Spectrophotometry Quiz
advertisement

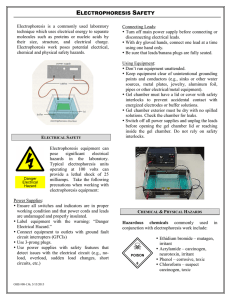
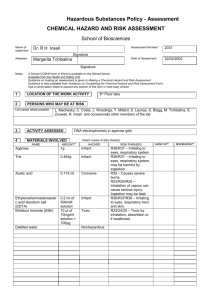
Electrophoresis Exam 60 Points Date________________ Name_____________________________ (4 points each, 24 points total) MULTIPLE CHOICE __D__ 1) All of the following are reasons to use TRIS during an electrophoresis except A) To stabilize the pH B) To conduct electricity C) To maintain the shape of the molecules D) To stain the molecules __D__ 2) Which stain causes DNA to glow orange when exposed to UV light? A) Agrose B) Polyacrylamide C) Methylene blue D) Ethidium bromide __C__ 3) A circular plasmid was cut with a restriction enzyme and three bands were visualized after electrophoresis. How many cuts were made in the plasmid? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 __A__ 4) What is Agar? A) Solid media on which bacteria grow B) Liquid media for bacterial growth C) Region on a bacterial operon D) Matrix used for vertical get electrophoresis “This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solution is copyrighted by the institution that created it. Internal use by an organization and/or personal use by an individual for non-commercial purposes is permissible. All other uses require the prior authorization of the copyright owner.” __C__ 5) How can colorless proteins be monitored during electrophoresis? A) Coomassie blue stain B) Silver stain C) PAGE loading dye D) Ethidium bromide __C__ 6) What is the purpose for SDS during electrophoresis? A) Stain the proteins for visualization B) Use as a loading dye C) Denature the proteins and give them a negative charge D) Conduct electricity 7. (8 Points) List and explain the factors that DNA migration in Agrose depend on. 1. Agarose Concentration Using different concentrations gels resolve different sizes of DNA fragments – Higher concentrations of agarose for small DNAs – Low agarose concentrations allow resolution of larger DNAs 2. Voltage As voltage applied to a gel is increased, larger fragments migrate proportionally faster that small fragments 3. Electrophoresis Buffer _DNA fragments will migrate at somewhat different rates in these two buffers due to differences in ionic strength _Buffers not only establish a pH, but provide ions to support conductivity 4. Effects of Ethidium Bromide _Binding of ethidium bromide to DNA alters its mass and rigidity, and therefore its mobility 8. (4 Points) Explain what is meant by amphoteric compounds? How does that affect the compound’s mobility in gel electrophoresis? Be specific. – Their net charge therefore is determined by pH of medium in which they are suspended • In a solution with a pH above its isoelectric point, a protein has a net negative charge and migrates towards anode in an electrical field • Below its isoelectric point, protein is positively charged and migrates towards cathode “This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solution is copyrighted by the institution that created it. Internal use by an organization and/or personal use by an individual for non-commercial purposes is permissible. All other uses require the prior authorization of the copyright owner.” 9. (4 Points) What is SDS? Why does it get added to proteins in electrophoretic separations? – sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) • Denatures proteins into polypeptide strands • Gives each polypeptide strand an overall negative charge 10. (20 Points) Fill in the blank places at the table below: Horizontal or vertical? Why are they poured horizontal or vertical? Separates large molecules or small ones? Lets you tell small differences between sizes of bands? Can be reheated and poured? Powder is toxic? Solid is toxic Agarose Horizontal Because you can. It’s easier to pour a horizontal gel than it is to pour a vertical gel. Both, but better for large molecules Polyacrylamide Vertical Need glass plates for structure- very thin gels that need support. Air speeds up polymerization. If the gel was poured open to air, it would not solidify evenly. Both, but better for small molecules No Yes Yes No No No Yes No “This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solution is copyrighted by the institution that created it. Internal use by an organization and/or personal use by an individual for non-commercial purposes is permissible. All other uses require the prior authorization of the copyright owner.” Type of molecules run in this type of gel Big gaps or small gaps in gel? Expense? Mostly DNA DNA or proteins Bigger gaps than with polyacrylamide Agarose is about $1 a gramconsidered expensive. Smaller gaps Gels usually bought prepoured. Cost $5-7 per gel. “This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solution is copyrighted by the institution that created it. Internal use by an organization and/or personal use by an individual for non-commercial purposes is permissible. All other uses require the prior authorization of the copyright owner.”




![Student Objectives [PA Standards]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006630549_1-750e3ff6182968404793bd7a6bb8de86-300x300.png)