Deltas: Source of most of the coastal sediment
advertisement

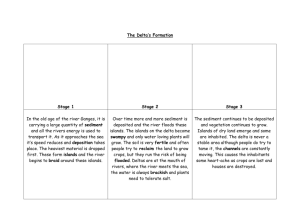
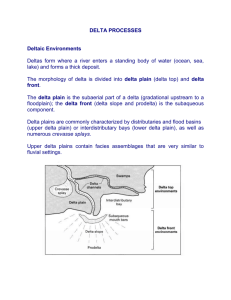
Deltas: Source of most of the coastal sediment Site of much human settlement: proximity to the sea, abundant food supply (fish etc.), and fertile ground. Modern people have also realized that they are the source of many petroleum deposits. Delta development More sediment than can be reworked by coastal processes Change in sediment transport (loss of unidirectional current in the ocean/lake) River system significance and Plate Tectonic Setting Drainage basin area Topography Continental Margin width (active vs. passive margin) Climate and Glaciers-reduce size of continental shelf Mississippi R. delta Ohio, Missouri, Miss. Rivers Young part of delta is 5000-6000 years old 16 recognizable lobes of the delta 50% of Louisiana has been formed by the river in the last 6000 years Environments Transitional between terrestrial and marine Gradational boundaries between environments DISTRIBUTARY CHANNELS Major environments are: Delta Plain-mainly river influenced (terrestrial) Delta Front-mainly subtidal (marine) Prodelta (subtidal) Delta Plain-coastal extension of the river system Channels and their deposits onto the floodplain, channel cut off and oxbow lakes, crevasse splays, levees, etc. Flooding brings sediment (vertical accretion) to the delta plain as the water slows down and deposits its sediment load Channel Migration/Distributaries, produce lateral accretion Delta Front Seaward edge of the delta plain-generally subtidal region of delta Suspended and bedload sedimentation as water velocity drops at end of distributary channel (distributary mouth bar may develop-causing the channel to bifurcate) Suspended load material may move farther offshore Deltas divided into River Dominated Tide Dominated Wave Dominated River Dominated: Widely separated river mouth bars and distributary channels. Fluvial (river) processes dominate-channel/levee/crevasse splay. Interdistributary channel areas alternately fill in and erode as the channel switches. Tide Dominated Tidal channel-style distributary channels, often funnel shaped and longitudinal bars reworked by strong tides. Often full of ill-defined maze of tidal current ridges. Flood and ebb tide produces sedimentary structures indicative of two directional currents Wave dominated deltas Wave processes redistribute most of the sediment supplied to the delta front. Regular beach shorelines, sand spits, and Abandoned beach ridges are common.