Lesson 1 | Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
advertisement

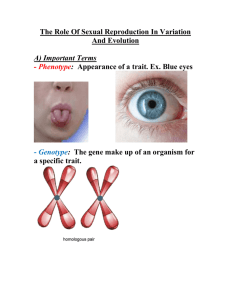
Name Date Class Lesson Outline LESSON 1 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis A. What is sexual reproduction? 1. produces an offspring when genetic materials from two different sex cells combine. a. The female sex cell, a(n) , forms in an ovary. b. The male sex cell, a(n) , forms in a testis. 2. During a process called , an egg cell and a sperm cell join together. The new cell that forms is called a(n) . B. Diploid Cells 1. Organisms that reproduce sexually make two kinds of cells— cells and sex cells. 2. Body cells are ; they have pairs of chromosomes. 3. If a zygote has too many or too few , it will not develop properly. 4. Different organisms have different 5. of chromosomes. are pairs of chromosomes that have genes for the same traits arranged in the same order. C. Haploid Cells 1. Sex cells are ; they have only one chromosome from each pair of chromosomes. 2. In , one diploid cell divides and makes four haploid cells. D. The Phases of Meiosis 1. Meiosis involves two divisions of the nucleus and the . These divisions, known as meiosis I and meiosis II, result in four haploid cells. 2. During , the reproductive cell grows and duplicates its chromosomes. 3. During meiosis I, each pair of duplicated homologous chromosomes . 4. After meiosis I, the two cells formed during this stage go through a second division 10 of the and cytoplasm called meiosis II. During meiosis II, sister separate to produce four haploid cells. Reproduction of Organisms Name Date Class Lesson Outline continued E. Why is meiosis important? 1. Meiosis forms sex cells with the correct haploid number of . This maintains the correct number of chromosomes in organisms when sex cells join. 2. Meiosis creates genetic variation by producing cells. F. How do mitosis and meiosis differ? 1. During and cell division, a body cell and its nucleus divide once and produce two identical cells. 2. During , a reproductive cell and its nucleus divide twice and produce four cells––two pairs of identical haploid cells. G. Advantages of Sexual Reproduction 1. Sexual reproduction produces that have a new combination of DNA. This results in genetic among individuals. 2. Genetic variation gives individuals within a population slight differences that might be an advantage if the 3. changes. breeding has been used to develop desirable traits in plants and animals. H. Disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction 1. One disadvantage of sexual reproduction is that organisms have to grow and develop until they are mature enough to produce cells. 2. Another disadvantage is that searching for a mate takes time and energy and might expose individuals to predators, , or harsh environmental conditions. Reproduction of Organisms 11 Name Date Class Content Practice A LESSON 1 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: On the line before each definition, write the letter of the term that matches it correctly. Each term is used only once. 1. production of an offspring through the combination of egg and sperm A. diploid cell B. egg C. fertilization 2. female sex cell D. haploid cell E. homologous 3. male sex cell chromosomes F. meiosis 4. joining of egg and sperm G. sexual reproduction H. sperm 5. the cell formed by fertilization I. zygote 6. body cell or zygote, which has pairs of chromosomes 7. male or female sex cell that has only one chromosome from each pair 8. process by which one diploid cell divides into four haploid cells 9. two chromosomes that have genes for the same traits in the same order Directions: On the line before each statement, write T if the statement is true or F if the statement is false. 10. Sexual reproduction produces offspring that is identical to the parents. 11. The nucleus divides in meiosis I and again in meiosis II. 12. During meiosis, the number of chromosomes in each cell stays the same. Reproduction of Organisms 13 Name Date Class Content Practice B LESSON 1 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Answer each question or respond to each statement on the lines provided. 1. Define sexual reproduction. 2. What are male and female sex cells, and where are they made? 3. Explain what a zygote is. Use the terms egg cell, sperm cell, and fertilization in your explanation. 4. Compare a diploid cell and a haploid cell. Include where each cell is located. 5. Which process divides one diploid cell and makes four haploid cells? How many times does the nucleus divide during this process? 6. What are homologous chromosomes? 14 Reproduction of Organisms Name Date School to Home Class LESSON 1 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Use your textbook to answer each question. 1. The production of an offspring resulting from the combination of genetic materials of two different cells is called sexual reproduction. How is a zygote formed in sexual reproduction? 2. Diploid cells have pairs of chromosomes, whereas haploid cells have only one chromosome from each pair. Which cells are sex cells, diploid cells or haploid cells? 3. Meiosis and mitosis are similar processes in which an organism produces new cells. What are the differences between the processes of meiosis and mitosis? 4. Meiosis produces cells that are not genetically identical to the parent cell. What are the advantages and disadvantages of sexual reproduction? 18 Reproduction of Organisms Name Date Class Key Concept Builder LESSON 1 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Key Concept What is sexual reproduction, and why is it beneficial? Directions: Work with a partner to answer each question or respond to each statement on the lines provided. 1. Name the type of reproduction that occurs when the genetic materials from two different cells combine to produce an offspring. 2. What are egg cells? 3. What are sperm cells? 4. Explain the relationship between fertilization and a zygote. 5. What happens to a zygote? 6. Compare the DNA of an offspring to the DNA of its parents. 7. Why do offspring from the same parents usually have a different set of traits? Reproduction of Organisms 19 Name Date Class Key Concept Builder LESSON 1 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Key Concept What is the order of the phases of meiosis, and what happens in each phase? Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. Some terms may be used more than once or not at all. diploid haploid homologous chromosomes meiosis mitosis sister chromatids 1. In meiosis, one cell divides to make four cells. 2. A cell has half the chromosomes of a cell. 3. A cell has pairs of chromosomes. 4. Pairs of chromosomes that are not identical but have genes for the same trait arranged in the same order are . 5. Each pair of has one chromosome from the mother and one chromosome from the father. 6. In 7. During , the two chromosomes are always identical. , two divisions of the nucleus and the cytoplasm occur. 8. When a cell duplicates one chromosome, two are formed. 9. During interphase of mitosis and meiosis, two are formed for each chromosome. 10. A reproductive cell goes through interphase before beginning I, but not before 11. Prophase I and Prophase II are stages in 20 II. . Reproduction of Organisms Name Date Class Key Concept Builder LESSON 1 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Key Concept Why is meiosis important? Directions: Answer each question on the lines provided. 1. If a male organism has 40 chromosomes in each body cell, how many chromosomes does a female of the same species have in each body cell? 2. How many homologous pairs of chromosomes does the male have? 3. How many chromosomes would be in a sperm cell and in an egg cell? 4. How many chromosomes would be in an offspring? 5. How many pairs of homologous chromosomes would be in an offspring? 6. What is the difference between a diploid cell and a haploid cell? 7. How does meiosis help maintain diploid cells in offspring? Use the terms chromosomes, diploid, haploid, fertilized egg, and sex cells in your answer. 22 Reproduction of Organisms Name Date Challenge Sequencing Meiosis The diagrams show the stages of meiosis in scrambled order. To the left of each diagram, label and sequence the stages in the correct order. To the right of each diagram, include a brief description of what happens during each stage. Class LESSON 1