The Horizon System
advertisement
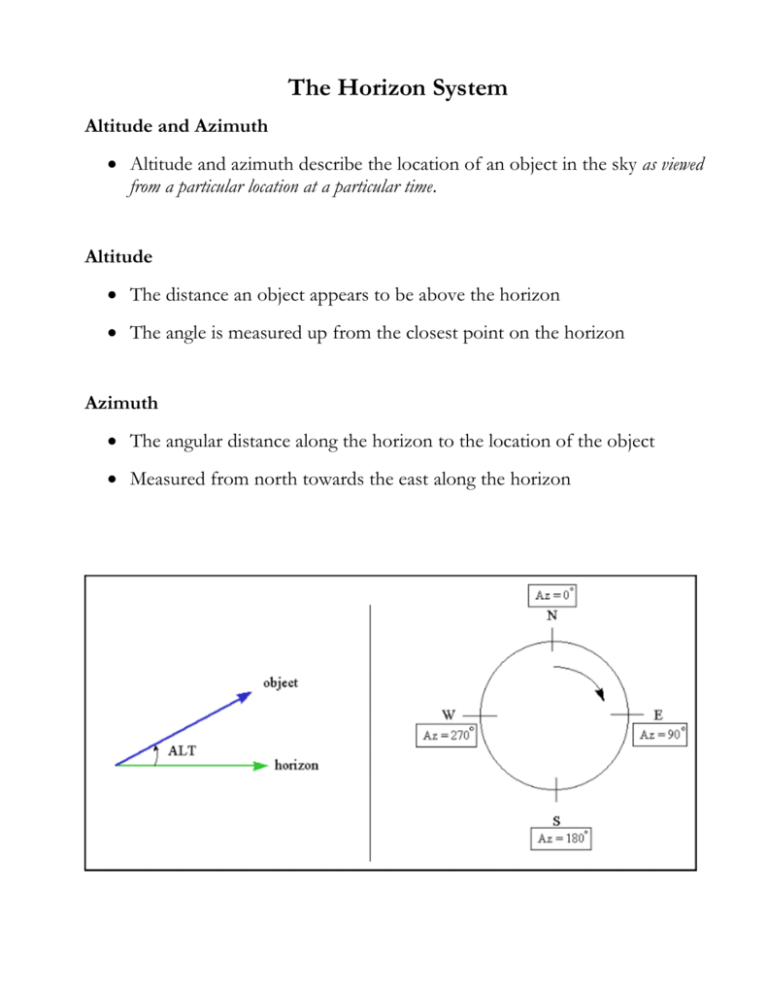
The Horizon System Altitude and Azimuth Altitude and azimuth describe the location of an object in the sky as viewed from a particular location at a particular time. Altitude The distance an object appears to be above the horizon The angle is measured up from the closest point on the horizon Azimuth The angular distance along the horizon to the location of the object Measured from north towards the east along the horizon The Changing Night Sky At any location on Earth, the altitude of the NCP equals the latitude. Ithaca is located at 42 degrees North latitude So as seen in Ithaca, the altitude of the North Celestial Pole (NCP) is 42 degrees. Like the Sun, stars rise in the east and set in the west. Through the night, a star moves across the sky as the Earth rotates. As seen in Ithaca, some of the stars close to the North Celestial Pole never set = circumpolar stars The path that the Sun follows changes from day to day because of the Earth's tilt on its axis. The Sky as Seen at Different Locations of Earth At different latitudes, different portions of the celestial sphere are visible. Northern latitudes - cannot ever see stars around the South Celestial Pole. Southern latitudes - cannot ever see stars around the North Celestial Pole. At the North Pole, all of the stars are circumpolar. Only half of the stars are above the horizon, but they are always above it. At the equator, all of the stars are visible but only for half of the time. Hawaii lies at 19 degrees north latitude. Can you figure out what Theta (in the diagram below) is?