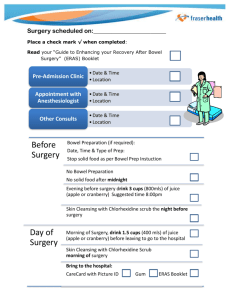
Pathology - keala . org
advertisement
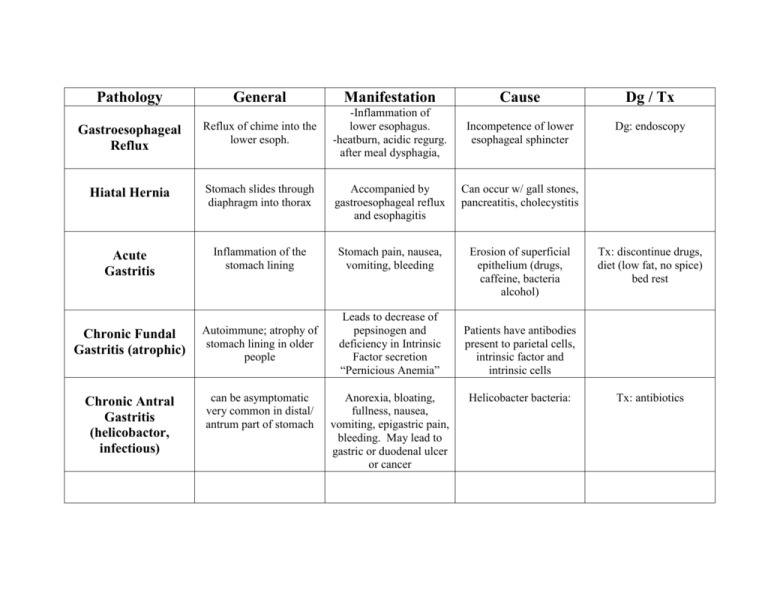
Pathology General Manifestation Cause Dg / Tx Gastroesophageal Reflux Reflux of chime into the lower esoph. -Inflammation of lower esophagus. -heatburn, acidic regurg. after meal dysphagia, Incompetence of lower esophageal sphincter Dg: endoscopy Hiatal Hernia Stomach slides through diaphragm into thorax Accompanied by gastroesophageal reflux and esophagitis Can occur w/ gall stones, pancreatitis, cholecystitis Acute Gastritis Inflammation of the stomach lining Stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, bleeding Erosion of superficial epithelium (drugs, caffeine, bacteria alcohol) Chronic Fundal Gastritis (atrophic) Autoimmune; atrophy of stomach lining in older people Leads to decrease of pepsinogen and deficiency in Intrinsic Factor secretion “Pernicious Anemia” Chronic Antral Gastritis (helicobactor, infectious) can be asymptomatic very common in distal/ antrum part of stomach Anorexia, bloating, fullness, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, bleeding. May lead to gastric or duodenal ulcer or cancer Tx: discontinue drugs, diet (low fat, no spice) bed rest Patients have antibodies present to parietal cells, intrinsic factor and intrinsic cells Helicobacter bacteria: Tx: antibiotics Pathology General Manifestation Causes Dg / Tx Peptic Ulcer Pain after eating, bloating, nausea, vomiting Exposure of mucous membranes to acid and pepsin Gastric Ulcers An ulceration of muscularic mucosa of lower esophagus, stomach or duodenum Common in older people; erosion of mucous lining Pain after eating, bloating, nausea, vomiting Imbalance btw ulcerpromoting and (mucosa) protective factors Dg: clinical symptoms, endoscopy, xray, gastric analysis Tx: see gastric ulcers Dg: see peptic ulcers Tx: antacids, surgery, antibiotics, diet, etc Acute Appendicitis Inflammation of the vermiform appendix Pseudomembranous Enterocolitis Peritonitis Acute inflammation of the large or large and small intestines , associated with antibiotics Acute inflammation of the visceral and parietal peritoneum with pus on the abdominal wall Pain (right side abd), Obstruction of the lumen, Tx: surgery to remove, nausea, vomiting twisting, lymphoid esp. with abscess diarrhea, fever (low), hyperplasia formation or perforation leukocytosis leading to peritonitis Rapid diarrhea, exudate Toxin producing Tx: change in antibiotics, on surface of large and/or bacteria, resistant to fluid replacement small intestines. antibiotics multiply trigger mucous prod., fibrin, inflame. response Abdominal pain, Bacteria from intestinal Tx: surgery, antibiotics distension or tenderness, tract penetrate after fever, tachycardia, perforation of the tachypnea, chills, appendix or peptic ulcer, vomiting, leukocytosis, penetrating wounds or shock ectopic pregnancy Pathology General Manifestation Causes Crohn’s Disease Chronic transmural inflammatory disease affecting the distal ileum and colon Irritable bowel, abdominal pain, fever, anorexia, weight loss, chronic diarrhea, right lower quadrant mass unknown etiology; may be autoimmune, dietary factors, bacteria, smoking – affects young adults, runs in families Disease with development of small, multiple outpouchings through the muscular wall of the sigmoid colon Motility disorder of the small and large intestines, as a reaction to stress, mostly affecting women. Excess mucous production Pain, diarrhea, bleeding. Can lead to perforation, abscess or fistula formation Related to low fibre diet and aging Abdominal distress, variation in stool consistency, bloating, flatulence, headache, fatigue, depression, anxiety, food intolerances Loss of appetite, weight loss, abdominal discomfort or pain, abdominal mass, anemia (occur after metastasizations) May cause bleeding, altered bowel movement No anatomic cause. Triggered by stress, occurs in people with inherited increased sensitivity to gastrointestinal motility Colonic Diverticulosis Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS, spastic colon) Carcinoma of the Stomach Hyperplastic Polyps Arises from the gastric mucosa and spreads into the stomach wall, metastasizes into regional lymph nodes and liver Small protrusion from mucosal lining Cured meats (sodium nitrates, MSG) pickled food. Associated with gastritis or stomach ulcers Dg / Tx Dg: x-ray, endoscopy Tx: anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, surgery (obstruction, abscess, fistulas) Tx: diet, bed rest, Iv alimentation, antibiotics, surgery Dg: made after exclusion of other diseases Tx: Diet and excersize, detox, sedation, antidepressant therapy, psychotherapy, stress releif Dg: x-ray, gastroscopy, biopsy Tx: surgery Pathology General Manifestation Villous Adenoma Raised broad-based mass (polyp) shaped like a huge villi. Often precancerous Most common polyp type. With stem coming off of the large intestine Growth turns into hundreds of polyps, will turn into cancer Bleeding and altered bowel movement, if any. Adenocarcinomas, growing slowly, arise in the mucosa and expand into lumen and through colonic wall Tumors of the Right Colon: Pain, palpable mass, anemia, dark red or brownish blood in stool Tumors of the Left Colon: Grow circumferentially, ulcerate, cause pain, cramps, obstruction and altered bowel movement, bright red blood on stool surface Pedunculated Adenoma Familial Adenomatous Polyposis Carcinoma of the Colon and Rectum Cont’d “ Causes Dg / Tx Tx: surgery, colonostomy Bleeding and altered bowel movement, if any. Happens within a family (if one person has it, all are monitored) Tx: surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, immunotherapy Dg: endoscopy, x-rays, presence of carcinoembryonic antigen Cont’d “ Rectal Carcinomas Up to 15 cm from anus, invade prostate, vagina, lungs