IBC-34
advertisement

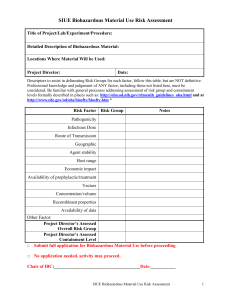
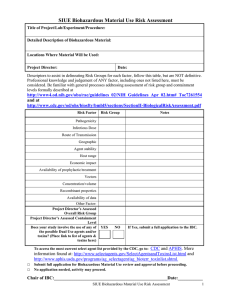
University of Nebraska Medical Center Biosafety Policies and Procedures TITLE: Biosafety Risk Factor Assessment Process to Determine Appropriate Containment [UNMC-IBC34] OVERVIEW: Each planned experiment where biohazard agents are used must undergo an initial risk assessment to decide on the appropriate containment for an experiment. This policy gives guidance on the steps necessary to conduct a biosafety risk assessment APPLIES TO: All research undergoing review by the Institutional Biosafety Committee DEFINITION(S): Not applicable PROCEDURES: Refer to the IBC website at <<www.unmc.edu/ibc/>> and link to the page entitled, “Exempt Experiments” for examples of experiments that are exempt from the NIH Guidelines and thus do not require registration with the IBC. For experiments that are not exempt, Addendum 1 provides a template to conduct a Biosafety Risk Assessment as part of the process in preparing an IBC protocol. This assessment includes the following risk factor categories as they pertain to the biohazardous agent under review: Pathogenicity/virulence Infectious dose Route of spread Communicability Environmental stability Host range Economic aspects Availability of prophylactic and therapeutic treatments Vectors Concentration/volume Recombinant properties For the IBC Application, the Principal Investigator is required to complete a biosafety risk assessment to complete Section II, Part 3 (Biosafety Level of Containment) of the IBC submission form, Protocol for Research Involving Biohazardous Material. The overall Risk Group Classification will be used by the IBC to determine the appropriate containment for the proposed experiment. The IBC will ultimately be responsible for setting the containment level for the requested experiment. IBC34_011907 1 University of Nebraska Medical Center Biosafety Policies and Procedures RECORD KEEPING: A copy of the Biosafety Risk Assessment Summary will be included with the protocol paperwork in the IBC office. OTHER INFORMATION: The NIH Guidelines state that, “the IBC must approve the risk assessment and the biosafety containment level of….experiments” [Section II-A-3, Comprehensive Risk Assessment] and “the IBC is responsible for….reviewing research….(which) should include….an independent assessment of the containment levels required……for the proposed research” [Section IV-B-2-b-(1)]. REFERENCES: NIH Guidelines, Section II, Safety Considerations STATUS: Drafted: Approved: IBC34_011907 November 20, 2006 January 12, 2007 2 University of Nebraska Medical Center Biosafety Policies and Procedures UNMC IBC Biosafety Risk Assessment Summary IBC# _______________________ (to be determined by the IBC Office) Title of Project ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Principal Investigator ______________________________ Date __________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Risk Factor Risk Group Pathogenicity/virulence _________ Infectious Dose _________ Route of Spread _________ Communicability _________ Environmental stability _________ Host range _________ Economic impact _________ Availability of prophylactic/treatment _________ Vectors _________ Concentration/volume _________ Recombinant properties _________ Overall Risk Group _________ Recommended Containment Level _________ Notes:_______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ IBC34_011907 3 University of Nebraska Medical Center Biosafety Policies and Procedures Risk Factor Assessment Outline Pathogenicity/virulence RG1 Unlikely to cause disease, low individual and community risk. RG2 Mild or moderate disease with moderate individual risk and low community risk; any pathogen that can cause disease but under normal circumstances, is unlikely to be a serious hazard to a healthy worker, the community, livestock, or the environment. RG3 Serious livestock, poultry or wildlife disease with high individual risk and low community risk; any pathogen that usually causes serious disease or can result in serious economic consequences or does not ordinarily spread by causal contact from one individual to another. RG4 Severe livestock, poultry or wildlife disease with high individual risk and high community risk; any pathogen that usually produces very serious and often fatal disease, often untreatable and may be readily transmitted from one individual to another or from animal to human or vice-versa, directly or indirectly, or by casual contact. Infectious dose RG1 RG2 RG3 RG4 Not applicable High Medium Low (rare cause of human disease) (>1,000 organisms) (10-1,000 organisms) (1-10 organisms) Route of spread RG1 RG2 RG3 RG4 Not applicable (rare cause of human disease) Primary exposure hazards are through ingestion, inoculation, and mucous membrane route May be transmitted through airborne route; direct contact or via vectors Readily by aerosol transmission Communicability RG1 RG2 RG3 RG4 Not applicable (rare cause of human disease) Geographical risk of spread if released from the laboratory is limited. Geographical risk of spread if released from the laboratory is moderate Geographical risk of spread if released from the laboratory is high. Environmental stability RG1 RG2 RG3 RG4 Not applicable Short term survival (days), can survive under ideal conditions Moderately resistant (days to months) Highly resistant (months to years), e.g. spores. Host range RG1 RG2 RG3 RG4 Not applicable Infects a limited number of species Infects multiple species Infects many species Economic aspects RG1 RG2 RG3 RG4 Not applicable Limited economic impact Severe economic impact Extreme economic impact Availability of prophylactic and therapeutic treatments RG1 RG2 RG3 RG4 Not applicable Effective treatment and preventative measures are available Prophylactic and/or treatments may or may not be readily available Prophylactic and/or treatments are not available Vectors RG1 RG2 IBC34_011907 Not applicable Do not depend on vectors or intermediate hosts for transmission 4 University of Nebraska Medical Center Biosafety Policies and Procedures RG-3 RG4 May depend on vectors or intermediate host for transmission May depend on vectors or intermediate host for transmission. Concentration/volume RG1 RG2 RG3 RG4 Not applicable Low quantity of high titer High quantity (10 liters or more) of high titer as described by the BMBL Not applicable Recombinant properties RG1 Recombinant is a RG1 organism and modifications have not changed the risk; low probability of RG2 replication-incompetent virus becoming competent RG2 Recombinant is a RG2 organism and modifications have not changed the risk, DNA from RG2 or RG3 organism is transferred into RG1 organism but not the whole genome, DNA from RG4 organism is transferred into RG1 organism, or the recombinant is a RG3 or RG4 organism and the modification has resulted in proven attenuation; moderate probability of RG2 replication-incompetent virus becoming competent RG3 Recombinant is a RG3 organism and modifications have not change the risk, the recombinant is based on a RG2 organism; however, the modifications have increased to RG3 organism. RG4 Recombinant is a RG4 organism and modifications have not changed the risk, DNA from RG4 organism is transferred into RG1organism in absence of demonstration of lack of virulence or pathogenicity. IBC34_011907 5