STUDY GUIDE FOR MARINE BIOLOGY 180: QUIZ 3 (Ch
advertisement

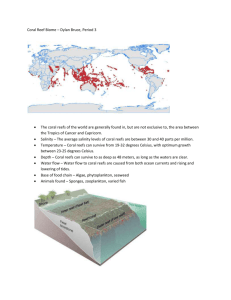
STUDY GUIDE FOR MARINE BIOLOGY 180: QUIZ 3 (Ch. 7-9) The 50-point exam will be composed of 25 multiple choice, True/False, and matching type questions. Understand the following concepts & be able to answer the questions below. NOTE: A portion of Ch. 6 (sections on Marine Mammals & Vertebrate senses) will also be covered on this Quiz. You are responsible for questions #21-27 on the Quiz 2 study guide. Also, you are not responsible for questions #13-16 from Ch. 9 on the Quiz 3 study guide. They will be on the final exam instead. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ch. 7: Estuaries What are estuaries, where are they found, & what are their characteristics? What are the values of estuaries (why are they important)? Why have they been altered & unappreciated? What are the major types of estuaries & how are they formed? Understand basic estuarine circulation & tidal flushing? How do animals deal with changing salinities in estuaries? What are the differences between osmoconformers & osmoregulators? Be familiar with the different habitats (mudflats, salt marsh, etc.) within estuaries, where they are found & typical types of organisms that inhabit each zone. What is the Pacific Flyway? Why do birds use this flyway? Why are estuaries prone to environmental pollution? What are some of the sources? How do toxins bioaccumulate in the food chain (higher animals)? What are DDT & PCB’s & why are they harmful to marine organisms? What is eutrophication & how do fertilizers & sewage entering the marine environment impact coastal zones & species (Hint: think of the Gulf Coast Dead Zone)? What has happened to California’s coastal wetlands (estuaries)? What percent has been lost in Southern Calif.? What is wetland restoration & how do scientists repair damage to estuaries? Be familiar with restoration efforts in local O.C. estuaries (Newport, Bolsa Chica). What types of threats or problems due estuaries continue to face? Ch. 8: Temperate & Coastal Seas In what latitudes are temperate seas found & what constitutes the coastal zone? What types of organisms are commonly found in the coastal zone? What are epifauna & infauna & how do they feed? How do most benthic species reproduce? What is broadcast spawning & what are its advantages & disadvantages? What are meroplankton? What types of factors influence the settling of benthic larvae in their adult habitat? Be familiar with how tides impact the intertidal zone. What types of conditions & stresses do marine species face during high & low tides? Understand the basic characteristics of sandy beaches (how they’re formed, typical species, etc.). How do species like sand crabs (Emerita sp.) obtain their food? What is unique about the reproductive habits if California Grunion (How do they use beaches, when do they spawn, etc.)? How does the rocky intertidal support such a great diversity and abundance of organisms despite the harsh living conditions along the shore? 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Be familiar with the different zones in the rocky intertidal (where they’re located, general conditions, population sizes, typical species, & adaptations of some species to zone conditions). How does most oil enter the coastal ecosystems? How does the type of oil impact the habitat differently? How do large, localized oil spills (tankers, etc.) impact coast marine species? How can humans help to save some animals? In what ways do humans clean up oil spills. Why is scrubbing the intertidal with high pressure, hot water sometimes more damaging than other methods or even leaving things alone? Where is the subtidal zone, what are its general characteristics, & what types of species are common? What are some of the common impacts to kelp forests (natural & human induced)? How does sewage from outfalls damage kelp forests? How is Orange County wastewater treated (primary & secondary treatment)? What is the ultimate fate of wastewater from our homes? What types of things are not removed from wastewater despite primary & secondary treatment? Ch. 9 Tropical & Subtropical Shallow Seas What is a major limiting factor in tropical seas? How do biological organisms like mangroves, seagrasses, & coral reefs alleviate this problem? Be familiar with how coral reefs are formed & how they grow. How do hard (stony) corals differ from soft corals? What are the environmental limitations of hard corals? How do reef inhabitants impact coral? Where are corals found, what temperatures & salinities do they prefer? Why are corals only found in the photic zone? What are zooxanthellae & how do they aid coral survival? What do coral provide zooxanthellae in return? Be familiar with how coral reefs are formed and the general types of reefs. How did Charles Darwin contribute to our understanding of reef formation? How do coral reproduce both sexually & asexually? Be familiar with the threats to coral. What causes coral bleaching? What do coral expel when stressed that lead to bleaching? How does land development & farming impact corals (sedimentation, freshwater runoff, fertilizer, sewage)? How do nutrients cause algae growth & how does algae impact coral? How does overfishing & destructive fishing methods impact coral? What are Crown of Thorns seastars & how do they harm coral. How do excess nutrients (Hint: think of the video about the Great Barrier reef) & overfishing of predators cause an increase in the Crown of Thorns population? What are some of the common types of fish that inhabit coral reefs & what do reef provide these fish? What types of unique symbiotic relationships have reef fish established? How does coloration benefit fish in reefs? What are some of the unique ways the fish use color to aid survival, reproduction, etc. What types of tetrapods are common in tropical & subtropical shallow seas?