LECTURE 1: The Headache Headache
advertisement

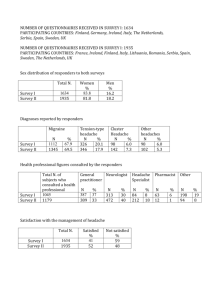
LECTURE 1: The Headache Headache - one of the most frequent painful conditions of the person, the population meeting at 25-40 %. In structure of painful syndromes its prevalence takes the third place after pains in a back and articulate pains. Result of long-term scientific and clinical researches on a way of ordering HEADACHE was creation of the International classification which consists of 13 sections and includes: a migraine; a pressure headache; claster headache; various headache, not connected with structural damages; headache, the heads connected with a trauma; headache, caused by vascular frustration; headache, caused by intracranial processes of not vascular nature; headache, connected with the use of chemical substances or their cancellation; headache, connected with внемозговой an infection; headache, caused by metabolic infringements; headache or the obverse pains caused by a pathology of a skull, a neck, an eye, ears, a nose, additional bosoms, a teeth, a mouth or other structures of a skull and the person; краниальные a neuralgia, morbidity of nervous trunks and деафферентационные pains; not classified headache. Secondary (symptomatic) headaches. The headache can be the leader (and at the initial stage - unique) the complaint at more than 45 various diseases: to a vascular pathology, a craniocereberal trauma, tumours, infectious diseases, эндокринной pathologies etc. To diagnostics criteria symptomatic headache presence of clinical symptoms of the basic disease data of laboratory and tool inspections confirming presence of the basic disease HEADACHE is new symptoms or appears HEADACHE other type, directly connected with the beginning or an aggravation of the basic disease HEADACHE disappears at successful treatment of the basic disease Headache at a craniocereberal trauma At diagnostics posttraumatic HEADACHE it is necessary to remember a Latin proverb: « After that »does not mean« owing to that ». Posttraumatic HEADACHE appears in the first 14 days after a trauma. Sharp posttraumatic pains can be caused intracranial hematomas, traumatic субарахноидальным a hemorrhage, a brain bruise, and also damage of superficial fabrics and inflammatory in them inflammatory and vascular infringements. At disappearance of a painful syndrome in 8 weeks after a trauma it is possible to speak about sharp posttraumatic HEADACHE, at большей its duration diagnose chronic posttraumatic HEADACHE. Chronic posttraumatic pains do not depend on weight of a trauma, months or years can remain, to have a progressing current, in other words, get independent character. In a situation when HEADACHE develops later than in 14 days, more often in the remote period CHMT in some months after a trauma, патогенез it, as a rule, it is not connected with traumatic influence. Transferred ЧМТ-strong стрессорное influence, therefore very often arises the headache of pressure having the psychogenic nature, is more rare мигренеподобные be ill. The pain has the diversified character: stupid, pressing, drilling, is more rare-pulsing. Thus, for diagnostics posttraumatic HEADACHE observance of time parametres (an interval between ЧМТ and occurrence HEADACHE no more than 14 days) is necessary first of all. In other cases develops, apparently, more often meeting primary HEADACHE (HEADACHEН). For its treatment psychotropic preparations, psychological and social rehabilitation are used first of all. Head бол at sharp infringements of brain blood circulation. Frequency and character of a headache at sharp infringements of brain blood circulation essentially differ depending on form ОНМК. At hemorrhage HEADACHE it is observed at the overwhelming majority sick (96 %). Patients feel intensive, bilateral HEADACHE in a kind «blow in a head», some patients have a sensation of a spreading hot liquid in a head, strong tightening, and then распирание. At survey HEADACHE not always comes to light during the first hours diseases as the patient can be in a condition of psychomotor excitation or in a coma. It is defined ригидность occipital muscles. The body temperature raises. For presence acknowledgement субарахноидального hemorrhages spend lumbal a puncture, КТ, МРТ, for reason finding-out-angiografiju at which detection arterial an aneurysm is possible, and also vascular malformation. At ischemic stroke HEADACHE is not облигатным or a typical sign of disease. It is marked only at third of patients, its intensity moderated, a pain have stupid pressing character, and the discomfort in a head is frequently felt. HEADACHE arises during the beginning of a sharp ischemia, however can and precede an ischemic stroke; it is marked in the period of harbingers, as a rule, in a combination to dizziness and eye dimness. If HEADACHE arises later, than in 2 weeks after a stroke патогенез it, most likely, it is not connected with sharp infringement of brain blood circulation and develops on other mechanisms. Neurologic research reveals очаговую organic semiology; paraclinical researches КТ or МРТ - verify presence of a heart attack of a brain. At геморрагическом a stroke (a hemorrhage in a brain) HEADACHE the HELL, usually in a combination to dizziness, a nausea, vomiting develops sharply, usually in the afternoon, at height of activity of the patient, against raised. HEADACHE can be the first symptom of disease, its expressiveness depends on volume of an intrabrain hematoma. Carry out neurologic research for revealing очаговой and общемозговой semiology (consciousness frustration, менингеальные signs). For acknowledgement геморрагического character of a stroke carrying out КТ or МРТ is necessary. Люмбальная the puncture is informative in case of blood break in ликвороносные ways (желудочки a brain). HEADACHE at encephalopathies. De - A syndrome progressing multifocal or diffuse the brain defeats, shown neurologic, neuropsychology and-or mental infringements. It is caused by chronic vascular brain insufficiency and-or repeated episodes of sharp infringements of brain blood circulation. ДЭ arises in advanced age. Most great value in its development the atherosclerosis, an arterial hypertension and their combination, though possible and other reasons (have rheumatism, defeats of vessels in other aetiology, diseases of blood, etc.). The specified features allow to believe, that chronic vascular brain insufficiency at ДЭ is not ethyological factor HEADACHE. Other type of cefalgia (see HEADACHE at elderly) In this case takes place, is formed HEADACHE pressure or secondary HEADACHE, connected with myofascial craniofascial craniocervical syndromes against an osteochondrosis of the backbone rather extended in this age group more often; HEADACHE, connected with infringement of venous outflow, hypoxic HEADACHE as a result of accompanying somatic diseases or a syndrome апное in a dream. The headache connected with an arterial hypertensia. Establishment of reason HEADACHE at patients with ARTERIAL HYPERTENSIA - a problem difficult. On the one hand HEADACHE the-major clinical sign of increase the HELL, with another - extremely often arises a situation when the patient with ARTERIAL HYPERTENSIA does not have correlation between frequency, intensity HEADACHE and increase the HELL, and reception гипотензивных means does not spend to its reduction. Often ARTERIAL HYPERTENSIA flows in in general without HEADACHE. The numerous researches spent on patients, suffering ARTERIAL HYPERTENSIA, have allowed to draw a conclusion that chronic ARTERIAL HYPERTENSIA average or even high degree is not reason HEADACHE. HEADACHE, caused ARTERIAL HYPERTENSIA, can arise at sharp lifting in 24 hours after its normalisation. Such fluctuations the HELL are marked at crysis current ARTERIAL HYPERTENSIA, a hypertensive crisis, presence feohromocitoma, eklampsion. To thicket at patients with ARTERIAL HYPERTENSIA HEADACHE have the mixed character - HEADACHE, connected with sharp liftings the HELL, can be combined with HEADACHE, caused by venous insufficiency, primary HEADACHE, first of all with HEADACHEН. HYPERTENSYON HEADACHE. Increase of intracranial pressure - the important factor патогенеза HEADACHE. It arises in the basic result of such terrible diseases, as a tumour of a brain, inflammatory diseases of a brain (a meningitis, арохноидиты, энцефалиты, a brain abscess) which in the absence of adequate and timely treatment death of the patient can lead. Гипертензионные HEADACHE have a characteristic clinical picture. At the analysis цефалгии first of all it is necessary to pay attention of "danger symptoms» which testify to possible progressing neurologic suffering with development of an intracranial hypertensia and secondary character HEADACHE to presence: Occurrence in short enough term unusual on character (early not observed at the given patient) HEADACHE Прогредиентно accruing HEADACHE Morning HEADACHE Occurrence HEADACHE after physical pressure, strong потягивания, cough or sexual activity Dependence of expressiveness HEADACHE on head and body position Increase or occurrence of new accompanying symptoms in the form of vomiting, temperature, stable neurologic semiology Occurrence мигреноподобных attacks for the first time after 50th years. «Danger symptoms» demand detailed neurologic and ophthalmologic inspection, and also нейровизуальзации (КТ, МРТ) for an exception of current organic process. At tumours of a brain intensity of a headache depends on rates of growth of a tumour and its localisation rather ликворных ways. At a meningitis (an inflammation of soft brain covers) гипертензионная the headache can be accompanied hyperextens of heads, tonic pressure of muscles of a neck (rigid occipital muscles), flexors by a pose of finiteness’s, increase a body temperature, consciousness infringement. HEADACHE, connected with reception of chemical substances or their cancellation. HEADACHE can be display of collateral actions of many medical products. Usually it develops in the beginning of treatment and is more often meets at patients disease of the cardiovascular system, receiving сосудо expanding preparations (nitroglycerine, nitrosorbid, etc.), hypotensiv, antiaritmical means, etc. The list of the medical products, capable to cause HEADACHE is presented in table 1. The Causal relationship between a drug intake and development HEADACHE is established more often retrospective, if: Development HEADACHE on time coincides with reception of medicinal substance Developed collateral reaction coincides with representation about the mechanism of action of a preparation at cancellation of medical product HEADACHE disappears At repeated application of preparation HEADACHE arises again At appointment of a combination of the medical products, capable to cause HEADACHE, their cancellation should be spent consistently. HEADACHE can arise also at the use of alcohol and its substitutes. Deterioration of ecological conditions, especially in large cities, pollution of atmospheric air by exhaust gases, and also a poisoning with industrial poisons can become reason HEADACHE. HEADACHE at metabolic frustration HEADACHE can arise at patients with metabolic infringements arising against the most various somatic and эндокринных diseases. In such cases HEADACHE are combined with signs of metabolic infringements and stop at their normalisation. If HEADACHE last more than 7 days after successful treatment of metabolic infringements, it is possible to believe, that they are caused by other mechanisms. Hypoxia and hypercapnia The most frequent reasons HEADACHE - Hypoxia , hypercapnia and their combination. Similar metabolic infringements happen a hypoventilation consequence at diseases of lungs - a bronchial asthma, a pneumosclerosis, an emphysema more often, etc. is more rare гиповентилляцию the obstruction of the top respiratory ways, reduction of excursion of a thorax at the expense of weakness of respiratory muscles (causes at миастении, a poisoning, sedative means, etc.). Hypoksical HEADACHE develop at mountain illness and are combined with a short wind, cardiovascular infringements, dizziness, the general weakness, emotional infringements. As we already spoke, primary HEADACHE (a migraine, a pressure headache, кластерная HEADACHE), and the symptoms connected with it are the centre of a clinical picture and unite in independent nozological the form. Among primary HEADACHE the most widespread forms are a pressure headache (HEADACHEН) and a migraine. According to different authors, HEADACHEН it is observed in 32-70 % of cases. According to the International classification (1988) allocate incidental and chronic HEADACHEН. Each of the listed forms can be subdivided on HEADACHEН with involving pericranial muscles, i.e. its morbidity at manual palpation, or without that. However such division has no essential clinical value and as believes the majority of researchers, reflects various stages and mechanisms патогенеза HEADACHEН. The diagnosis incidental HEADACHEН is based on following criteria: A.Nalichie, at least, 10 episodes of the headache corresponding to criteria Б-Г. The number of days with such headache is less 180 for a year and 15 in a month. Proceeds from 30 minutes till 7 days. V.Nalichie, at least, two of following characteristics of a pain: compressing or squeezing (not pulsing) character easy or moderate intensity (the pain can reduce efficiency of activity, but does not limit it) bilateral localisation a pain amplifies at circulation on a ladder or similar physical activity. G.Nalichie of two below-mentioned characteristics: absence of a nausea or vomiting (the anorexia can be observed) absence of a combination of a photo-and a phonophobia (one of them can be observed only). Basic difference chronic HEADACHEН is repeatability of attacks HEADACHE more than 180 days in a year or 15 and more days in a month. Prevalence of a migraine is a little bit less and on the average than 16 % of patients with HEADACHE. For M without aura the International association had been developed following diagnostic criteria: 1. Unilateral localisation of a headache. 2. Pulsing character of a headache. 3. The intensity of a pain reducing activity of the patient and accruing at physical activity and walking. 4. Presence at least one of following symptoms: a nausea, vomiting, sveto - or звукобоязнь. 5. Duration of an attack from 4 till 72 o'clock. 6. Presence not less than 5 attacks answering to listed criteria. The aura is shown by local neurologic symptoms which accrue throughout 5-20 minutes and completely disappear within one hour. As well as at m without aura, to an attack can precede продромальный the period. Diagnostics of M with aura is based on criteria: d 2 attacks which are meeting the requirements of point is accompanied, at least, by three of four following characteristics: n one (and more) completely the reversible symptoms specifying on local cerebral корковую or стволовую dysfunction n at least, one symptom of aura gradually develops within more than 4 minutes, or two and more symptoms develop consistently n any symptom of aura 60 minutes do not proceed longer; if them more than one, duration of aura proportionally increases n a headache arises after aura during the different time period which is not exceeding 60 minutes (it can arise also before aura or together with it). At diagnostics HEADACHEН or M it is necessary to consider possibility of similar clinical displays at secondary HEADACHE, that causes observance of one of following positions: the anamnesis, somatic and neurologic inspection do not find out presence of organic disease, other type of a headache, медикаментозно the provoked headache or краниальной a neuralgia; the anamnesis, somatic or neurologic inspections assume possibility of organic disease, but it is excluded by corresponding researches; organic disease is available, but attacks of a headache of pressure are not caused by this disease. Despite simplicity of the resulted diagnostic criteria of the statistican shows, that at the first reference of the patient the migraine is diagnosed in 26 % of cases, and HEADACHEН only in 1 % of cases. Thus 38 % of sick M never consulted to the doctor, from them of 41 % were engaged in self-treatment, 15 % did not hope, that the doctor can really help them. In group of patients with HEADACHEН 64 % never consulted at the doctor; 32 % were engaged in self-treatment; 13 % did not trust doctors. In practice doctors often should face with so-called transformed HEADACHE, as a rule, getting a chronic current. As the most frequent transforming initial HEADACHE factors are considered: abusing by analgetics and ergothamin (50-67 %), development of depressive displays (40-70 %), stress (22-67 %), an arterial hypertensia (1,5-10 %), application of the preparations which have been not connected with treatment HEADACHE (1,5-3,8 %). In many cases transforming factors remain not identified (22 %). For today this group GB has received the name chronic daily (or nearly so daily) HEADACHE (ХЕHEADACHE). ХЕHEADACHE it is not recognised as separate нозологической forms in International classification HEADACHE and is the collective concept which has united various types HEADACHE on the basis of the time characteristic, i.e. quantity of episodes HEADACHE which should exceed 15 days in a month (or 180 days in a year), and duration of each episode should exceed 4 hours. Nevertheless ХЕHEADACHE a widespread clinical problem. Approximately 40 % of the patients observed in specialised clinics, fall under this category HEADACHE. For a designation of this clinical condition terms were at various times used: chronic HEADACHE pressure, a migraine with HEADACHEН, the transformed migraine, etc., actually reflecting pathogenetic updating of initial type HEADACHE, but not completely corresponding to diagnostic criteria primary HEADACHE. Classification ХЕHEADACHE is offered: 1. A chronic headache of pressure. 2. Complex HEADACHE, an including migraine and a pressure headache: the transformed migraine; developed from a pressure headache. In turn, two last forms can be медикаментозно induced or to develop under the influence of other factors. 3. Again arisen daily персистирующая HEADACHE. 4. A chronic hemicrany (Hemicrania continua). Besides, allocate secondary ХЕHEADACHE: connected with a cerebral infection; the heads connected with a trauma and changes in cervical department of a backbone; connected with vascular frustration. Among secondary ХЕHEADACHE influence of the transforming factors set forth above is distinctly traced. At hypertensive illness, for example, as accompanying chronic HEADACHEН symptoms were observed: vomiting in 18 %; dizziness in 86 %; a phonophobia in 57 % of 60 % chronic cervicogen HEADACHE (CHEADACHE) 18 % vomiting, 24 % sveto - or звукобоязнью, 20 % feeling of alarm are accompanied by a nausea. There are data about a combination primary and secondary HEADACHE, in particular, CHEADACHE in 84 % of cases are combined with a migraine, in 42 % with HEADACHEН, in 14 % with both forms HEADACHE. Treatment Therapy of patients with CHEADACHE difficult enough problem. These patients often have physical and emotional medicamentous dependence which is accompanied by low tolerance to the psychogenic influences, shown frustration of a dream and depression. Reception of medicines on purpose detoxication and correction comorbid the factors including is basic: dependence on medicines, personal deviations (boundary and эндогенные frustration), visochno-maxillary dysfunction, intracranial hypo-or a hypertensia. Detoxication is a difficult stage of treatment and often demands hospitalisation. Cancellation symptoms can be observed and persist within weeks. The most effective in these cases is the multimodal approach including аутогенную therapy, based on the biological feedback focused on a muscular tone or skin temperature, individual behavioural therapy, family therapy, the physical exercises, an adequate explanation of effects of medicines and a supervision continuity. The general principles of treatment include: the explanation to the patient of byeffects in comparison with positive potential before is begun treatment the termination of chronic and frequent use soothing, ergothamin and caffeine of the containing preparations cancelling efficiency of current treatment treatment begins with small doses, gradually increasing them depending on possibility of the patient to transfer treatment and by-effects duration of treatment approximately from six weeks to three months as the majority of the preparations used for treatment, have latent time of occurrence of effective action stopping treatment, to do it gradually within several days or weeks, to avoid effect of sudden cancellation. In cases медикаментозно the induced occurrence of any form ХЕHEADACHE treatment is carried out in two stages: a stage of cancellation of preparations and a stage of selection of the therapy adequate to diagnosed form HEADACHE. Upon termination of the period detoxication (if it is required) usual preventive therapy is spent. Preventive treatment HEADACHEН should reduce frequency and-or weight of attacks HEADACHE. It is spent, if: HEADACHE more often, than 2 times week, and their duration more than 3-4 hours; HEADACHE can potentially lead to medicamentous overdose or cause significant invalidity. Treatment HEADACHE begins with energizers or any of preparations of specific treatment of attacks of M. Amytryptilin is a choice preparation, begin treatment about 12,5-25 mg for the night, gradually raising a dose on 12,5-25 mg each 3-6 days to 50-100 mg/day. Therapeutic action begins from 2-3 weeks. It is necessary to remember presence of by-effects, in particular, from антихолинергического actions of a preparation and contra-indications to its application. Main objective preventive, i.e. межприступного treatments is decrease in frequency and weight of the attacks, providing the maximum restriction thus displays of by-effects of applied medicines. To the preparations used with that end in view, concern: b-blokatory (propranolol), антиконвульсанты (carbamazepine, вальпроаты), energizers, not steroid anti-inflammatory preparations (Нурофен Plus), verapamil. Treatment of attacks of a migraine can be divided into nonspecific and specific therapy. Similar division means possibility of use of some the preparations, capable to suspend development of an attack of a migraine (specific treatment) without direct аналгезирующего actions whereas other group of preparations (nonspecific treatment) has the basic action decrease in intensity of actually painful syndrome. Such approach to attack therapy is to a certain extent any, but at the same time underlines possibility of pathogenetic treatment to what it is represented for today. Preparations of nonspecific action concern simple both combined анальгетики and not steroid противовоспатительные means. Necessary addition of treatment often is application метоклопрамида. Specific preparations are: derivatives эрготамина (0,1 % a solution гидротартрата эрготамина till 15-20 a thaw or 1-2 mg in tablets, or дигидроэрготамин in shape назального an aerosol); arterial hypertensiaонисты 1B/D-receptors серотонина. The estimation of efficiency of spent therapy should be focused not only on intensity of a painful syndrome, but also on degree of expressiveness and duration послеприступного conditions дезадаптации. In most cases psychotherapeutic methods of treatment can be necessary addition. The summary on lecture on a theme "Headache". The lecture material is devoted a syndrome of a headache and intended for students бакалавриато a 6-course. In the given lecture the description of concept of a headache, mechanisms of development of headaches (the vascular mechanism, change of physical and chemical properties, гидроцефальный the mechanism, a brain hypostasis), the classification of headaches including primary and secondary headaches is given. The characteristic of a sharp and chronic headache is resulted. Principles and criteria of diagnostics, development mechanisms, differential diagnostics of primary headaches, such as a migraine, a pressure headache, кластерная and a periodic headache are considered. Classification and migraine clinic, principles of its treatment, including specific and symptomatic therapy is in detail resulted.