Porifera-related terms Asconoid – simplest canals Synconoid – more
advertisement

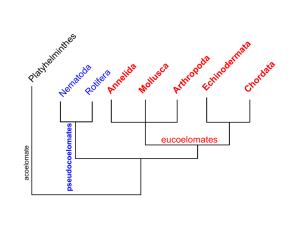
Porifera-related terms Asconoid – simplest canals Synconoid – more complex canals Leukonoid – best canals Cnidaria-related terms Gland cell – for digestion Gastral filaments – stinging cells inside the gut of scyphozoans Solenia – gastrodermal tubes in hexacorallia Platyhelmithes-related terms Rhabdite – rod like defensive structures and the cells that produce them in turbellaria. Protonephridia (flame cells) – the excretory system in flatworms. Nephridiopore – where the uric acid comes out. Annelida-related terms Mesentry – partitions between the right and left side of the body Septa - partitions between coelom sacs Peritoneum ( – )קרום צפקepithelial mesoderm that lines the coelom. Parapodia – body wall that protrudes and serves as gills (mostly polychaeta) Crop – where food is stored Gizzard – where food is digested mechanically and with acidic enzymes. Intestine – where food is digested mechanically and with alkaline enzymes. Rectum – where water and nutrients are reabsorbed. (meta)nephridia – excretory system Nephrostome – funnel opening in one segment. Nephridiopore – excretory site in the next. Palps – sensory appendages in polychaeta Sex atrium – where semen stored is after fuckies Trochophores – Larvae that develop via metabolous Clitellum – thick band on oligochaeta that secretes mucus for fuckies. Vesiculae seminalis – stores semen before fuckies (oligo) Recepticula seminalis – stores semen after fuckies (oligo) Arthropoda-related terms Epicuticle- external layer Procuticle – internal layer, made of Exocuticle and endocuticle Apodem – inward fold of the epidermis that serves as an attachment for muscles. Holometabolous – cocoon Hemimetabolous – no cocoon Haemolymph – mixture of blood and coelom fluid. Haemocoelom – the joint blood-coelom system Proto-, deutero- tritocerebrum – the three brains of arthropods. Sensillae (seta) – sensory hairs growing through the cuticle. Retinulae – photosensitive cells Omatidia – one cell of a compound eye Rhabdom – the pillar running down the middle containing rhodopsin Mandibles – main upper jaws Maxillae – auxiliary jaws Hypopharynx – lower jaws Malpighian tubes – drain into intestine Coxal glands – absorb waste in spiders Echinodermata-related terms Ambulacral – system of water legs designed for movement Madreporite – the water's entrance into the echinoderm Stone canal – connects the madreporite with the ring canal Ring canal – supplies water to the water canals Pyloric duct – tube in each arm for digestion Pyloric caecum – digestive tract Aristotle's lantern – chewing mechanism in sea urchins Pedicellaria – small pincers that remove waste from the echinoderms body