GASES
advertisement
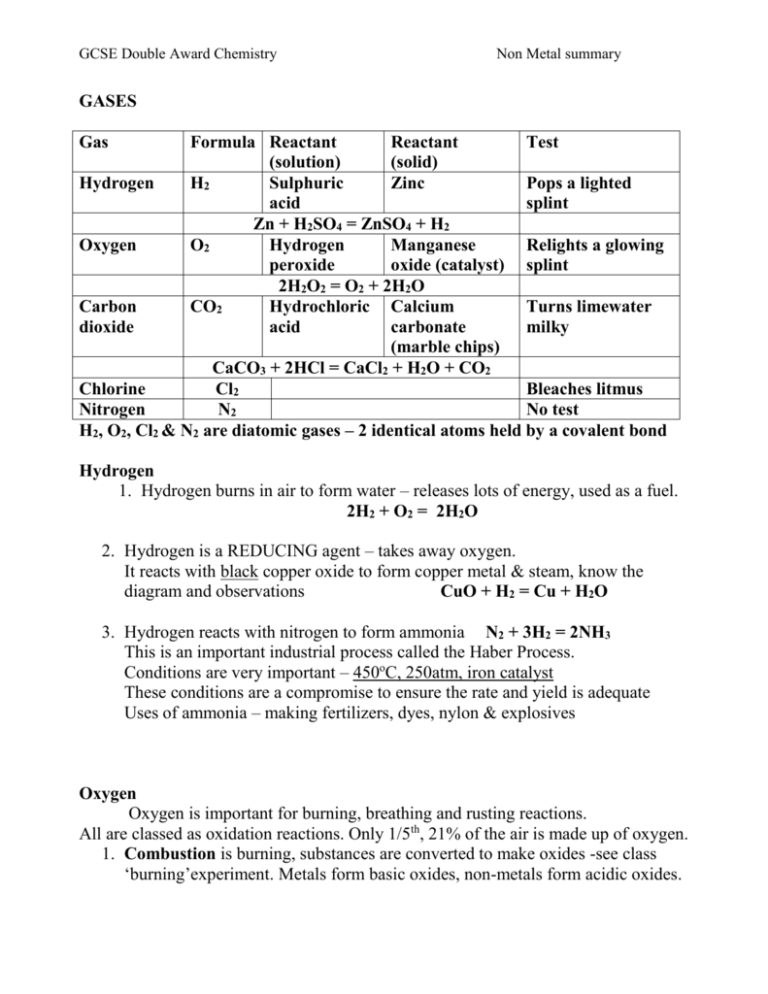
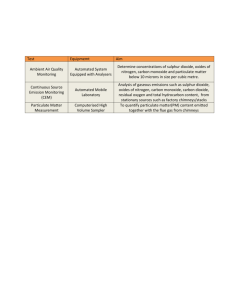
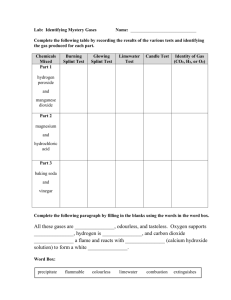
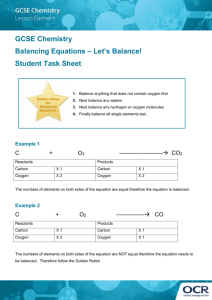
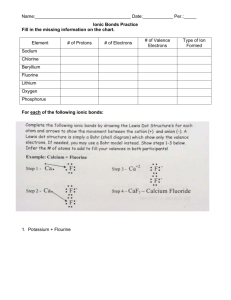
GCSE Double Award Chemistry Non Metal summary GASES Gas Formula Reactant Reactant Test (solution) (solid) Hydrogen H2 Sulphuric Zinc Pops a lighted acid splint Zn + H2SO4 = ZnSO4 + H2 Oxygen O2 Hydrogen Manganese Relights a glowing peroxide oxide (catalyst) splint 2H2O2 = O2 + 2H2O Carbon CO2 Hydrochloric Calcium Turns limewater dioxide acid carbonate milky (marble chips) CaCO3 + 2HCl = CaCl2 + H2O + CO2 Chlorine Cl2 Bleaches litmus Nitrogen N2 No test H2, O2, Cl2 & N2 are diatomic gases – 2 identical atoms held by a covalent bond Hydrogen 1. Hydrogen burns in air to form water – releases lots of energy, used as a fuel. 2H2 + O2 = 2H2O 2. Hydrogen is a REDUCING agent – takes away oxygen. It reacts with black copper oxide to form copper metal & steam, know the diagram and observations CuO + H2 = Cu + H2O 3. Hydrogen reacts with nitrogen to form ammonia N2 + 3H2 = 2NH3 This is an important industrial process called the Haber Process. Conditions are very important – 450oC, 250atm, iron catalyst These conditions are a compromise to ensure the rate and yield is adequate Uses of ammonia – making fertilizers, dyes, nylon & explosives Oxygen Oxygen is important for burning, breathing and rusting reactions. All are classed as oxidation reactions. Only 1/5th, 21% of the air is made up of oxygen. 1. Combustion is burning, substances are converted to make oxides -see class ‘burning’experiment. Metals form basic oxides, non-metals form acidic oxides. GCSE Double Award Chemistry Non Metal summary Water is a neutral oxide and aluminium & zinc are amphoteric ie. both acidic and basic. Compounds also form their oxides when they burn: Methane + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water CH4 + 2O2 = CO2 + 2H2O 2. Breathing is RESPIRATION. Glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water 3. Rusting is the oxidation of iron in the presence of water. Rust is hydrated iron III oxide, look up the methods used to prevent rust. Carbon Dioxide 1. Carbon dioxide is an acid gas, it dissolves in water to form a weak acid known as carbonic acid H2CO3. H2O + CO2 = H2CO3 (Look up its role in Hard water) 2. Carbon dioxide reacts with sodium hydroxide to form a white crust of sodium carbonate NaOH + CO2 = Na2CO3 + H2O 3. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas and contributes to global warming – know effects Chlorine Chlorine is a pale green toxic gas, it has many uses as a disinfectant – know all uses It is made from the electrolysis of seawater (brine), the chloro-alkali industry Sodium chloride + water ---------------Hydrogen+ chlorine + sodium hydroxide (cathode) (anode) Chlorine will displace bromides & iodides, they will change to display their colour. Chlorine + sodium bromide = bromine + sodium chloride Green gas colourless solution =red/orange solution Cl2 + 2NaBr = Br2 + 2NaCl Chlorine + sodium iodide = iodine + sodium chloride (colourless to brown) Cl2 + 2NaI = I2 + 2NaCl GCSE Double Award Chemistry Non Metal summary Nitrogen Nitrogen is an unreactive gas, it has a triple bond so too much energy is needed to break the bond. Know uses. Ammonia NH3 as above WATER Water is a covalent molecule – draw it out. Water is essential to all life Water of crystallisation is the water bonded inside a crystal. Salts with water are Hydrated, when the water is removed are Anhydrous Hydrated Copper sulphate crystals = anhydrous copper sulphate + water CuSO4.5H2O = CuSO4 + 5H2O Blue white Anhydrous copper sulphate is used as a chemical test for water; colour change white to blue Water pollution is caused by fertilisers, detergents and sewage – read up effects Sulphur Sulphur is a yellow solid, it has a low melting point, is insoluble in water and a poor conductor of electricity. Sulphur is found in volcanic areas and is an impurity in fossil fuels (acid rain). 1. Sulphur burns with a blue flame to form fuming sulphur dioxide S + O2 = SO2 2. Sulphur reacts with metals to form metal suphides (experiment) This is an exothermic reaction that glows red even when the heat is removed Fe + S = FeS The oxides of sulphur form strong acids; SO2 forms sulphurous acid, H2SO3 SO3 forms sulphuric acid, H2SO4 Acid rain is caused by the acidic gases released by burning fossil fuels & erupting volcanoes; sulphur dioxide & sulphur trioxide are examples. It affects Scandinavian countries most due to prevailing winds blowing the acidic gases north & due to the cold conditions increasing the solubility of the gases. Acid rain has many negative environmental effects; kills plants, kills fish, removes nutrients from soil, corrodes buildings and statues, etc Acid rain must be reduced by: Burning less fossil fuels,Desulphurising fossil fuels Cleaning (scrubbing) exhaust gases by lining chimneys with limestone Using alternative energy sources