Enzymes - Florida State College
advertisement

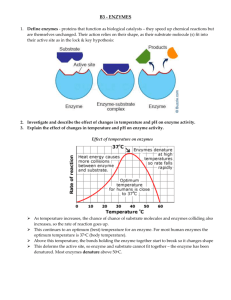
Enzymes Enzymes are vital chemicals in all living things. They are proteins that speed up, and control, the chemical reactions inside the cells. If enzymes do not function properly, the cell or even the whole organism can die. This chapter will look at enzymes, and also some deficiency diseases, where people are born with a lack of a particular enzyme. A) Web site name: Florida State College Jacksonville Web URL: http://web.fscj.edu/David.Byres/enzyme1.html Read “Mechanisms of Enzyme Action” 1). What are the two main roles of enzymes? ___________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2). What is a “substrate”? ___________________________________________ 3). In the first diagram (with sucrase), is the substrate broken apart into two products, or are two substrates joined to make a single product? _____________________________________________________________ 4). What are two ways that the barrier of activation energy can be overcome? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 5). If the temperature of an enzyme controlled reaction increased from 10oC to 30oC, the reaction rate will typically : a) double b) triple c) quadruple d) increase 9-fold 6). What happens to most enzymes above 50oC ? ________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 7). Which organisms have enzymes that can work efficiently at –2oC ? _____________________________________________________________ 8). What is the optimum pH for pepsin? _______________________________ 9). What is inhibition? _____________________________________________ 10). Chemicals that are very similar to the true substrate are ________________ inhibitors. 11). Why are non-competitive inhibitors unaffected by substrate concentration? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 12). What is a “prosthetic group”? _____________________________________ 13). Why does the stomach lining not get digested by pepsin? _______________ _____________________________________________________________ 14). What type of reaction is done by Lyases? ___________________________ 15). How are the following enzymes used commercially? a) Substilin : __________________________________________________ b) Glucose oxidase : ____________________________________________ B) Web site name: Maricopa Community College Web URL: http://www2.estrellamountain.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookEnzym.html#Enzymes Read “Enzymes: Organic Catalysts” 16). What is a “catalyst”? ____________________________________________ 17). How do catalysts lower the activation energy? ________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 18). Carbonic anhydrase causes chemicals to react ________ times faster than without the enzyme. 19). What is the “induced fit hypothesis”? _______________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 20). What are “thermolabile enzymes” ? ________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 21). What is the optimum pH for the enzyme Arginase? ____________________ 22). How does sulfanilamide kill bacteria? ______________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 23). Which of the four competitive inhibitors shown in the diagram is the most similar in structure to succinate? __________________________________ 24). What effect do the following inhibitors have ? a) nerve gas : _________________________________________________ c) Penicillin : _________________________________________________ Some people are born with a lack of a particular enzyme. One example of a “deficiency genetic disease” like this is called Tay-Sachs disease. C) Web site name: Disabled World Web URL: http://www.disabled-world.com/disability/types/tay-sachs.php Read “Tay-Sachs Disease” 25). In Tay-Sachs disease, which fatty substance builds up in nerves? _______________________________________ 26). Which enzyme has a “lack of sufficient activity” in Tay-Sachs disease? _____________________________ 27). What are the symptoms in children with this disease? _________________ ____________________________________________________________ 28). What are the symptoms for the rare form of Tay-Sachs disease (TSD) that occurs in people in their twenties? _______________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 29). Which populations have a high risk of TSD? _____________________________________________________________ 30). How can carriers of the disease be identified? ______________________ 31). If both parents are carriers of TSD, what is the chance of their child being born with TSD? _____% 32). Which chromosome carries the gene for TSD? ______________________ 33). People who are carriers of TSD have a _____% chance of passing on the active gene to their children. D) Web site name: Medicine Net Web URL: http://www.medicinenet.com/g6pd_deficiency/article.htm 34). Which part of the body is mainly affected by this condition? ___________ 35). What are three symptoms of hemolytic anemia? _____________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 36). Which food can cause hemolytic anemia ? ___________________________ 37). How many people worldwide suffer from this deficiency? ______________ 38). Which disease does this G6PD deficiency protect people against? _____________________________________________________________ 39). In which parts of the world is G6PD deficiency most common? _____________________________________________________________ 40). Why is this deficiency more common in men than in women? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ E) Web site name: Science Daily Web URL: http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2013/03/130308111312.htm 41). How soon could anti-aging drugs be on the market? __________________ 42). Which diseases could this drug prevent? ______________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 43). What is the target enzyme? ___________________________ 44). What two things can switch on this enzyme naturally? __________________________________________________ 45). Where is resveratrol found in small quantities? ________________________ 46). Why is this new drug unusual in the history of pharmaceuticals? ______________________________________________________________ 47). Which disease are statin drugs used to prevent? ________________________ 48). What possible problems or disadvantages could result if in future this new drug is widely prescribed to prevent age related diseases? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 49). Would you personally like to “live to 150”? Explain why. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________