 2. Barbiturates Seconal 3. Tranquilizers Vistaril 4. Regional Anesthesia b. Epidural c. Spinal d. Pudendal 5. Local Anesthesia 6. General Anesthesia B used mainly with cesarean births Notes: IV. Goals of Pain Management Provide maximal relief of pain with maximal safety for mother and fetus V. Nursing Care Collaborate with mother to determine the most effective method of pain relief during each stage and phase of labor. Anesthesia Given During Labor and Delivery General Anesthesia Gas inhaled; given during delivery; the entire body is affected; no consciousness. Disadvantages B nausea, slow to fully awaken, sluggishness or respiratory depression in infant. Regional Anesthesia Injection of anesthetic agent so that they come into no direct contact with nervous tissue. Small fibers that conduct sensation of pain, temperature, pressure, and touch can be blocked without affecting the large fibers to maintain muscle tone, position, and motor function. Paracervical Block Injection of small quantities of caine drug through vagina into outer rim of cervix Used in active labor (4-7 cm) *For labor not delivery. Helps dilatation and effacement Complete relief of lower uterine pain, cervix, upper vagina. Does not affect lower vagi and perineum Can‘t be given after 8 cm. Drug easily and rapidly absorbed into maternal blood and thus into baby causing fetal bradycardia. Can push in delivery. Epidural Block Caine drug injected through a catheter placed in epidural space around spinal cord. In lumbar 3-5 Used for L&D. Given at 5-6 cm. In primi; at 4-5 cm. multi. Used for C-birth Naval to toes. Loss of bearing down and bladder sensation. May take up to 30 minutes to take effect. Hard to get in proper position while in labor. May slow or stop labor. May need to augment with pitocin. Increased use of forceps. Maternal drop in blood pressure, chills, shakes, nausea, vomiting. With hypotension in mom will see fetal decelerations and bradycardia. Requires skilled person to do this procedure. Caudal Block Caine drug injected through catheter placed in lower epidural/caudal space Used for L&D. Must lie in lateral Sims position for administration. Area affected is cervix, low vagina, perinea area. Nursing implications are much the same as an epidural. Spinal/Saddle Block Caine drug injected through dura to sub-arachnoid into the spinal fluid in the spinal canal. Used for delivery. Given late in second stage, when fetal head is on the perineum. Used for C-birth. Naval to toes or below; breasts to toes. May cause hypotension. Need for woman to lie flat for 6-12 hours after the block, and possible headache afterwards. Nurse needs to assess maternal vital signs and FHR. Consent must be signed prior to procedure. Must help in positioning woman. Forceps delivery because no urge to push. Pudendal Block With use of trumpet needle guide insert through vagina both sides to pudendal nerves. (Runs lateral to tip of ischial spines.) Used for delivery and third stage, and repair of episiotomy. No help with contractions. Lower 2/3 of vagina and perineum May be given by physician or anesthetist. Simple and safest and most useful. Does not depress neonate. Local Anesthesia Injection of anesthetic agent into the subcutaneous tissue of perineum in a fan-like pattern. Used for repair of episiotomy. May cause swelling of perineum. Analgesics Given During Labor and Delivery Sedatives Seconal Nembutal Reduce amount of analgesia and promote relaxation and decreases apprehension. Given in latent phase No effect on pain. May slow labor. May depress baby. Tranquilizers Phenergan Vistaril Reduces anxiety, N&V, potentiate analgesics Slow labor, drop in maternal B/P Narcotic Analgesics Stadol *Given in active stage. If effective will provide some pain relief. The woman should be able to maintain relaxation techniques, and see no change in contractions. Complications: Slow labor, drop in maternal B/P. If given late in labor will depress baby and have to give Narcan.