Speech Perception: Invariance, Segmentation, Categorical Perception
advertisement
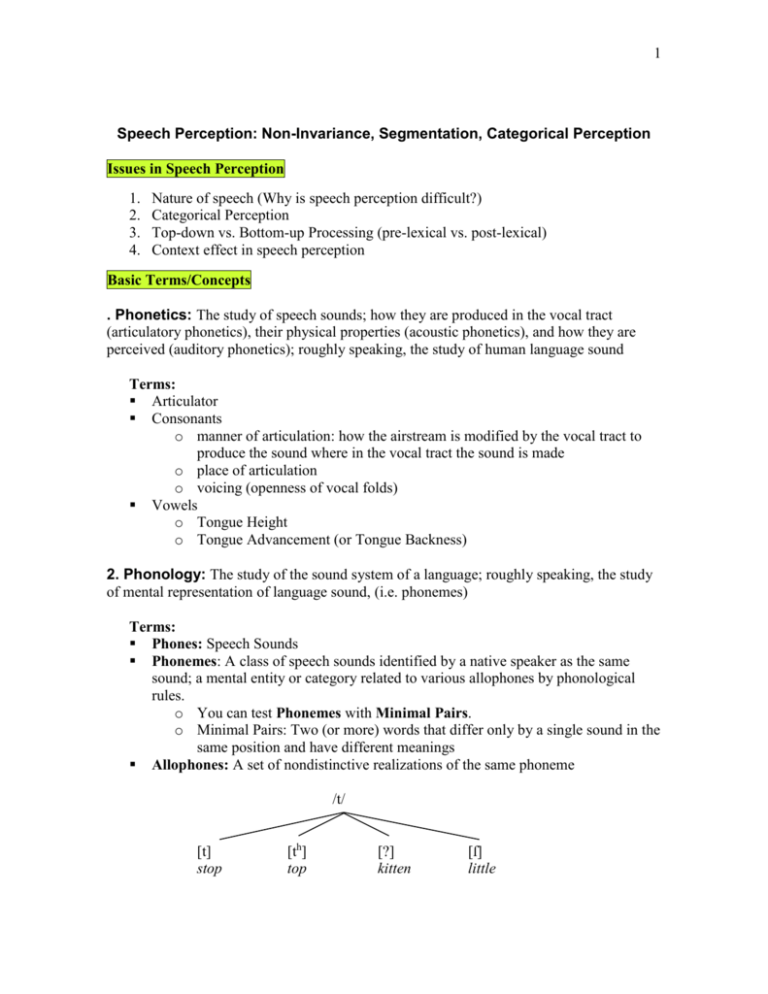
1 Speech Perception: Non-Invariance, Segmentation, Categorical Perception Issues in Speech Perception 1. 2. 3. 4. Nature of speech (Why is speech perception difficult?) Categorical Perception Top-down vs. Bottom-up Processing (pre-lexical vs. post-lexical) Context effect in speech perception Basic Terms/Concepts . Phonetics: The study of speech sounds; how they are produced in the vocal tract (articulatory phonetics), their physical properties (acoustic phonetics), and how they are perceived (auditory phonetics); roughly speaking, the study of human language sound Terms: Articulator Consonants o manner of articulation: how the airstream is modified by the vocal tract to produce the sound where in the vocal tract the sound is made o place of articulation o voicing (openness of vocal folds) Vowels o Tongue Height o Tongue Advancement (or Tongue Backness) 2. Phonology: The study of the sound system of a language; roughly speaking, the study of mental representation of language sound, (i.e. phonemes) Terms: Phones: Speech Sounds Phonemes: A class of speech sounds identified by a native speaker as the same sound; a mental entity or category related to various allophones by phonological rules. o You can test Phonemes with Minimal Pairs. o Minimal Pairs: Two (or more) words that differ only by a single sound in the same position and have different meanings Allophones: A set of nondistinctive realizations of the same phoneme /t/ [t] stop [th] top [?] kitten [ſ] little 2 Nature of speech 1. Non-discreteness of speech signal (linearity issue): There is no sharp physical break between adjacent sounds in a syllable (e.g. b + a + d bad) 2. Segmentation problem (there are no consistent gaps between words in connected speech as there are in written language Input She’ll officially She’s a must to avoid By loose analogy The parade was illegal into opposing camps Is he really? I can’t fit any more on in closing the effective firing rate Error Sheila Fishley She’s a muscular boy. By Luce and Allergy The parade was an eagle into a posing camp Israeli? I can’t fit any, moron enclosing the effect of ... 3. Invariance problem (coarticulation, allophonic variation, diversity in speakers, speed of speech): phoneme’s acoustic properties change across contexts: i.e. they are NOT invariant; e.g. context dependence in consonant (/di/ vs. /du/) 4. Normalization issue (articulator variation, variations in accent, loudness & pitch, and rate) Characteristics of Human Speech Perception 1. Categorical perception: A special pattern of results in identifying and discriminating speech stimuli that differ systematically along a phonetic continuum. In categorical perception, listeners are only able to discriminate between stimuli that are identified as members of two phoneme categories. this pattern of response is suggestive of perceptual discontinuity across a continuously varying physical dimension. a. /p/ vs. /b/ distinction by Voice Onset Time ( 0 – 30 ms: /b/, 30 – 60 ms: /p/) b. Voice Onset Time (VOT): The interval of time between the release of air pressure in the production of word-initial stops and the onset of vocal cord vibration associated with the voicing of the following vowel c. Excellent discrimination across phoneme boundaries, but poor discrimination within a category (correct discrimination shows its peak at the boundary of two categories) 2. Example of categorical perception 3 3. Prototype (Goodness-of-fit): single idealized representation (version) of a phoneme vs. storage of a whole range of exemplars Context effect in Speech perception 1. Bottom-up processing: a listener’s perceptual analysis of the physical sound pattern of speech “upward” from the level of the recognition of phonemes to eventually comprehension of sentence meaning (auditory analysis phonetic analysis phonological semantic syntactic level levels of analysis 2. Top-down processing: The use of prior knowledge or linguistic expectations to facilitate word recognition and rapid sentence comprehension (semantics and syntax perception of syllables and words) 3. Phoneme Monitoring Task: press button when a target sound is heard a. prelexical vs. postlexical code b. word vs. non-word c. probable word vs. less probable word a. phoneme identification vs. word recognition 4. Phoneme Restoration: participants report that the deleted phoneme is perceptually restored even they know it is missing (locating the cough in the speech, comparison between replacing a phoneme vs. adding a noise (result: no detection suggesting pre-lexical perception) The state governors met with their respective legi*latures convening in the capital city. It was fond that the *eel was on the shoe. it was found that the *eel was on the orange. It was found that the *eel was on the axle. It was found that the *eel was on the table. 5. Controversy about whether or not we need to identify phonemes before recognizing a word: research data suggest pre-lexical identification of a phoneme.