Five Themes of Geography Notes
advertisement

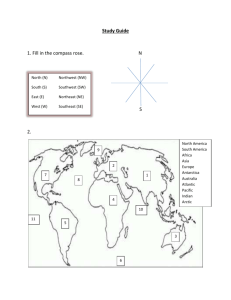
Five Themes Outline I. Location: Knowing where you are. Absolute Location: an exact position on a globe, found by using the grid system of lines of latitude and longitude. o Example: New Zealand is located at 45S, 175E Relative Location: The location of a place in relation to surrounding cities, countries, physical features, landmarks, and streets. o Example: Walnut Springs Middle School is north of E. Walnut street and south of College street. II.Place: What a place is like. What features make this location similar to or different from another place? What does a place look like physically, and what specific objects/structures can be found there? These specific characteristics can be physical characteristics, like land shape and size, plant and animal life, or climate. These characteristics can also be man-made objects, like clothing, buildings, music, or language. o Example: Old Faithful Geyser in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming III. H/EI: People adapt and modify their surroundings to make them more comfortable and easier to live in. Adapting: Wearing a coat in winter to stay warm Modifying: Building a bridge over a river Depending: Fish from the ocean for a food source IV. Movement: How people in one place make contact with a person in another place; or the exchange of goods and ideas. Example: A newspaper is the exchange (movement) of ideas Example: Selling an item on ebay is the exchange (movement) of goods People migrating from one region to another regions is the movement of people V. Region: Areas that share common characteristics. These characteristics can be physical features, human traits, political boundaries, or religion. Physical Region: area of land with a common physical feature Political Region: area of land with a political boundary o Example: The Sahara desert in Africa is a region of the world Five Themes Outline I. ___________________: Knowing where you are. ___________________: an exact position on a globe, found by using the grid system of lines of latitude and longitude. o Example: New Zealand is located at __________S, __________E ___________________: The location of a place in relation to surrounding cities, countries, physical features, landmarks, and streets. o Example: Walnut Springs Middle School is north of E. Walnut street and south of College street. II. ___________________: What a place is like. What features make this location __________ to or __________ from another place? What does a place look like physically, and what specific objects/structures can be found there? These specific characteristics can be __________ characteristics, like __________ shape and size, plant and animal life, or climate. These characteristics can also be __________objects, like clothing, buildings, music, or language. o Example: Old Faithful Geyser in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming III. ___________________: People __________ and __________ their surroundings to make them more comfortable and easier to live in. __________: Wearing a coat in winter to stay warm __________: Building a bridge over a river __________: Fish from the ocean for a food source IV. ___________________: How people in one place make contact with a person in another place; or the exchange of goods and ideas. Example: A newspaper is the exchange (movement) of ideas Example: Selling an item on ebay is the exchange (movement) of goods People migrating from one region to another regions is the movement of people V. ___________________: Areas that share common characteristics. These characteristics can be __________ features, __________ traits, __________ boundaries, or __________. __________ Region: area of land with a common physical feature __________ Region: area of land with a political boundary o Example: The Sahara desert in Africa is a region of the world