Gas Laws
advertisement

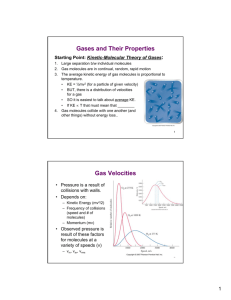
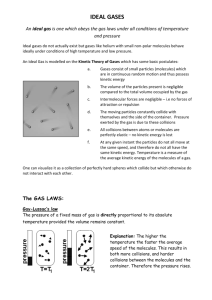
GASES Characteristics of gases Gases are highly compressible and occupy the full volume of the container they are in When a gas is subjected to increased pressure, its volume decreases Gases always form homogeneous mixtures with other gases Gas Laws Boyles Law o The volume of a fixed quantity of gas , at constant temperature, is inversely proportional to its pressure o V = 1/P x constant Charles Law o The volume of a fixed quantity of gas at constant pressure is directly proportional to its absolute temperature o V = T x constant Avogadros Law o Gay-Lussac: At a given temperature and pressure, the volumes of gases that react with one another are ratios of small whole numbers o Avogadros hypothesis: Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules o Avogadros Law: The volume of a gas at constant temperature and pressure is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas. V = constant x n o 22.4 L of any gas at 0 degrees C and 1 atm contain 6.02 x 1023 molecules The Ideal Gas Equation o PV = nRT where R = 0.08206 L atm/mol K o 1 mole of gas at STP( 0 degrees C, 273.15 K, 1 atm) is 22.4 L o In general if we have a gas under 2 sets of conditions: P1 V1/ n1T1 = P2V2/ n2T2 Gas density and molar mass o M =dRT/P Gas mixtures and partial pressures o Daltons Law of partial pressures: the total pressure of a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each component Kinetic Molecular Theory Gases consist of large numbers of molecules in constant random motion. Energy is transferred during collisions, but average kinetic energy is constant at constant temperature Average kinetic energy is proportional to absolute temperature Effects of an increase in volume(at constant temp) o The average kinetic energy remains the same o Pressure decreases( molecules have farther to go to hit walls) Effects of increased temp(at constant volume) o The average kinetic energy increases o There are more collisions with the container o Therefore, pressure increases Grahams Law Average kinetic energy is related to mass (KE =1/2 MV2) So for 2 gases at the same temp, v will be proportional to the mass. Lower mass molecules will move faster Effusion is the escape of gas molecules through a tiny hole into an evacuated space Diffusion is the spread of one substance through space or another substance