There has/have
advertisement

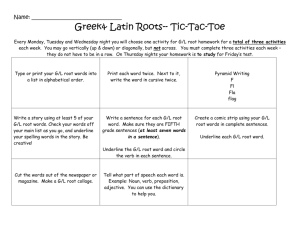
Error No.: 8 Error: There has/ have Some common examples 1. 2. 3. 4. *There will not have any paper in the printer. *On the road, there have many cars. *And there has a big park in the centre of the city. *There have a lot of people in the room. Core grammatical problem 1. Misuse of the verb HAVE to express the existential or presentative function, for which the verb to BE (there BE structure) should be used. Probable causes of this structural problem L1-related factors: 1. The corresponding meaning in Chinese/Cantonese is expressed using 有, have. e.g.: 馬 路 上 有 很 多 車. 嗰 度 有 好 多 人. 2. The word there in a there BE sentence is mistakenly regarded as the sentence-initial adverb in Cantonese 嗰 度. L2-related factors: 1. Inadequate understanding of the correct usage of the there BE sentence structure. 2. Inadequate mastery of the different forms of the verb to BE. 3. Probable confusion due to such acceptable structures as there have been… and there has been…. Correction procedure To help students (Ss) overcome the structural problem as in sentences (1) to (4), teacher (T) can go through the following correction procedure with students (Ss): 1. T shows two sentences. (i) There are many books on the table. (ii) *There has a bird on the tree. 2. T asks Ss to underline the verb in sentence (i). 3. T asks Ss to underline the verb in sentence (ii). 4. T tells Ss that both sentences tell us Something is/are somewhere. T then asks Ss ‘What is something’ in sentence (i)? 5. T asks Ss ‘What is somewhere’ in sentence (i)? 6. T asks Ss to rewrite sentence (i) using the form Something is/are somewhere. i.e. (iii) Many books are on the table. 7. T asks Ss to compare sentence (i) with sentence (iii), especially the verbs. 8. T helps Ss to find out that the two verbs in sentence (i) and (iii) are the same. 9. T repeats steps 4 – 5 using sentence (ii). 10. T asks Ss to rewrite sentence (ii) using the form Something is/are somewhere. i.e. (iv) A bird is on the tree. 11. T asks Ss to compare sentence (ii) with sentence (iv). 12. T helps Ss to find out that the two verbs in sentence (ii) and (iv) are NOT the same. 13. T tells Ss that Something has somewhere. There has something somewhere. 14. T tells Ss that the structure There Be something somewhere should be used. 15. By the time Ss have become familiar with the there BE structure, T can remind them that there is another possible word order: [ somewhere ] , there BE [ something ] e.g. On the wall, there is a painting. OR [ somewhere ] , there BE [ someone ] e.g. In the room, there are five boys. Follow-up exercise A. Editing / Proofreading T selects some authentic excerpts of student writing containing this structural problem, and asks Ss to correct it either on their own or in pairs. B. Translation from Chinese into English 1. 外 面 有 三 個 人. 2. 深 圳 有 很 多 香 港 遊 客. 3. 馬 路 上 有 很 多 車.