Lab_1 pH and Protein Solubility-instructor
advertisement

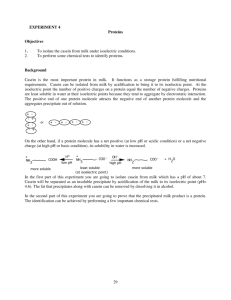
pH and Protein Solubility Materials: Casein 2M HCl 2M NaOH Analytical balance Magnetic stirrer and Stirring bar DI water 0.1M NaOH 600mL Beaker or Flask 2mL Pipets, graduated Safety: Wear gloves and goggles Procedures: Initial Casein Solution: Add 25mL of 0.1M NaOH and stirring bar to a 600ml beaker or flask on a magnetic stirrer Add 225mL of DI water and stir at moderate speed Add 1g of casein and stir to dissolve (soln. will be slightly cloudy) Insert pH probe in solution and record pH value Casein Solution after HCl: With rapid stirring add 2M HCl in 0.5mL increments using a graduated pipet After 1-2mL of acid has been added, the cloudiness will reach a maximum (Isoelectric Point pH at isoelectric point is 4-5) Insert pH probe in the solution and record pH value Continue adding 2M HCl in 0.5mL increments until solution is clear again (Cloudiness will fade and ppt. will redissolve after addition of 2-3mL of acid, when the pH drops below the isoelectric point, pH≤ 2) Casein Solution after NaOH: Continue to stir the soln. reverse the process by adding 2M NaOH in 0.5mL increments using a clean graduated pipet After 2-3mL has been added protein will ppt. out again (isoelectric point) Continue adding NaOH in 0.5mL increments with stirring until soln. is clear again (soln. will clear after additional 1-2 mL of NaOH, pH > 10-12) Discussion: Casein is principal protein in milk (80% of total protein content) Casein is a phosphoprotein (it contains a large # phosphate groups attached to amino acid side chains in its polypeptide structure) Negatively charged phosphate groups are balanced by positively charged calcium ions and are responsible for the high nutritional calcium content in milk Casein is almost completely insoluble in water at neutral pH=7 Casein, like other proteins, is an ionic species containing amino groups and carboxyl groups on its terminal amino acid It also contains a variety of other acidic and basic groups on the side chains of its non-terminal amino acids. The effect of pH on the solubility of casein reflects the ionization of the acidic and basic groups in its structure At high pH: casein will have net negative charge due to ionization of all acidic side chains (CO2-) in its structure B/c casein is ionized at high pH values; it is soluble in dilute NaOH soln. At low pH: casein will have a net positive charge due to the protonation of all basic side chains (NH3+) in its structure B/c casein is ionized at low pH values; it is also soluble in strongly acidic soln. At intermediate pH: casein will contain roughly equal numbers of positively and negatively charged groups protein will have a net charge of zero casein is insoluble in neutral soln. b/c it is not charged under these conditions solubility of protein is usually minimum at its isoelectric point Isoelectric point: pH at which a protein has a net charge of zero for casein do to the attached phosphate groups the isoelectric point is close to pH=4 This project is funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community Based Job Training Grant as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: against any individual in the United States, on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age disability, political affiliation or belief; and against any beneficiary of programs financially assisted under Title I of the Workforce Investment Act of 1998 (WIA), on the basis of the beneficiary’s citizenship/status as a lawfully admitted immigrant authorized to work in the United States, or his or her participation in any WIA Title I-financially assisted program or activity. “This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solution is copyrighted by the institution that created it. Internal use by an organization and/or personal use by an individual for non-commercial purposes is permissible. All other uses require the prior authorization of the copyright owner.”