Rotation Curriculum - Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility
advertisement

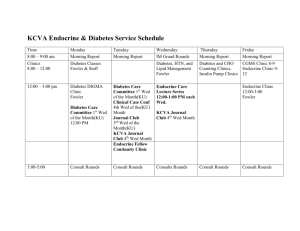
Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility Rotation Schedule Time 8:00 – 9:00 am Monday Morning Report Clinics 8:00 – 12:00 GYN Endo Clinic 12:00 – 1:00 pm Diabetes Care Committee 3rd Wed of the Month 1:00 pm – 5:00 pm OB-High Risk Tuesday IM Grand Rounds Clinical Case Conf 4th Wed of the Month Journal Club 3rd Wed of the Month Endocrine Fellow Clinic Wednesday IM Grand Rounds Thyroid Tumor Board 2nd Wed 7:00 AM GYN Endo Clinic Thursday Morning Report GYN Endo Clinic Endocrine Fellow Core Lecture Series GYN Endo Clinic Friday Morning Report GYN Endocrinology and Infertility Rotation Rotation Director: Linda Nelson, MD Associate Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Kansas, School of Medicine Faculty: Department of OB-GYN KU Medical Center Leland Graves, III, MD Leigh Eck, MD Rajib Bhattacharya, MD David Robins, MD Rudruidee Karnchanasorn, MD Candice Rose, MD Wayne Fowler, MD, PhD Fellowship Coordinator: Location: Lanie Draper (913)-588-6841 University of Kansas Hospital Department of OB-GYN University of Kansas Department of Internal Medicine Duration: One month block rotation in year one or two or the Endocrine Fellowship Educational Goals: 1. To provide a comprehensive experience with the clinical features, diagnosis, natural history, prevention and treatment of disorders of reproduction. 2. Acquisition of a knowledge-base and cognitive skills to be an effective consultant and practitioner of the discipline of Endocrinology 3. To acquire/maintain a professional demeanor, ethical standards and humanistic qualities required to be an effective, respected physician 4. To provide education to others and develop life-long learning skills 5. Maintain skills in general internal medicine 6. To produce a graduate who is competent, compassionate, and certifiable by the ABIM in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism Objectives: 1. 2. Hands-on experience with history taking and examination of a large number of cases representative of the specialty GYN Endocrinology and Infertility as well as general endocrinology. Analysis of the clinical clues and laboratory data to arrive at a differential diagnosis. 3. 4. 5. 6. Providing a plan for further evaluation and/or therapy. Utilizing diagnostic and therapeutic modalities in the most cost-effective manner. Learn the pathogenesis, pathophysiology of a broad array of d diseases of reproduction and reproductive health. Understand the usefulness and limitations of diagnostic and therapeutic modalities. Methods: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Case based, small group interactive discussions Problem-oriented reading Role modeling by experienced faculty Interactions with other housestaff and faculty Case base conferences Didactic lectures Patient management with supervision of faculty Principle Teaching/learning Activities Conferences Endocrinology Journal Club (JC): The third Tuesday of each month, located in the Cray Diabetes Center Conference room in the Endocrinology outpatient clinic. 12:001:00 pm. Articles are present for critical review by faculty and residents. Each resident will present one article during his or her rotation. The resident will receive assistance from a faculty member in choosing an appropriate article. Endocrinology Round Table (ERT): This conference includes the faculty of the University of Kansas School of Medicine and the University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine as well as the Endocrinologist of the greater Kansas City area. Invited speakers present topics of significance in Endocrinology. Fellow are encouraged to attend. Dinner is served. This conference is held 4-6 times per year. Clinical Case Conference (CCC): This conference takes place on the last Wednesday of each month in the Cray Diabetes Conference room, 12:00-1:00. The staff with discussion of diagnostic and management issues presents unusual and difficult cases. Endocrinology Core Curriculum (ECC): This conference occurs weekly with the residents, students and endocrinology fellows. ECC is held on Tuesday mornings 7:30 – 8:30 am in the clinic conference room. Clinical cases are presented by the faculty in the various areas of Endocrinology. Discussion of diagnostic and management of various endocrinological areas are discussed. GYN Endocrine and Reproductive Clinics (GYN ENDO): These clinics will take place under the direction and supervision of Dr. Linda Nelson in department of OB-GYN at KU Medical Center. They will occur Tuesday mornings, Wed. mornings and all day Thursday. Patient in seen in these clinics will include patients with menstrual abnormalities, polycystic ovarian syndrome, and infertility disorders. High Risk Obstetric clinic HROB: The fellow will participate in high risk obstetric clinic with the emphasis on gestational diabetes recognition and management as well as the management of pregnancy in the patient with previously diagnosed diabetes type 1 or type 2. This clinic is a multidisciplinary clinic involving physicians, nurse educators, and dieticians. Outpatient Phone Consultation (OCS) patient phone calls are discussed. Issues of diagnosis and management are reviewed with the fellow. There is no in hospital night call. The Endocrine fellow will participate in weekend consultation rounds. When on call the fellow may be required to return to the hospital to provide consultation. This occurs rarely. Fellows will be given and average of one day off of all responsibilities per week. Home beeper call will not be counted towards total duty hours (not to exceed 80 yours per week). Educational Goals, Learning Activities and Evaluation Tools by Competency Legend for learning activities: EC-Endocrinology outpatient clinics. ECSEndocrinology in-patient consultation service. ECC-endocrinology core curriculum. CCC-clinical case conference. ERT- endocrine round table. EJ-endocrinology journal club. Legend for evaluation techniques: VE-verbal evaluation and mid and end rotation; miniCEX-mini Clinical Evaluation Exercise; SE-self-evaluation, WE-written examination. NCE- Nurse Clinician Evaluation 1st Year Fellow CORE COMPETENCY: PATIENT CARE Goal: Develop and demonstrate expertise in consultation and assessment care management of endocrinology patients. Objectives: Learning Evaluation Activities Tools Perform efficient, focused interview and physical EC, ECS VE examination Diagnosed and initiate treatment EC, ECS, OPC, CCC, VE, ERT, JC, Provide appropriate patient follow-up EC, ECS, VE CORE COMPETENCY: MEDICAL KNOWLEDGE Goal: : Demonstrate knowledge and competency in understanding disease process, diagnosing treating various common endocrine diseases Objectives: Beginning competency to diagnose and treat the follow diseases: Thyroid Diseases Hyper and hypothyroid disorders Nodular thyroid disease Thyroid Cancer Goiter Pituitary disorders Prolactinoma Non-functioning adenoma Hypopituitarism Adrenal Disorders Hyperaldosteronism CAH Hirsuitism Gonadal Disorders Testicular dysfunction Ovararian failure PCOD Gonadal dysgenesis. Primary and Secondary Amenorrhea Infertility Menopause Dysfunctional uterine bleeding Hirsuitism and virilization Male infertility Male hypogonadism Gynecomastia Screening for Endocrinologic causes of infertility Use of semen analysis Testicular biopsy Anatomic evaluation of the female reproductive tract. Experience in Ovulation indection with clomiphene Gonadotropins GnRH Review of the the techniques of Artificial insemination GIFT IVF Learning Activities EC, ECS, JC, CCC, ERT, OCS, GYN ENDO Evaluation Tools VE, WE Diabetes in Pregnancy Diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes Management of the patient with type 1 diabetes during pregnancy CORE COMPETENCY: PRACTICE BASED LEARNING AND IMPROVEMENT Goal: Learn to investigate and evaluate personal patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence related to endocrinology, and improve personal patient care practices. Objectives: Identify gaps in knowledge Develop evidence-based strategies for filling in knowledge gaps Learning Activities EC, ECR, EC, ECR, Evaluation Methods VE, SE, NCE VE, SE, NCE CORE COMPETENCY: INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS Goal: Demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills in medical practice that develop and maintain effective information exchange and collaboration with endocrinology patients and family members as well as other professional associates Objectives: Learning Evaluation Activities Methods Exhibits compassion towards patients EC, ECS VE, mini-CEX, SE Listens well to patients Explains treatment plans, rationale, and risks and benefits to patients in understandable language Concludes patient visits by asking if the patient has any questions Facilitates effective patient care by communicating patient issues and treatment recommendations to colleagues, nursing, and ancillary staff Writes notes and signs name legibly. CORE COMPETENCY: PROFESSIONALISM Goal: Demonstrate commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles, and sensitivity to a diverse endocrinology patient population Objectives: Learning Evaluation Activities Methods Behave professionally toward patients, families, EC, ECR, VE, SE, NCE colleagues and all members of the healthcare team CORE COMPETENCY: SYSTEM BASED PRACTICE Goal: Demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and the ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care in that is of optimal value to their endocrinology patients. Objectives: Learning Evaluation Activities Methods Understanding the team approach to comprehensive EC, ECS, CCC, VE, WE diabetes management JC Participation in Certified Diabetes Educator Diabetes Care Dietician Committee Social Service Economic Burden and available assistance. Understanding how to utilize computer tools to assure quality health care goals across the practice (Areas in bold will be an emphasis of this rotation) 2nd Year Fellow CORE COMPETENCY: PATIENT CARE Goal: Demonstrate continued and proficient expertise in consultation and assessment care management of endocrinology patients. Objectives: Learning Evaluation Activities Tools Perform efficient, focused interview and physical EC, ECS VE examination Diagnosed and initiate treatment EC, ECS, OPC, CCC, VE, ERT, JC, Provide appropriate patient follow-up EC, ECS, VE CORE COMPETENCY: MEDICAL KNOWLEDGE Goal: : Demonstrate continued knowledge and competency in understanding and teaching disease process, diagnosis and treatment of various common endocrine diseases Objectives: Learning Evaluation Activities Tools Continued competency to diagnose and treat the EC, ECS, JC, CCC, VE, WE follow diseases: ERT, OCS, GYN ENDO Thyroid Diseases Hyper and hypothyroid disorders Nodular thyroid disease Thyroid Cancer Goiter Pituitary disorders Prolactinoma Non-functioning adenoma Hypopituitarism Adrenal Disorders Hyperaldosteronism CAH Hirsuitism Gonadal Disorders Testicular dysfunction Ovararian failure PCOD Gonadal dysgenesis. Primary and Secondary Amenorrhea Infertility Menopause Dysfunctional uterine bleeding Hirsuitism and virilization Male infertility Male hypogonadism Gynecomastia Screening for Endocrinologic causes of infertility Use of semen analysis Testicular biopsy Anatomic evaluation of the female reproductive tract. Experience in Ovulation indection with clomiphene Gonadotropins GnRH Review of the the techniques of Artificial insemination GIFT IVF Diabetes in Pregnancy Diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes Management of the patient with type 1 diabetes during pregnancy CORE COMPETENCY: PRACTICE BASED LEARNING AND IMPROVEMENT Goal: Demonstrate competency in ability to investigate and evaluate personal patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence related to endocrinology, and improve personal patient care practices. Objectives: Identify gaps in knowledge Develop evidence-based strategies for filling in knowledge gaps Learning Activities EC, ECR, EC, ECR, Evaluation Methods VE, SE, NCE VE, SE, NCE CORE COMPETENCY: INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS Goal: Demonstrate continued competent interpersonal and communication skills in medical practice that develop and maintain effective information exchange and collaboration with endocrinology patients and family members as well as other professional associates Objectives: Learning Evaluation Activities Methods Exhibits compassion towards patients EC, ECS VE, mini- CEX, SE Listens well to patients Explains treatment plans, rationale, and risks and benefits to patients in understandable language Concludes patient visits by asking if the patient has any questions Facilitates effective patient care by communicating patient issues and treatment recommendations to colleagues, nursing, and ancillary staff Writes notes and signs name legibly. CORE COMPETENCY: PROFESSIONALISM Goal: Demonstrate commitment to carrying out and teach professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles, and sensitivity to a diverse endocrinology patient population Objectives: Learning Evaluation Activities Methods Behave professionally toward patients, families, EC, ECR, VE, SE, colleagues and all members of the healthcare team NCE CORE COMPETENCY: SYSTEM BASED PRACTICE Goal: Demonstrate continued competent ability and teaching approach to increase an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and the ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care in that is of optimal value to their endocrinology patients. Objectives: Learning Evaluation Activities Methods Understanding the team approach to comprehensive EC, ECS, CCC, JC VE, WE diabetes management including: Participation in Diabetes Care Certified Diabetes Educator Committee Dietician Social Service Economic Burden and available assistance. Understanding how to utilize computer tools to assure quality health care goals across the practice (Areas in bold will be an emphasis of this rotation) Resources: Up-to Date: Provided by the University of Kansas Medical Center, On Line William’s Text book of Endocrinology: Provided by the Endocrine division Important Endocrine Journals available on line to the Fellows: Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism Diabetes Diabetes CARE Journal of Bone and Mineral Research New England Journal of Medicine JAMA Evaluation: The fellow will receive verbal and written evaluation by the faculty responsible for the consultative service at the completion of each month. The faculty responsible for the evaluation will receive input from all faculty involved in the rotation that month.