TWO DIFFERENT ALTITUDES
advertisement

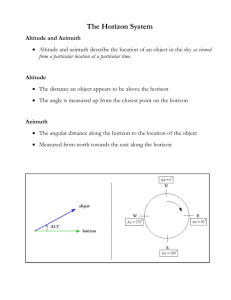
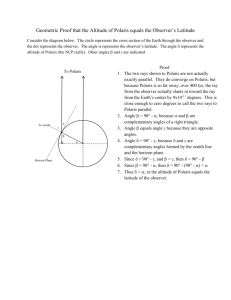
TWO DIFFERENT ALTITUDES! There are two different ways the word "altitude" can be used in science! For each definition, describe a situations where that meaning of "altitude" would be used. Which one is used in observing astronomy? 1. The common usage of the word "Altitude" is the DISTANCE of a point above SEA LEVEL or the ground, in units of FEET or METERS. This type of altitude does not change. _ _ _ _ _ __ | / ______|____/ The mountain’s altitude is 900 meters above sea level. / \ \ \_ | The plane’s altitude is 10,000 feet. _______|____________ 2. "Altitude" can also mean the vertical ANGLE between the HORIZON (where the distant ocean or earth meets the sky) and a POINT IN THE SKY. Units range from 0 degrees at the horizon to 90 degrees at the zenith, directly overhead. This altitude changes according to the time and latitude of the observer. DEFINITIONS FOR THE TEST: altitude -- is the vertical angle of an object, measured in degrees from the horizon. zenith -- the point that is straight "up" or directly over the observer's head, measured as 90 degrees altitude from the horizon. quadrant -- a navigational instrument made from 1/4 of a circle protractor and ranges from 0 degrees at the horizon to 90 degrees at zenith. It measures altitude, a vertical angle. azimuth -- is the compass direction of a celestial object. It is the horizontal angle that begins at 0 degrees pointing North, and increases clockwise around the observer's horizon. So an object due north has an azimuth of 0°, one due east 90°, south 180° and west 270°. horizon -- is the horizontal line that surrounds the observer where the sky seems to meet the earth or ocean. The horizon has an altitude of 0 degrees. compass -- a navigational instrument that points to the north magnetic pole, which can be several degrees from true north, depending on the location of the observer on the earth's surface. The Big Dipper is part of the constellation Ursa Major. The two stars of the Big Dipper farthest from the handle are the pointer stars that point directly to Polaris. Polaris, the “pole star” is also known as the North Star. The imaginary line that runs through Earth's north and south poles points to Polaris. Polaris seems to stays in the same place in the sky while other stars appear to "rise" and "set". The altitude of Polaris is the same as the observer's latitude. North Magnetic Pole -- The north magnetic pole of the earth is the wandering point on the Earth's surface that all magnetic compasses point towards. It is currently in Canada. STUDY GUIDE FOR 3/31 TEST Match the words with their definitions: 1. Part of the constellation Ursa Major is called the _________________. zenith altitude compass 0° pointer stars latitude 180° Big Dipper azimuth Polaris 90° North Magnetic Pole horizon 34° north quadrant 2. In the Big Dipper, the two farthest stars from the handle are the _____________. 3. These stars lead directly to Polaris, and are called the ______________. 4. The North Star and the Pole Star are names for ___________. 5. The imaginary line that runs through Earth's north and south poles points to _______. 6. Like the sun and the moon, the stars appear to "rise" and "set.” However, one star appears to stay in the same place in the sky, and is called ___________. 7. The altitude of __________ is the same as the observer's ___________. 8. In the Los Angeles area, the altitude of Polaris is _________. 9. The horizontal line that surrounds the observer is the _____________. 10. The sky seems to meet the earth or ocean at the ____________. 11. An object with an altitude of 0 degrees is at the _____________. 12. The point that is straight "up" or directly over the observer's head is the ________. 13. An object at 90 degrees altitude from the horizon is at the ____________. 14. A navigational instrument made from a quarter (1/4) circle protractor is a _________. 15. A ___________measures altitude from ___° at the _______ to ___ ° at the _______. 16. The vertical angle of an object from the horizon is the ____________. 17. The horizontal angle of an object clockwise from _______ is called the __________. 18. The compass direction measured by the 360 degrees of a circle is called the _______. 19. Starting from the reference point of north at 0 degrees, _______ increases clockwise around the observer's horizon. 20. An object due north has an ________ of ___°, due east 90°, south ____° and west 270°. 21. A navigational instrument that always points in one direction is called a ___________. 22. The wandering point on the Earth's surface that all magnetic compasses point towards is the ______________________. 23. Depending on the location of an observer on the earth's surface, the North Pole can be several degrees away from the ________________. 24. The __________________ is currently in Canada, but has drifted by Alaska, Russia and Greenland in the past. 25. Draw the Big Dipper with pointer stars leading to Polaris. 26. Describe a situation where finding the North Star would be important. 27. Describe in detail how you would use a quadrant to find your latitude.