Understanding By Design Unit Template
advertisement

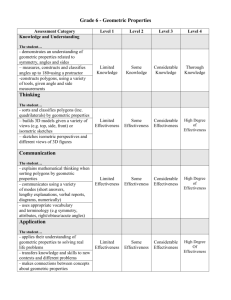
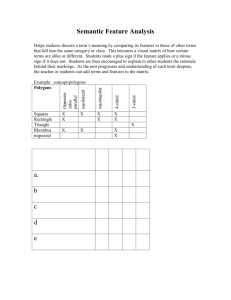
Understanding By Design Unit Template Title of Unit Subject Area (s) Teachers Gr The Foundations of Geometry Tim Math Joy Decker, Kay Johnson, Laura Lee Desired Results (Stage 1) Essential Content (Subject Area) Standards Shape, Dimension and Geometric Relationships: Geometric figures are described by the in the plane. National Education Technology Standards Creativity and Innovation (Choose 2-3 to focus on Communication and Collaboration Research an Critical Thinking, Problem-Solving and Decision-Making Understandings Overarching Understanding (“Big Idea”) Real world and geometric structures are composed of shapes and spaces with specific properties. Supporting Understandings Shapes are defined by their properties. Polygons result from straight, closed, non-intersecting lines. Shapes have a purpose for designed structures. Digital Citizenship Essen (connected to u What properties are ass Why are specific geome What are some differen geometric figures? Why do we classify sha How do geometric elem around us? Knowledge Skills -vocabulary associated with geometry: vertex, line, ray, line segment, polygon, irregular polygon, parallel, perpendicular, convex, concave, obtuse, acute, right, quadrilateral, quadrangle etc. -properties and names of polygons -properties of angles, parallel lines and line segments - use a compass and st figures -name, draw and label -distinguish defining ch polygons, triangles, and Students will know… Students will be able to… -compare/contrast quad -name, draw and label -classify quadrangles ac Assessment Evidence (Stage 2) Assessment of Overarching Understanding/Big Idea The summative assessment consists of the completion of a student project which demonstrates their un use of geometric concepts. This is demonstrated through the production of a schematic featuring an or standards-based geometric elements. Assessment Criteria (students will be able to… student application of Six Facets of U - label different geometric elements on their schematic (facet 1-explanation) combine different geometric elements to illustrate a meaningful structure or creature (facet 2-interpreta appreciate the geometric architecture throughout the world (facet 5-empathy) Assessment Tool (describe type of assessment tool to be used here - post completed Rubric for Geometric Schematic Assessment Strategy (performance task description) Your goal is to produce a schematic f creature made up of standards-based RoleStudents are researchers, interpreters, a Convince teachers and peers of their un Audience how they make up structures. SituationDisplay completed work for evaluation -Produce a rough draft of a geometric s Goal Product/Performance-Use rough draft to generate a digital ve -Display finished product in a group se Students must meet the criteria outlined Standards (Attached) Evidence of development of supporting understandings, kn (identify assessment criteria, strategies and tools for each) Students will understand that shapes are defined by their properties. Strategy:Investigate the relationship between elements of geometry. Tool: Successful completion of "Definition Match" Study Link 1.6 Students will understand that polygons result from straight, closed, non-intersecting lines. Strategy: Sort shapes into polygons/non-polygons and compare properties of all shapes. Tool: Math Journal p. 10 Students will identify how orientation of lines within space dictates specific polygons. Strategy: Students will complete a chart of labeled polygons with number of sides and illustration. Tool: "Geometry Polygons" page. Studects will recognize and convey that shapes have a purpose for designed structures. Strategy: Identify with a digital camera shapes that support school structures. Then use that back schematic. Tool: Use of digital software and digital cameras. Evidence of student application of selected National Educational Technology S of the unit? (Note: assessment of the NETS standards should be integrated with asses knowledge and skills and embedded within unit learning activities) Learning Experiences (Stage 3) Consider the questions in the boxes below as you design learning experiences achievement of desired results. 1) Building Background Knowledge: Read about "Geometry In Our World" from Student Resource Book pa 2) Investigate points, rays, lines, and angles through a SMARTboard activity. Read from SRB p. 76-81 and p p. 6. 3) Determine characteristics of polygons. Read SRB p. 82-83, sort/classify shapes as polygons or not as a wh check for understanding. 4) Classify quadrangles based on their specific properties. Study Link 1.4 5) Classify all polygons and geometric elements based on their specific properties using "Definition Match" 6) Students will complete a chart of labeled polygons with number of sides and illustration. 7) Students will learn how to construct circles using a compass. Successful completion of journal pages 15-1 8) Students will recognize and convey that shapes have a purpose for designed structures through use of a d school structures. 9) Students will produce a schematic featuring an original structure or creature made up of standards-based Use “Where To…” as a tool to assess the quality and scope of unit learning experiences. How will you cause students to you guide them in rehearsing, r work? Where are your students headed? Where have they been? How will you How will you help students to e make sure the students know where they are going? growing skills, knowledge, and unit? How will you hook students at the beginning of the unit? How will you tailor and otherw to optimize the engagement an without compromising the goal What events will help students experience and explore the big idea and How will you organize and sequ questions in the unit? How will you equip them with needed skills and optimize the engagement and a knowledge? From: Wiggins, Grant and J. Mc Tighe. (1998). Understanding by Design, Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development ISBN # 0-87120-313-8 (ppk)