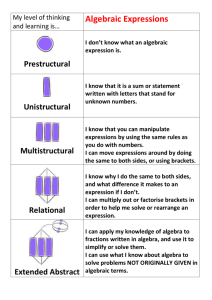
Course Title - Novato Unified School District
advertisement
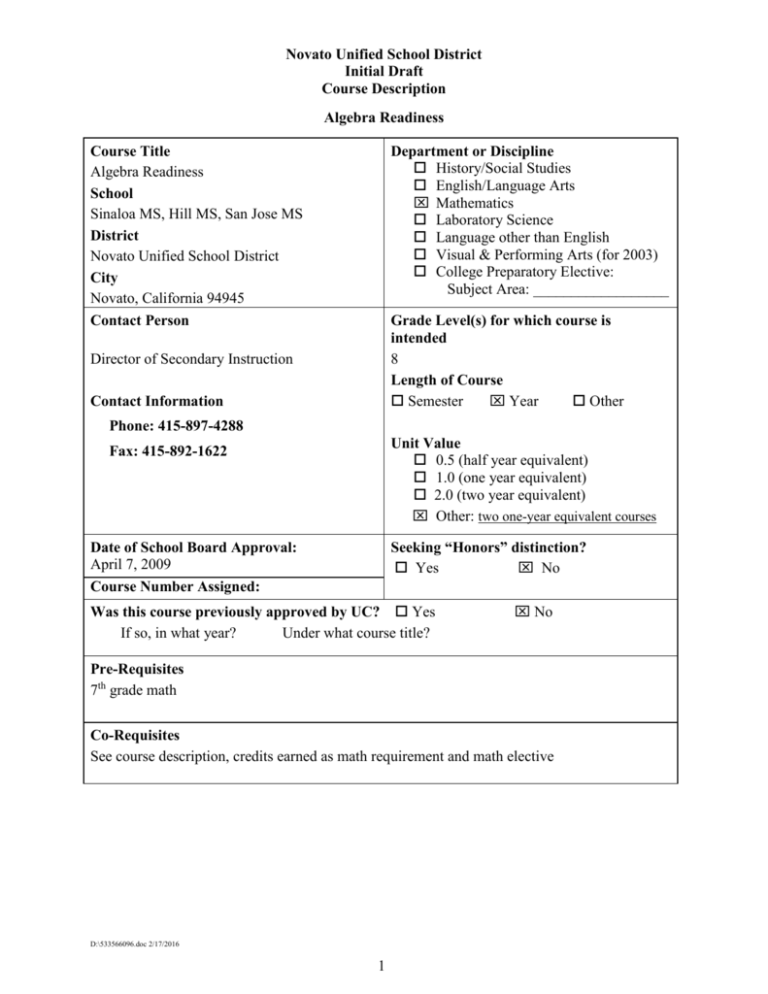
Novato Unified School District Initial Draft Course Description Algebra Readiness Course Title Algebra Readiness School Sinaloa MS, Hill MS, San Jose MS District Novato Unified School District City Novato, California 94945 Contact Person Department or Discipline History/Social Studies English/Language Arts Mathematics Laboratory Science Language other than English Visual & Performing Arts (for 2003) College Preparatory Elective: Subject Area: __________________ Grade Level(s) for which course is intended 8 Length of Course Semester Year Other Director of Secondary Instruction Contact Information Phone: 415-897-4288 Unit Value 0.5 (half year equivalent) 1.0 (one year equivalent) 2.0 (two year equivalent) Other: two one-year equivalent courses Fax: 415-892-1622 Seeking “Honors” distinction? Yes No Date of School Board Approval: April 7, 2009 Course Number Assigned: Was this course previously approved by UC? Yes If so, in what year? Under what course title? No Pre-Requisites 7th grade math Co-Requisites See course description, credits earned as math requirement and math elective D:\533566096.doc 2/17/2016 1 Novato Unified School District Initial Draft Course Description Algebra Readiness Brief Course Description for Academic Planning Guide (student friendly) This course is a double period course designed for students who are two to three years behind in mathematics and not ready for Algebra. The curriculum has been designed to help students overcome weak preparation in mathematics. It utilizes an approach that accelerates student learning up to the level needed for advanced mathematics courses. The curriculum scaffolds mathematics standards to prepare for the fundamental principles of Algebra. COURSE CONTENT A. Course goals and/or major student outcomes ● The goal of this course is to have an explicit and cohesive curriculum based on mathematical concepts. ● Instruction will reinforce and strengthen concepts and skills introduced in 2nd through 7th grades. ● Emphasis will be placed on 13 of the 7th grade standards and 3 of the Algebra 1 standards. ● Students will gain confidence by working at levels appropriate to their abilities while raising their content knowledge and strengthening their skills. ● Students will be better prepared for college-prep mathematics at the high school level. ● Students will use mathematical language to express their understanding of the material B. Course Objectives-specific student learning objectives Objectives. Students will Understand 1. the foundations of algebra using appropriate diagrams, numbers and letters and basic number properties 2. various properties of Standards Grade 5 – Algebra and Functions 1.0 Students use variables in simple expressions, compute the value of the expression for specific values of the variable, and plot and interpret the results 1.2 Use a letter to represent an unknown number; write and evaluate simple algebraic expressions in one variable by substitution. 1.3 Understand and compute positive integer powers of nonnegative integers; compute examples as repeated multiplication. Grade 5 – Mathematical Reasoning 2.3 Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Grade 6 – Algebra and Functions 1.3 Apply algebraic order of operations and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to evaluate expressions; and justify each step in the process. Grade 4 – Number Sense D:\533566096.doc 2/17/2016 2 Novato Unified School District Initial Draft Course Description Algebra Readiness the number system, including place value, number lines, rational numbers, percents, and operations 3. factors and fractions with the ability to simplify through knowledge of prime factors, common multiples, GCF and LCM as well as operations using fractions 4. concepts, properties and operations of positive and negative numbers including integers, fractions and decimals 5. comparing quantities in 1.0 Students understand the place value of whole numbers and decimals to two decimal places and how whole numbers and decimals relate to simple fractions. Students use the concepts of negative numbers: 3.2 Demonstrate an understanding of, and the ability to use, standard algorithms for multiplying a multi digit number by a two-digit number and for dividing a multi digit number by a one-digit number; use relationships between them to simplify computations and to check results. Grade 6 – Mathematical Reasoning 1.2 Formulate and justify mathematical conjectures based on a general description of the mathematical question or problem posed. Grade 7 – Number Sense 1.3 Convert fractions to decimals and percents and use these representations in estimations, computations, and applications 1.5 Know that every rational number is either a terminating or repeating decimal and be able to convert terminating decimals into reduced fractions. Grade 4 – Number Sense 1.7 Write the fraction represented by a drawing of parts of a figure; represent a given fraction by using drawings; and relate a fraction to a simple decimal on a number line. Grade 5 – Number Sense 2.0 Students perform calculations and solve problems involving addition, subtraction, and simple multiplication and division of fractions and decimals 2.4 Understand the concept of multiplication and division of fractions. Grade 6 – Number Sense 2.2 Explain the meaning of multiplication and division of positive fractions and perform the calculations (e.g., 5/8 ÷ 15/16 = 5/8 x 16/15 = 2/3). 2.4 Determine the least common multiple and the greatest common divisor of whole numbers; use them to solve problems with fractions (e.g., to find a common denominator to add two fractions or to find the reduced form for a fraction). Grade 6 – Mathematical Reasoning 2.5 Express the solution clearly and logically by using the appropriate mathematical notation and terms and clear language; support solutions with evidence in both verbal and symbolic work. Grade 4 – Number Sense 1.8 Use concepts of negative numbers (e.g., on a number line, in counting, in temperature, in "owing"). Grade 5 – Number Sense 2.1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of the results. Grade 6 – Number Sense 2.3 Solve addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division problems, including those arising in concrete situations, that use positive and negative integers and combinations of these operations. Grade 6 – Mathematical Reasoning 2.4 Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Grade 6 – Algebra and Functions 1.3 Apply algebraic order of operations and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to evaluate expressions; and justify each step in the process. Grade 6 – Algebra and Functions 2.0 Students analyze and use tables, graphs, and rules to solve problems D:\533566096.doc 2/17/2016 3 Novato Unified School District Initial Draft Course Description Algebra Readiness a variety of contexts using ratios, solving proportions, connecting scale factor and similarity of figures, and represent these concepts with a variety of methods including diagrams, charts and tables 6. slope as a constant ratio, graphing linear equations with an emphasis on real applications. Students will also discover connections between parallel and perpendicular lines and other geometric relationships. 7. variables, expressions, equations and exponents, both positive and negative, as an introduction to algebra. 8. the interpretation of solutions to real life involving rates and proportions Grade 6 – Number Sense 1.3 Use proportions to solve problems (e.g., determine the value of N if 4/7 = N/ 21, find the length of a side of a polygon similar to a known polygon). Use crossmultiplication as a method for solving such problems, understanding it as the multiplication of both sides of an equation by a multiplicative inverse. Grade 7 – Algebra and Functions 3.4 Plot the values of quantities whose ratios are always the same (e.g., cost to the number of an item, feet to inches, circumference to diameter of a circle). Fit a line to the plot and understand that the slope of the line equals the quantities. 4.2 Solve multi step problems involving rate, average speed, distance, and time or a direct variation. Grade 7 – Mathematical Reasoning 2.5 Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning. Grade 4 – Algebra and Functions 1.5 Understand that an equation such as y = 3 x + 5 is a prescription for determining a second number when a first number is given. Grade 5 – Algebra and Functions 1.5 Solve problems involving linear functions with integer values; write the equation; and graph the resulting ordered pairs of integers on a grid. Grade 5 – Statistics, Data Analysis, and Probability 1.4 Identify ordered pairs of data from a graph and interpret the meaning of the data in terms of the situation depicted by the graph. Grade 7 – Algebra and Functions 3.3 Graph linear functions, noting that the vertical change (change in y- value) per unit of horizontal change (change in x- value) is always the same and know that the ratio ("rise over run") is called the slope of a graph. Grade 7 – Mathematical Reasoning 2.6 Express the solution clearly and logically by using the appropriate mathematical notation and terms and clear language; support solutions with evidence in both verbal and symbolic work. Grade 7 – Algebra and Functions 1.1 Use variables and appropriate operations to write an expression, an equation, an inequality, or a system of equations or inequalities that represents a verbal description (e.g., three less than a number, half as large as area A). 2.1 Interpret positive whole-number powers as repeated multiplication and negative whole-number powers as repeated division or multiplication by the multiplicative inverse. Simplify and evaluate expressions that include exponents. 4.1 Solve two-step linear equations and inequalities in one variable over the rational numbers, interpret the solution or solutions in the context from which they arose, and verify the reasonableness of the results. Grade 7 – Mathematical Reasoning 1.2 Formulate and justify mathematical conjectures based on a general description of the mathematical question or problem posed. Algebra 1 2.0 Students understand and use such operations as taking the opposite, finding the reciprocal, taking a root, and raising to a fractional power. They understand and use the rules of exponents. 4.0 Students simplify expressions before solving linear equations and inequalities in one variable, such as 3(2x-5) + 4(x-2) = 12. Grade 7 – Measurement and Geometry 1.3 Use measures expressed as rates (e.g., speed, density) and measures expressed as products (e.g., person-days) to solve problems; check the units of the solutions; D:\533566096.doc 2/17/2016 4 Novato Unified School District Initial Draft Course Description Algebra Readiness situations and problem solving. and use dimensional analysis to check the reasonableness of the answer. Grade 7 – Mathematical Reasoning 1.3 Determine when and how to break a problem into simpler parts. 2.2 Apply strategies and results from simpler problems to more complex problems. 3.2 Note the method of deriving the solution and demonstrate a conceptual understanding of the derivation by solving similar problems. Algebra 1 5.0 Students solve multistep problems, including word problems, involving linear equations and linear inequalities in one variable and provide justification for each step. C. Outline Topics/Units/Themes Foundations of Algebra Number System Factors and Fractions Positive and Negative Numbers Ratio and Proportionality Showing Relationships with Graphs Key Activities/Assignments/ Standard(s) addressed in Key Activities Expressions, Equations and Exponents Using Equations to Solve Problems Use diagrams to show two amounts are equal Learn strategies for interpreting, representing and solving word problems Use the various identities and properties of operations Represent addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division on number lines Recognize and write equivalent fractions Convert fractions to decimals and decimals to fractions Use inverse operations Use concepts of prime and composite numbers Use exponents to express a prime factorization of a number, greatest common factors, and least common multiple Order decimals or fractions and place them on the number line Use the distributive property in relation to negative and positive numbers Add, subtract, multiply and divide positive and negative numbers Use inequalities in comparing rational numbers Use ratio to compare numbers using division Use proportionality to model problems Solve problems using dimensional analysis Explore similar polygons Draw a line given two points Show that relationships between quantities can be represented using tables, graphs, and formulas Solve word problems that describe situations modeled by arithmetic operations Use the number properties to write equivalent expressions that represent the same quantity Use algebraic terminology correctly Evaluate expressions with negative exponents Apply the Pythagorean Theorem Apply cumulative concepts to real world situations Communicate the results of problem solving investigations in written form and in oral discussion D:\533566096.doc 2/17/2016 5 Novato Unified School District Initial Draft Course Description Algebra Readiness D. Texts and supplemental instructional materials America's Choice: Ramp-Up to Algebra, California Algebra Readiness Program E. Instructional methods and strategies Direct Instruction Problem solving activities Math note-taking and journal writing Student modeling of problem solving strategies Independent practice Cooperative learning groups F. Assessment methods and/or tools Publisher tests / assessments Math notebook and journals Class participation Homework Teacher designed tests / assessments Class discussion and oral response G. Assessment criteria Students will be using standards-based assessments aligned to the California Mathematics Frameworks Mastery of course content standards Completion and accuracy of work Thoroughness of work Ability to think critically and problem solve D:\533566096.doc 2/17/2016 6