CHAPTER 14 LECTURE NOTES: STRESS & HEALTH
advertisement
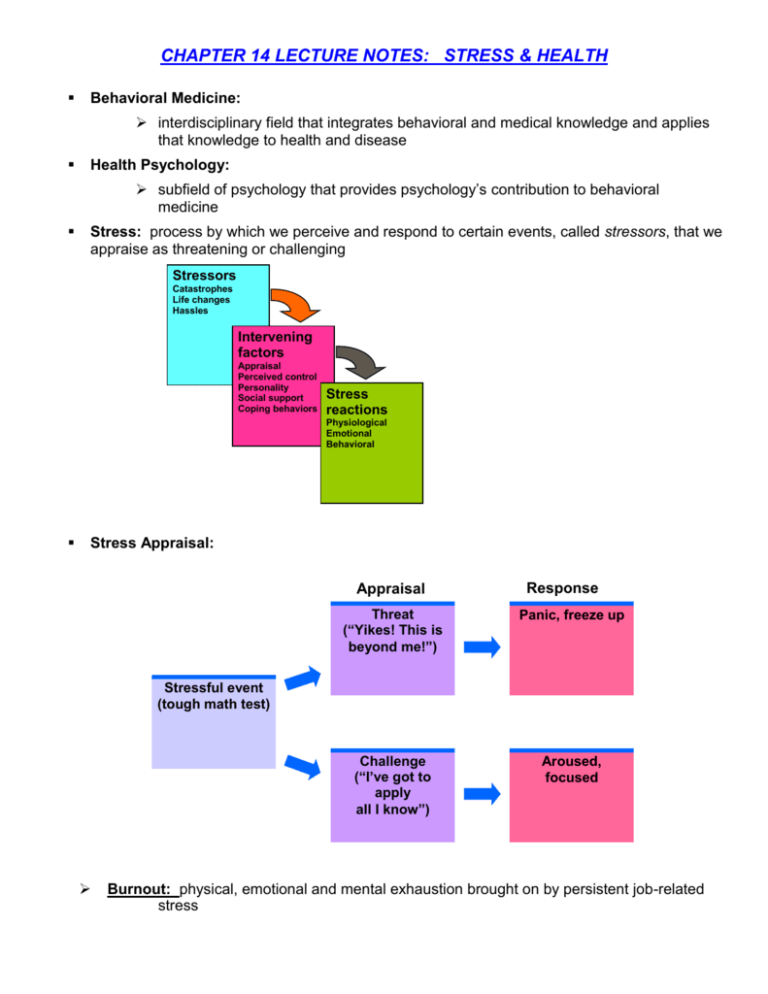
CHAPTER 14 LECTURE NOTES: STRESS & HEALTH Behavioral Medicine: interdisciplinary field that integrates behavioral and medical knowledge and applies that knowledge to health and disease Health Psychology: subfield of psychology that provides psychology’s contribution to behavioral medicine Stress: process by which we perceive and respond to certain events, called stressors, that we appraise as threatening or challenging Stressors Catastrophes Life changes Hassles Intervening factors Appraisal Perceived control Personality Social support Coping behaviors Stress reactions Physiological Emotional Behavioral Stress Appraisal: Appraisal Response Threat (“Yikes! This is beyond me!”) Panic, freeze up Challenge (“I’ve got to apply all I know”) Aroused, focused Stressful event (tough math test) Burnout: physical, emotional and mental exhaustion brought on by persistent job-related stress The body’s resistance to stress can only Last so long before exhaustion sets in Stress resistance Stress or occurs Phase 1 Alarm reaction (mobilize resources) Phase 2 Resistance (cope with stressor) Phase 3 Exhaustion (reserves depleted) General Adaptation Syndrome: Selye’s concept of the body’s adaptive response to stress in three stages The body’s resistance to stress can only last so long before exhaustion sets in Stress resistance Stressor occurs Stressful Life Events: Phase 1 Alarm reaction (mobilize resources) Phase 2 Resistanc e (cope with stressor) Phase 3 Exhaustion (reserves depleted) Catastrophic Events: earthquakes, combat stress, floods Life Changes: death of a loved one, divorce, loss of job, promotion Daily Hassles: rush hour traffic, long lines, job stress, burnout Stress and the Heart o Coronary Heart Disease clogging of the vessels that nourish the heart muscle leading cause of death in many developed countries o Type A: Friedman and Rosenman’s term for competitive, hard-driving, impatient, verbally aggressive, and anger-prone people o Type B Friedman and Rosenman’s term for easygoing, relaxed people Stress and Disease Psychosomatic Disease o psychologically caused physical symptoms Psychophysiological Illness “mind-body” illness any stress-related physical illness some forms of hypertension some headaches distinct from hypochondriasis-- misinterpreting normal physical sensations as symptoms of a disease Lymphocytes o two types of white blood cells that are part of the body’s immune system B lymphocytes form in the bone marrow and release antibodies that fight bacterial infections T lymphocytes form in the thymus and, among other duties, attack cancer cells, viruses, and foreign substances Negative emotions and health-related consequences: Heart disease Persistent stressors and negative emotions Release of stress hormones Immune suppression Unhealthy behaviors Autonomic nervous system effects (smoking, drinking, poor nutrition and sleep) (headaches, hypertension) Promoting Health Aerobic Exercise: sustained exercise that increases heart and lung fitness Biofeedback: system for electronically recording, amplifying, and feeding back information regarding a subtle physiological state blood pressure muscle tension Modifying Type A life-style can reduce recurrence of heart attacks Percentage 6 of patients with recurrent 5 heart attacks (cumulative 4 average) Control patients Modifying lifestyle reduced recurrent heart attacks 3 2 Life-style modification patients 1 0 1978 1979 1980 Year 1981 1982 Life events Personal appraisal Challenge Threat Personality type Easy going Nondepressed Optimistic Hostile Depressed Pessimistic Personality habits Nonsmoking Smoking Regular exercise Sedentary Good nutrition Poor nutrition Level of social support Close, enduring Lacking Tendency toward Health Illness Predictors of mortality 1 Relative risk of dying 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Not smoking Men Regular exercise Weekly religious attendance Women attendance Subfields of Alternative Medicine: Subfields of Alternative Medicine Alternative systems of medical practice Health care ranging from self-care according to folk principles, to care rendered in an organized health care system based on alternative traditions or practices Bioelectromagnetic applications The study of how living organisms interact with electromagnetic (EM) fields Diet, nutrition, life-style changes The knowledge of how to prevent illness, maintain health, and reverse the effects of chronic disease through dietary or nutritional intervention Herbal medicine Employing plan and plant products from folk medicine traditions for pharmacological use Manual healing Using touch and manipulation with the hands as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool Mind-body control Exploring the mind’s capacity to affect the body, based on traditional medical systems that make use of the interconnectedness of mind and body Pharmacological and biological treatments Drugs and vaccines not yet accepted by mainstream medicine Smoking-related early deaths Number of deaths per 100,000 33,34 8 1,68 6 1,13 5 Smoking Suicide Vehicle crash 55 6 20 2 HIV/ AIDS Homicide Cause of death Obesity and Weight Control Weight Discrimination: When women applicants were made to look overweight, subjects were less willing to hire 7 Willingness to hire scale (from1: definitely not hire) to 7: definitely hire) 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Women Normal Men Overweight