Rocks and Minerals Study Guide Minerals Name the five
advertisement
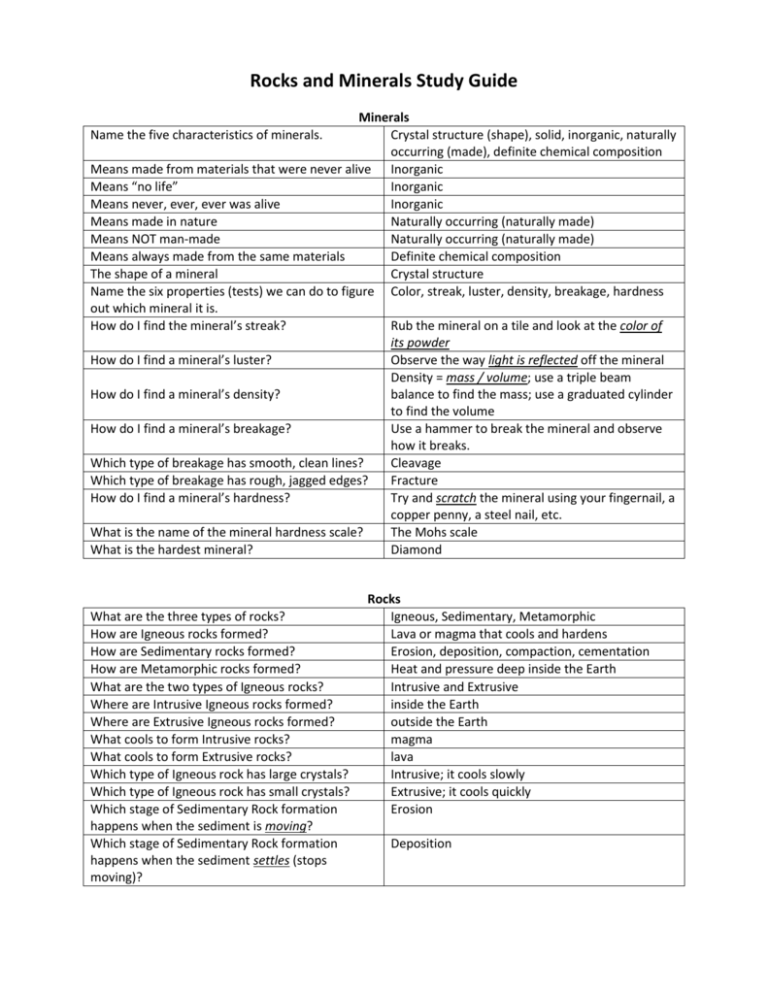
Rocks and Minerals Study Guide Minerals Crystal structure (shape), solid, inorganic, naturally occurring (made), definite chemical composition Means made from materials that were never alive Inorganic Means “no life” Inorganic Means never, ever, ever was alive Inorganic Means made in nature Naturally occurring (naturally made) Means NOT man-made Naturally occurring (naturally made) Means always made from the same materials Definite chemical composition The shape of a mineral Crystal structure Name the six properties (tests) we can do to figure Color, streak, luster, density, breakage, hardness out which mineral it is. How do I find the mineral’s streak? Rub the mineral on a tile and look at the color of its powder How do I find a mineral’s luster? Observe the way light is reflected off the mineral Density = mass / volume; use a triple beam How do I find a mineral’s density? balance to find the mass; use a graduated cylinder to find the volume How do I find a mineral’s breakage? Use a hammer to break the mineral and observe how it breaks. Which type of breakage has smooth, clean lines? Cleavage Which type of breakage has rough, jagged edges? Fracture How do I find a mineral’s hardness? Try and scratch the mineral using your fingernail, a copper penny, a steel nail, etc. What is the name of the mineral hardness scale? The Mohs scale What is the hardest mineral? Diamond Name the five characteristics of minerals. What are the three types of rocks? How are Igneous rocks formed? How are Sedimentary rocks formed? How are Metamorphic rocks formed? What are the two types of Igneous rocks? Where are Intrusive Igneous rocks formed? Where are Extrusive Igneous rocks formed? What cools to form Intrusive rocks? What cools to form Extrusive rocks? Which type of Igneous rock has large crystals? Which type of Igneous rock has small crystals? Which stage of Sedimentary Rock formation happens when the sediment is moving? Which stage of Sedimentary Rock formation happens when the sediment settles (stops moving)? Rocks Igneous, Sedimentary, Metamorphic Lava or magma that cools and hardens Erosion, deposition, compaction, cementation Heat and pressure deep inside the Earth Intrusive and Extrusive inside the Earth outside the Earth magma lava Intrusive; it cools slowly Extrusive; it cools quickly Erosion Deposition Which stage of Sedimentary Rock formation happens when sediment is pressed together to form layers? Which stage of Sedimentary Rock formation happens when sediment becomes glued together? Where are Metamorphic rocks formed? What does the word “morph” mean? What is a Metamorphic rock which has bands or layers? Which type of rock is formed from layers of sediment? Which type of rock would you probably find near water? Which type of rock is formed from weathered materials? Which type of rock would you probably find near a volcano? Which type of rock would you find very deep inside the Earth? Which type of rock is formed from molten material? Compaction Cementation Deep inside the Earth To change form Foliated Sedimentary Sedimentary Sedimentary Igneous Metamorphic Igneous Rock Cycle All rocks can be changed into any of the rock types because of the Rock Cycle! How would an Igneous Rock change into a It would be pushed down deep into the Earth. Metamorphic rock? Then the pressure of the layers on top of it and the heat from the mantle would make it change How would an Igneous Rock change into a It would be broken down by weathering and then Sedimentary Rock? go through erosion, deposition, compaction, and cementation How would an Igneous Rock change into another It would be melted down completely by lava or Igneous Rock? magma and then cool and harden again How would a Sedimentary Rock change into an It would be melted down completely by lava or Igneous Rock? magma and then cooled and hardened How would a Sedimentary Rock change into It would be broken down by weathering and then another Sedimentary Rock? go through erosion, deposition, compaction, and cementation again How would a Sedimentary Rock change into a It would be pushed down deep into the Earth. Metamorphic Rock? Then the pressure of the layers on top of it and the heat from the mantle would make it change How would a Metamorphic Rock change into an It would be melted down completed by lava or Igneous Rock? magma and then cooled and hardened How would a Metamorphic Rock change into a It would be broken down by weathering and then Sedimentary Rock? go through erosion, deposition, compaction, and cementation How would a Metamorphic Rock change into Deep in the Earth, the pressure of the layers on top another Metamorphic Rock? of the rock and the heat from the mantle would make it change again







