Colon rectal cancer (W95)
advertisement

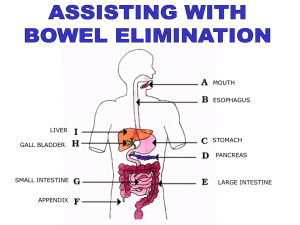
COLON/RECTAL CANCER Definition: Carcinoma of the colon and/or rectum, usually called colorectal cancer Etiology: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. causes about 20% of deaths from malignant disease in the US, in Western countries, it ranks second only to skin cancer most of the cancers occur in the rectum or sigmoid colon and 95% are adenocarcinomas it is predominantly a disease of the elderly; most patients are 60-75 years old females are at greater risk for colon cancer males are at greater risk for rectal cancer factors include: a. diet (low fiber, more animal protein, fat, and refined carbohydrates) b. familial adenomatous polyps of the colon c. previous hx of the disease d. women with a hx of breast or uterine CA e. UC and less significant, Crohn’s dz. Signs and Symptoms: 1. onset of sxs is very gradual and depends on the tumor location, size, type and complications (ie. tumor is irritating any adjacent organs, like the urinary bladder or the stomach; or if it leads to bowel perforation and peritonitis) 2. rectal bleeding 3. abdominal pain 4. change in bowel habits and/or size/shape/color of stool; esp. gradually increasing constipation and black stool 5. acute obstruction: colicky pain, increasing abdominal distention, failure to pass stools or gas 6. weight loss 7. anorexia Location specifics: a. right colon: may have palpable mass through abdominal wall; fatigue and weakness from anemia due to occult blood; obstruction (change in bowel habits) is usually a late sign b. left colon: obstruction is more of an issue here; often the patient will experience alternating constipation with diarrhea; stools may be overly bloody c. rectum: primary sxs is defecation of bloody stools Lab Findings: 1. 65% of tumors are evident upon digital or sigmoidscopic exam 2. sigmoidoscopy/colonoscopy: surpassed barium studies as the procedure of choice for diagnosis 3. biopsies of tumor 4. stool analysis for occult blood 5. elevated levels of CEA (serum carcinoembryonic antigen) 6. anemia (usually normochromic, normocytic) Course/Prognosis: 1. conventional treatment of choice is surgical resection and, less importantly, post-surgical procedures such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy and immunotherapy 2. post-surgical procedures have not been shown as particularly helpful or effective 3. prognosis varies with extent of disease, location in bowel, degree of wall infiltration, local or distant metastasis 4. in patients with CA limited to the mucosa, the 5 year survival rate is 70%; with spread to the lymph nodes it drops to 30% Differential Diagnosis: 1. hemorrhoids 2. diverticulitis (when it causes obstruction of the bowel) 3. UC 4. other GI dz. Nutrition: 1. 2. 3. alkaline fasts under physician supervision 7-21 days protection against colon CA: increase cellulose and hemicellulose food in diet [fiber] recommendations for all cancers: sea weeds, mushrooms (Chinese black, Shiitake), figs, beets, beet tops, papaya, mung beans, licorice, sea cucumbers, carrot, garlic, walnut, litchi fruit, mulberries, asparagus, pumpkin, burdock, dandelion greens, white fungus, taro roots, pearl barley, grains, fresh fruits and vegetables, squash, vitamin A rich foods Remedies: a. b. soup of black or ling zhi mushrooms and white fungus, bid boil together mung beans, pearl barley, adzuki beans and figs 1 COLON/RECTAL CANCER c. Avoid: 1. 2. 3. dandelion, burdock and chrysanthemum flower tea meat, chicken, cinnamon, anise, pepper, spicy foods, high fat foods, dairy products coffee, smoking constipation Supplements: 1. vitamin A (200,000 IU qd) [toxic dose] 2. vitamin C (8-14g qd) 3. vitamin E (800 IU qd) 4. calcium 5. selenium (300mcg qd) 6. acidophilus Hydrotherapy: 1. fever treatment 2. constitutional hydrotherapy Physiotherapy: 1. breathing exercises 2. aerobic exercise (mild) Botanicals: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Avena sativa: nervous debility of convalescence Baptisia tinctoria: for tumorous or malignant conditions Berberis aquifolium: disease due to cancerous cachexia Conium maculatum (toxic): pain of cancer Echinacea spp.: increases interferon production, purifies blood Gentiana lutea: bitter; promotes appetite, improves digestion in chronic debility Larrea divaricata (Mexican folklore) Phytolacca decandra (toxic): carcinoma, adenoma; hard, swollen lymph nodes Rumex crispus: to prevent early stages of cancer Taraxacum officinale: loss of appetite, weak digestion Trifolium pratense: alterative; purifies blood, cancerous diathesis; with daily use patients are slower in developing carcinoma after excision 12. Viola odorata: malignant disease, neoplasm in alimentary canal; after tumor extirpation to prtect from metastases; combines well with Galium sparine 13. Viscum album (toxic): tumor-inhibiting effects reported, mian use as follow-up therapy after surgery or radiation; extracts available: Iscador, Phenesol, Helixior Formulas: a. constitutional cleansing and CA support formula: Glycyrrhiza glabra (12g), Trifolium pratense (12g), Articum lappa (6g), Stillingia sylvatica (toxic) (6g), Berberis aquifolium (6g), Phytolacca decandra (toxic) (6g), Rhamnus purshiana (3g), Rhamnus frangula (toxic) (3g), Xanthoxylum americanum (3g); combine the dry herbs, place in 3 cups of water and simmer for 10-15 min., cool, strain and store in a dark glass jar; SIG: use 2-4 Tbsp. Tea in a 1/3 cup water adding 1-2 drops of saturated potassium iodide and 5-11 drops strong iodide (Lugol’s) solution; take qid, pc and before bed Homeopathy: 1. Alcohol: in potency useful for pains in CA 2. Alumen: obstinate constipation; stools hard as stone; hemorrhages of dark blood; rectal CA; abdomen colic; pain > from pressure; < when walking, with fullness and heaviness; first hard then soft stools and pains following; very weakening coliquative diarrhea; ulceration in rectum; painful excrescences; fetid; bloody 3. Cadmium iodum: ulceration of transverse colon; < extreme heat or cold; hates everything and everybody; CA from aluminum toxicity; itching of anus and rectum felt during the day only; constipation; frequent desire; tenesmus; abdomen bloated 4. Hydrastis canadensis: CA rectum; constipation aggravated by cathartic medicines; during stool, smarting, burning pains in rectum; after stool, burning and smarting in rectum; long lasting pain in rectum; hard, adherent 5. Nitric acid: bowels constipated with fissures in rectum; rectum feels torn; tearing pains during stools; violent cutting pains after stools, lasting for hours; hemorrhages form bowels, profuse, bright; diarrhea, slimy and offensive; after stools, irritable and exhausted; colic relieved from tightening clothes 6. Ruta graveolens: carcinoma affecting lower bowel; difficult feces, executed only with straining; constipation alternating with mucous, frothy stools; d/c of blood with stools; colic with burning or gnawing pain; frequent unsuccessful urging to stool; when sitting, tearing stitches in rectum 7. Scrophularia: colic below navel; pain in sigmoid flexure and rectum; several stools daily with tenesumus 2 COLON/RECTAL CANCER 8. Sepia: CA of rectum; feeling of relaxation and bearing down in abdomen; bleeding at stool and fullness of rectum; constipation; large, hard stools; feeling of ball in rectum; cannot strain; with great tenesmus and pains shooting upward; dark brown, round balls glued together with mucus; soft stool difficult; debilitating diarrhea 3