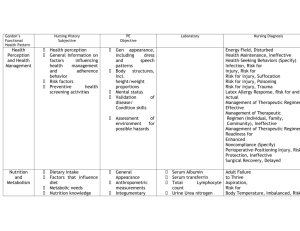
Issues:
advertisement

4. Impaired Oxygenation o Ineffective airway clearance related to increased production of thick mucus o AEB O2 medications 5. o o o o Pain Management Related to Incision Site Related to ostomy site Allergies: Latex, ibuprofen Nursing Progress notes said patient was intermittently irritable 3. Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity o Related to ostomy site, difficulty obtaining tight seal of appliance A.H. 17 months CF, Ileostomy Sept 25/06 1. Sleep Pattern Disturbance o Related to internal factors of illness effects (CF) o New ostomy appliance o Charts mentioning “did not sleep well” o Pain 2. Risk for Infection o Related to chronic pulmonary disease o Related to Ileostomy o Related to IV site o Related to PICC site o Related to chronic illness and decreased immune system Parking Lot Pain CSM Temperature Skin 6. Fever o Hyperthermia related to cystic fibrosis o Chest X-ray needed if temperature is 38C or higher Problem Intervention Obtain a sleep history including bedtime routines, history of sleep problems, changes in sleep with present illness and use of medications and stimulants Sleep Pattern Disturbance Assess level of pain and use of available pharmacological and non pharmacological approaches to pain management Provide pain relief shortly before bedtime and position the client comfortably for sleep Keep environment as quiet as possible for sleeping; anticipate IV monitors and other hospital machines Observe and report signs of infection such as redness, warmth, discharge and increased body temperature Risk for Infection Note and report laboratory values (eg. White blood cell count and differential, serum protein, serum albumin, and cultures) Assess skin for colour, moisture, texture and turgor. Keep Evaluation accurate ongoing documentation of changes. Preventative skin assessment protocol, including documentation, assists in the prevention of skin breakdown Carefully wash and pat dry skin, including skin fold areas. Use hydration and moisturization on all at-risk surfaces. Encourage Fluid Intake Measure and record a febrile client’s temperature at least every 4 to 6 hours or whenever a change in condition occurs. Use the same site for temperature measurement for a given client so that temperature trends are assessed accurately Fever Administer anti-pyretic medication per physicians orders, when infection-induced fever is above 40C and when the client cannot tolerate the increase in metabolic demand Assess fluid loss and facilitate oral intake or administer intravenous fluids to accomplish fluid replacement Monitor respiratory rate, depth and ease of respiration. Note abdominal breathing, use of accessory muscles, nasal flaring, retractions, irritability, confusion, or lethargy Impaired Oxygenation Auscultate breath sounds, noting decreased or absent sounds, crackles, or wheezes Monitor client’s oxygen saturation and blood gases Monitor for presence of pain and provide pain medication for comfort as needed If the client is cognitively impaired and unable to report pain and use a pain rating scale, assess and document behaviors that might be indicative of pain Pain Management Assume pain is present and treat accordingly in a client who has a pathological condition or who is undergoing a procedure thought to be painful For a young child use a Faces Pain Scale to determine the level of pain present Plan care activities around periods of greatest comfort whenever possible Monitor skin at least once a day for colour or texture changes, dermatological conditions, or lesions. Determine whether the client is experiencing loss of sensation Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity Monitor the client’s skin practices, noting type of soap or other cleansing agents used, temperature, frequency of skin cleansing Use a risk assessment tool to systematically assess immobilityrelated risk factors If consistent with overall client management goals, teach how to turn and reposition the client at least every 2 hours