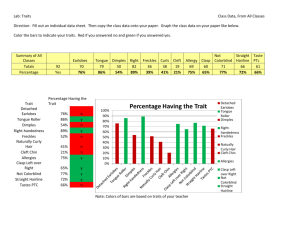
Human Characteristics Practicing forming genotypes and
advertisement

Human Characteristics Practicing forming genotypes and determining the phenotypes As you know, chromosomes work in pairs. The members of each chromosome pair are called homologous chromsomes, and the two chromosomes of each pair are approximately the same length, the same shape and carry alleles for the same genes. Each chromosome of a pair comes from a different parent: one from the mother through the egg and the other from the father through the sperm. At fertilization those like chromosomes pair up to form the homologous pairs in YOU. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, or a total of 46 chromosomes, per cell. Chromosomes 1-22 are called autosomes and the 23rd are the sex chromosomes. Only 22 of these pairs are truly homologous since, for males, the 23 rd pair is XY. The diagram below shows a generalization view of one pair of homologous chromosomes from an individual human. Assume that chromosome on the left is from the father and the one on the right is from the father (ladies first!). Example: From mom --------------- From dad F Freckled T can taste H Widow’s peak D no disease Rh+ M dimples e attached lobe The genotypes and corresponding phenotypes of the person above are: Genotypes Ff Tt Hh DD Rh+ RhMm ee Phenotypes Freckled taste ability Widow’s peak has the disease makes the protein dimples attached earlobes --------------- Characteristics f unfreckled Freckled skin t cannot taste h straight hairline D has disease chemical taste ability has a widow’s peak presence of a disease Rhm no dimples e attached lobe Rh blood factor dimples attached earlobe Analyze the information: 1. Which parent gave the allele for straight hairline? DAD 2. Did that parent have a straight hairline? POSSIBLY if he was Hh 3. Does this person have a straight hairline? NO 4. Does this person have the recessive trait attached earlobes? YES 5. If both parents have unattached earlobes, why does this person have attached? BOTH must be Ee and each gave the ‘e’ to the child Sample I: Jill From Mom From Dad Genotypes 1_____ ______________________________________ 2 _____ ______________________________________ 3 _____ ______________________________________ 4 _____ ______________________________________ Rh+ 5_____ ______________________________________ m E 6_____ ______________________________________ 7_____ ______________________________________ F t H d f t h d Rh+ m e I. Sample II: Tammy From Mom From Dad Genotypes F T h d f T h d + Rh m E Phenotypes Rh- m e I. Phenotypes 1_____ ______________________________________ 2 _____ ______________________________________ 3 _____ ______________________________________ 4 _____ ______________________________________ 5_____ ______________________________________ 6_____ ______________________________________ 7_____ ______________________________________ Sample III: Nancy From Mom From Dad Genotypes f t H d f t H D Rh- Rh- M e M e I. Phenotypes 1_____ ______________________________________ 2 _____ ______________________________________ 3 _____ ______________________________________ 4 _____ ______________________________________ 5_____ ______________________________________ 6_____ ______________________________________ 7_____ ______________________________________ Analysis: Remember, some of your answers maybe “possibly,” then give the “if scenario.” Was Jill’s father freckled? Was Jill’s mom freckled? Did either of Jill’s parents have the ability to taste? Are all of Tammy’s brothers and sisters have unattached earlobes? When Tammy has kids, will they have unattached earlobes? Does Nancy produce the Rh protein? Did both of her parents?